Design and development
In 1949 the US government canceled the Boeing XB-55 contract, which had been an effort to produce a subsonic replacement for the just-being-introduced Boeing B-47 Stratojet. The XB-55 project had started in 1947, but by the end of the decade it was apparent that if strategic penetration in warfare were to be successful at all, it would require aircraft much faster than the jet fighter aircraft which were then being placed into operation. Thus, the funding made available by the XB-55 cancellation was earmarked for the study of a supersonic medium bomber, and a request for proposals was extended to several aircraft companies.
Boeing submitted a proposal for a four-engine, high-wing aircraft with a highly streamlined fuselage. The four engines would be buried in thickened wing roots; the remaining wing planform was highly tapered.
Developed under weapons system designation MX-1965, the XB-59 was to have a crew of three, and would be powered by four GE J73-X24A turbojet engines, mounted in the roots of the 73-foot span wings. The landing gear would be similar to the bicycle arrangement found on the B-47 and B-52 Stratofortress, with wingtip-mounted outriggers.
The Boeing contract for the XB-59 was canceled in late 1952 after the Convair company's submission, designated B-58 Hustler, was selected for development.
The Boeing effort was a design study only, and no construction was involved.

The North American Aviation XB-70 Valkyrie is a retired prototype version of the planned B-70 nuclear-armed, deep-penetration supersonic strategic bomber for the United States Air Force Strategic Air Command. Designed in the late 1950s by North American Aviation (NAA) to replace the B-52 Stratofortress and B-58 Hustler, the six-engined, delta-winged Valkyrie could cruise for thousands of miles at Mach 3+ while flying at 70,000 feet (21,000 m).

The Convair B-58 Hustler, designed and produced by American aircraft manufacturer Convair, was the first operational bomber capable of Mach 2 flight.

The North American B-45 Tornado is an early American jet bomber designed and manufactured by aircraft company North American Aviation. It has the distinction of being the first operational jet bomber to enter service with the United States Air Force (USAF), as well as the first multiengine jet bomber to be refueled in midair.

The Northrop YB-49 was an American prototype jet-powered heavy bomber developed by Northrop Corporation shortly after World War II for service with the United States Air Force. The YB-49 featured a flying wing design and was a turbojet-powered development of the earlier, piston-engined Northrop XB-35 and YB-35. The two YB-49s built were both converted YB-35 test aircraft.

The Boeing B-50 Superfortress is an American strategic bomber. A post–World War II revision of the Boeing B-29 Superfortress, it was fitted with more powerful Pratt & Whitney R-4360 radial engines, stronger structure, a taller tail fin, and other improvements. It was the last piston-engined bomber built by Boeing for the United States Air Force, and was further refined into Boeing's final such design, the prototype B-54. Although not as well known as its direct predecessor, the B-50 was in USAF service for nearly 20 years.

The Boeing XB-15 was a United States bomber aircraft designed in 1934 as a test for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) to see if it would be possible to build a heavy bomber with a 5,000 mi (8,000 km) range. For a year beginning in mid-1935 it was designated the XBLR-1. When it first flew in 1937, it was the most massive and voluminous airplane ever built in the US. It set a number of load-to-altitude records for land-based aircraft, including carrying a 31,205 lb (14,154 kg) payload to 8,200 ft (2,500 m) on 30 July 1939.

The North American XF-108 Rapier was a proposed long-range, high-speed interceptor aircraft designed by North American Aviation intended to defend the United States from supersonic Soviet strategic bombers. The aircraft would have cruised at speeds around Mach 3 with an unrefueled combat radius over 1,000 nautical miles, and was equipped with radar and missiles offering engagement ranges up to 100 miles (160 km) against bomber-sized targets.
The Martin XB-16, company designation Model 145, was a projected heavy bomber designed in the United States during the 1930s.

The Martin XB-33 Super Marauder was a proposed World War II American bomber aircraft. It was designed by the Glenn L. Martin Company as the Martin Model 190 and was a high-altitude derivative of the company's B-26 Marauder. Two different designs were developed, first as a twin-engined aircraft and then as a four-engined aircraft. The four-engined version was ordered by the United States Army Air Forces, but the program was cancelled before any aircraft were built.

The XB-38 Flying Fortress was a single example conversion of a production B-17E Flying Fortress, testing whether the Allison V-1710 V type engine could be substituted for the standard Wright R-1820 radial engine during early World War II.

The Myasishchev M-50 is a Soviet prototype four-jet engine supersonic strategic bomber which never attained service. Only one flightworthy prototype was built, which was first flown in October 1959. The M-50 was constructed by the Myasishchev design bureau.
The Martin XB-68 was a supersonic medium tactical bomber with a crew of two that was proposed in 1954 to the United States Air Force. The project, however, was canceled before any aircraft were built.

The Convair XB-53 was a proposed jet-powered medium bomber aircraft, designed by Convair for the United States Army Air Forces. With a radical tailless, forward-swept wing design, the aircraft appeared futuristic; however, the project was canceled before either of the two prototypes were completed.

The Convair XB-46 was a single example of an experimental medium jet bomber which was developed in the mid-1940s but which never saw production or active duty. It competed with similar designs, the North American XB-45 and Martin XB-48, all of which saw little use after the successful development of the Boeing XB-47.

The Martin XB-48 was an American medium jet bomber developed in the mid-1940s. It competed with the Boeing B-47 Stratojet, which proved to be a superior design, and was largely considered as a backup plan in case the B-47 ran into development problems. It never saw production or active duty, and only two prototypes, serial numbers 45-59585 and 45-59586, were built.

The Boeing XB-55 was a proposed Boeing aircraft designed to be a strategic bomber. The XB-55 was intended to be a replacement for the Boeing B-47 Stratojet in United States Air Force (USAF) service.
The Boeing XB-56 was a proposal by Boeing for a re-engined version of the American jet-powered medium bomber aircraft, the B-47 Stratojet. The original designation for this modification was YB-47C.
The Sukhoi Su-10 or Izdeliye Ye was a Soviet turbojet-powered bomber aircraft built shortly after World War II.
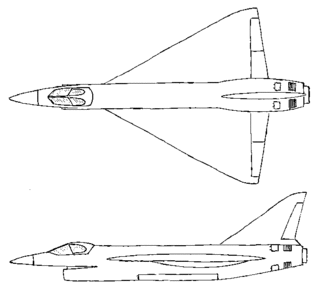
The Saab 36 was a cancelled Swedish supersonic bomber planned by Saab AB during the 1950s. The aircraft was intended to be able to carry an 800 kg free-falling nuclear weapon, but the Swedish nuclear weapons program was cancelled in the 1960s; the plans for the bomber had been cancelled in 1957. The Saab 36 was to be fitted with delta wings, as was the Saab 35 Draken fighter. The engine was to be a version of the British Bristol Olympus turbojet, the same engine powering the Avro Vulcan jet bomber.

The General Electric GE4 turbojet engine was designed in the late 1960s as the powerplant for the Boeing 2707 supersonic transport. The GE4 was a nine-stage, single-shaft, axial-flow turbojet based largely on the General Electric YJ93 which powered the North American XB-70 bomber. The GE4 was the most powerful engine of its era, producing 50,000 lbf (220 kN) dry, and 65,000 lbf (290 kN) with afterburner. The Boeing 2707 was cancelled in 1971, putting an end to further work on the GE4.
















