
The Makere are an ethnic group of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, living near the Bima River in the Northern part of the country. [1] [2] They speak the Mangbetu language. [3]

The Makere are an ethnic group of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, living near the Bima River in the Northern part of the country. [1] [2] They speak the Mangbetu language. [3]

Congo may refer to:
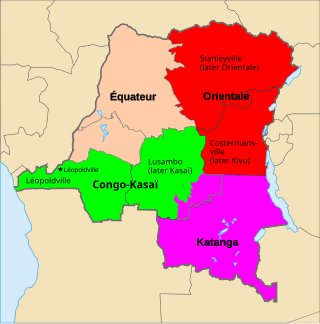
Katanga was one of the four large provinces created in the Belgian Congo in 1914. It was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1966 and 2015, when it was split into the Tanganyika, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba, and Haut-Katanga provinces. Between 1971 and 1997, its official name was Shaba Province.

Kinshasa, formerly named Léopoldville before June 30, 1966, is the capital and largest city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Once a site of fishing and trading villages along the Congo River, Kinshasa is now one of the world's fastest-growing megacities. With an estimated population of 16 million residents, it's the most densely populated city in the DRC and the most populous city in Africa. It is Africa's third-largest metropolitan area and the leading economic, political, and cultural center of the DRC. Kinshasa houses several industries, including manufacturing, telecommunications, banking, and entertainment. The city also hosts some of DRC's significant institutional buildings, such as the Palais du Peuple, Palais de la Nation, Court of Cassation, Constitutional Court, Cité de l'Union Africaine, Palais de Marbre, Stade des Martyrs, Immeuble du Gouvernement, Kinshasa Financial Center, and multiple federal departments and agencies.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a country in Central Africa. By land area, the DRC is the second-largest country in Africa and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 105 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous Francophone country in the world. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the economic center. The country is bordered by the Republic of the Congo, Central African Republic, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, Zambia, Angola, the Cabinda exclave of Angola, and the South Atlantic Ocean.
Congolese or Kongolese may refer to:

The Hema people or Bahema (plural) are a Bantu ethnic group who are concentrated in parts of Ituri Province in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo.
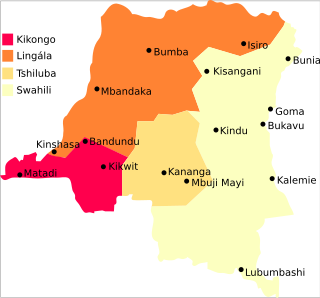
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a multilingual country where an estimated total of 242 languages are spoken. Ethnologue lists 215 living languages. The official language, since the colonial period, is French, one of the languages of Belgium. Four other languages, three of them Bantu based, have the status of national language: Kikongo-Kituba, Lingala, Swahili and Tshiluba.
Articles related to the Democratic Republic of the Congo include:

Allen's striped bat is a species of bat in the family Vespertilionidae, the vesper bats. It is native to Africa, where it occurs in Cameroon and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. This species can be found in lowland tropical moist forests. Little else is known about it.

Allen's spotted bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae found in the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, and Uganda. It is found in subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests.

The Trevor's free-tailed bat is a species of bat in the family Molossidae. It is found in Central and West Africa. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests and moist savanna.

The Republic of the Congo was a sovereign state in Central Africa, created with the independence of the Belgian Congo in 1960. From 1960 to 1966, the country was also known as Congo-Léopoldville to distinguish it from its northwestern neighbor, which is also called the Republic of the Congo, alternatively known as "Congo-Brazzaville". In 1964, the state's official name was changed to the Democratic Republic of the Congo, but the two countries continued to be distinguished by their capitals; with the renaming of Léopoldville as Kinshasa in 1966, it became also known as Congo-Kinshasa. After Joseph Désiré Mobutu, commander-in-chief of the national army, seized control of the government in 1965, the Democratic Republic of the Congo became the Republic of Zaire in 1971. It would again become the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1997. The period between 1960 and 1964 is referred to as the First Congolese Republic.

The Republic of the Congo is a country located on the western coast of Central Africa to the west of the Congo River. It is bordered to the west by Gabon, to the northwest by Cameroon, to the northeast by the Central African Republic, to the southeast by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south by the Angolan exclave of Cabinda, and to the southwest by the Atlantic Ocean.
Amba is a language spoken in parts of Uganda and the Democratic Republic of Congo by the Amba people. The Amba people call it Kwamba and it is known as Kihumu in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Amba has a 70% lexical similarity with Bera. Dialects include Kyanzi (Kihyanzi) and Suwa (Kusuwa).

Ngombe, or Lingombe, is a Bantu language spoken by about 150,000 people in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. In general, native speakers live on either side of the Congo river, and its many tributaries; more specifically, Équateur Province, Mongala District and in areas neighboring it. Ngombe is written in Latin script.
Komo is a Bantu language spoken by half a million people in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including an area around the major upriver port of Kisangani.
Mbole is a Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is spoken by the Mbole people, with a population of about 100,000 as of 1971 living in the Tshopo District, southwest of Kisangani in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Bala (Lobala) is a Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. According to Maho (2009), it includes Boko (Iboko).
Makere may refer to:
Zobia is a village in the Bas-Uélé province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Zobia Gauche was a station on the defunct Vicicongo line, a railway.