
Chlorophyta is a division of green algae informally called chlorophytes.

The sea lettuces comprise the genus Ulva, a group of edible green algae that is widely distributed along the coasts of the world's oceans. The type species within the genus Ulva is Ulva lactuca, lactuca being Latin for "lettuce". The genus also includes the species previously classified under the genus Enteromorpha, the former members of which are known under the common name green nori.

Sphaeropleales is an order of green algae that used to be called Chlorococcales. The order includes some of the most common freshwater planktonic algae such as Scenedesmus and Pediastrum. The Sphaeropleales includes vegetatively non-motile unicellular, colonial, or filamentous taxa. They have biflagellate zoospores with flagella that are directly opposed in direction : Sphaeroplea, Atractomorpha, Neochloris, Hydrodictyon, and Pediastrum. All of these taxa have basal body core connections. Motile cells generally lack cell walls or have only a very fine layer surrounding the cell membrane. Other common characteristics include a robust vegetative cell wall, cup-shaped chloroplasts with large pyrenoids, and relatively large nuclei.

Caulerpa is a genus of seaweeds in the family Caulerpaceae. They are unusual because they consist of only one cell with many nuclei, making them among the biggest single cells in the world.

Codium is a genus of edible green macroalgae under the order Bryopsidales. The genus name is derived from a Greek word that pertains to the soft texture of its thallus. One of the foremost experts on Codium taxonomy was Paul Claude Silva at the University of California, Berkeley. Silva was able to describe 36 species for the genus, and in honor of his work on Codium, the species C. silvae was named after the late professor.
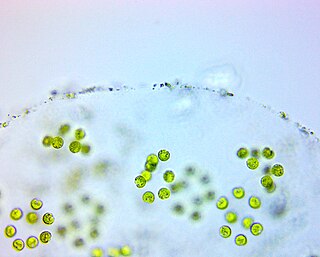
The Tetrasporaceae are a family of green algae, specifically of the Chlamydomonadales. They are found in freshwater habitats.
Characiosiphon is a genus of green algae in the family Characiosiphonaceae. It contains a single species, Characiosiphon rivularis.
Dictyochloris is a genus of green algae in the class Chlorophyceae. It is the sole genus of the family Dictyochloridaceae. It is commonly found in terrestrial and subaerial habitats.
Lobocharacium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiosiphonaceae. It contains the single species Lobocharacium coloradoense. It has been isolated from a pond in Colorado, United States.
Pseudomuriella is a genus of green algae, specifically of the class Chlorophyceae. It is the sole genus of the family Pseudomuriellaceae. It is a terrestrial alga that inhabits soils.

Trebouxia is a unicellular green alga. It is a photosynthetic organism that can exist in almost all habitats found in polar, tropical, and temperate regions. It can either exist in a symbiotic relationship with fungi in the form of lichen or it can survive independently as a free-living organism alone or in colonies. Trebouxia is the most common photobiont in extant lichens. It is a primary producer of marine, freshwater and terrestrial ecosystems. It uses carotenoids and chlorophyll a and b to harvest energy from the sun and provide nutrients to various animals and insects.
Trichosarcina is a genus of green algae in the order Ulotrichales. Filoprotococcus was once regarded as a synonym. However, Filoprotococcus is now considered valid in its own right. Trichosarcina is considered to be of uncertain validity.

Ulva linza is a green alga in the family Ulvaceae that can be found in British Isles.

Laurencia is a genus of red algae that grow in temperate and tropical shore areas, in littoral to sublittoral habitats, at depths up to 65 m (213 ft).

Ulva conglobata is a species of seaweed in the family Ulvaceae that can be found on Jeju Island of Korea, Qingdao province of China and Yokohama, Japan.

Blidingia marginata is a species of seaweed in the Kornmanniaceae family.
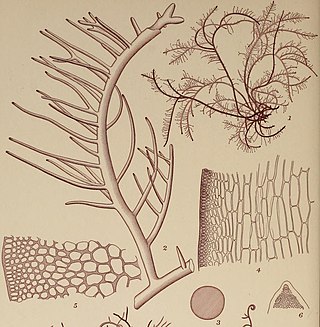
Hypnea is a genus of red algae, and a well known carrageenophyte.
Bracteamorpha is a genus of green algae in the order Sphaeropleales, and is the only genus in the family Bracteamorphaceae. It contains a single species, Bracteamorpha trainorii.












