Related Research Articles

Bandundu is one of eleven former provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It bordered the provinces of Kinshasa and Bas-Congo to the west, Équateur to the north, and Kasai-Occidental to the east. The provincial capital is also called Bandundu.
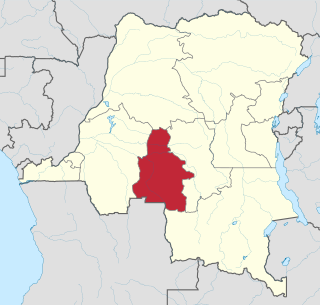
Kasaï-Occidental was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1966 and 2015, when it was split into the Kasaï-Central and the Kasaï provinces.

Ségou Region is an administrative region in Mali, situated in the centre of the country with an area of 64,821 km2 (25,028 sq mi), around 5% of Mali. The region is bordered by Sikasso Region on the south, Tombouctou and Mopti on the east, Burkina Faso to the southeast and the Koulikoro Region to the west. In 2009 it had 2,336,255 inhabitants, making it the second most populous region of Mali. Its administrative capital is the town of Ségou.

Uvira is the capital city of the Uvira Territory in the South Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It is situated between Lake Tanganyika and the Mitumba Mountains and covers an area of approximately 16km.
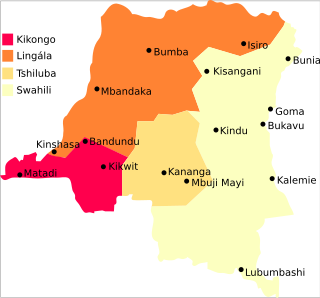
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a multilingual country where an estimated total of 242 languages are spoken. Ethnologue lists 215 living languages. The official language, since the colonial period, is French, one of the languages of Belgium. Four other languages, three of them Bantu based, have the status of national language: Kikongo-Kituba, Lingala, Swahili and Tshiluba.
Idiofa is a town in Kwilu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Lulua District was a district of the Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The city of Kananga was at the center of the district, but had a separate administration. In 2015 Lulua District became the province of Kasaï-Central.

Kwilu is a province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It's one of the 21 provinces created in the 2015 repartitioning. Kwilu, Kwango, and Mai-Ndombe provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Bandundu province. Kwilu was formed from the Kwilu district and the independently administered cities of Bandundu and Kikwit. Bandundu is the provincial capital. The 2020 population was estimated to be 6,682,300.
MadimbaTerritory is a territory in the Kongo Central Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Its seat is the town of Madimba. The region covers an area of 8,260 square miles and is situated 100 km from Kinshasa. It spans from the Lukusu River in the north to Kintano in the west, and from the Inkisi River in the west to Kinkosi-Luidi in the southeast. The territory borders Kasangulu Territory to the northeast, Kimvula Territory to the southeast, Mbanza-Ngungu Territory to the west, and Angola to the south. Madimba Territory is home to an approximate population of 463,132 residents.
The Ngiri Reserve is a protected area of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It is located in western Équateur province, in the Bomongo, Bikoro and Makanza territories, and covers a total area of 1,000 square kilometres (390 sq mi). It extends northward from the confluence of the Congo River and the Ubangi River. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) the reserve will conserve biodiversity and the ecosystem in the Ngiri triangle.
Idiofa Territory is an administrative area in the Kwilu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). The capital is the town of Idiofa.
Dibaya-Lubwe is a town in the Kwilu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is in Idiofa Territory. The town lies on the south shore of the Kasai River just below the point where it is joined by the Lubue River. As of 2012 the population was estimated to be 38,933.
The Kamtsha River is a tributary of the Kasai River. The river flows north through Idiofa territory of Kwilu province, Democratic Republic of the Congo to its mouth on the Kasai River.
The Lubue River runs from south to north through Idiofa territory, Kwilu province, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Near its origin in the south, where the Musanga River enters from the left, it is a small, winding river perhaps 12 metres (39 ft) wide obstructed by rocks and rapids. It becomes navigable at Mulasa, and below this point meanders through a very wide and wooded valley. It enters the Kasai near the town of Dibaya Lubue.
The Luele River runs from south to north through Idiofa territory, Kwilu province, Democratic Republic of the Congo. The river starts as a clear stream in a small valley near Idiofa. It grows in size rapidly due to many small tributaries, among which is the Punkulu River, and then meanders through a large valley before entering the Kasai River downstream from Mangai.
Eolo is a community in Idiofa Territory, in the Kwilu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It lies on the south shore of the Kasai River just downstream from the mouth of the Kamtsha River.

Luvungi, also known as Itara-Luvungi, is one of the groupements (groupings) within the Bafuliiru Chiefdom in the Uvira Territory of the South Kivu Province in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Situated on the Ruzizi Plain, it lies at the borders of Uvira Territory and Walungu Territory, in close proximity to the frontiers of Rwanda and Burundi. Luvungi is home to a population of approximately 85,000 individuals, predominantly consisting of Fuliru agriculturalists who play a vital role in the local community. There's also has a small population of Vira, Bembe, Lega, Shi, Burundians and Banyamulenge. Its economy is founded mainly on subsistence agriculture and the artisanal mining of cassiterite, an ore of tin.
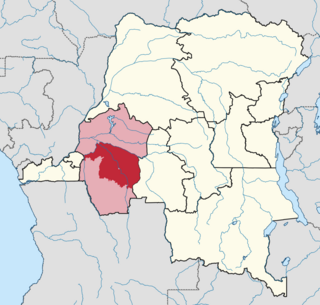
Kwilu District was a district of the Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It roughly corresponded to the present province of Kwilu.
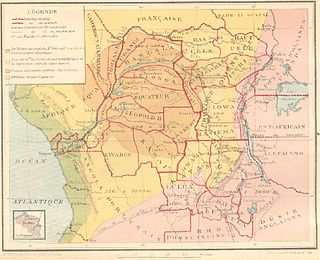
Congo-Kasaï was one of the four large provinces of the Belgian Congo defined in 1914. It was formally established in 1919, and in 1933 was divided into the new provinces of Léopoldville and Lusambo.

Katogota is a village located in the Itara-Luvungi grouping within the Bafuliiru Chiefdom in Uvira Territory of the South Kivu Province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Situated approximately 60 km south of Bukavu, Katogota is in close proximity to the Kamonyi and Rusagara villages, near the border regions of Rwanda and Burundi.
References
- ↑ Ethnologue.
- ↑ Schwetz 1924, p. 73.
- ↑ Plan stratégique.
- 1 2 Munzumi 2006, p. 20.
- ↑ RDC Ministère du Plan 2005.