Related Research Articles
Amba or AMBA may refer to:

The Bukusu people are one of the 17 Kenyan tribes of the Luhya Bantu people of East Africa residing mainly in the counties of Bungoma and Trans Nzoia. They are the largest tribe of the Luhya nation, with 1,188,963 identifying as Bukusu in the 2019 Kenyan census. They speak the Bukusu dialect.

Kasese District is a district in Western Uganda. Like most other Ugandan districts, it is named after its chief town and district headquarters, the town of Kasese.

The culture of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is extremely varied, reflecting the great diversity and different customs which exist in the country. Congolese culture combines the influence of tradition to the region, but also combines influences from abroad which arrived during the era of colonization and continue to have a strong influence, without destroying the individuality of many tribal customs.

Alur are a Nilotic ethnic group who live in northwestern Uganda and northeastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). They are part of the larger Luo group.

The Gwere people, also called Bagwere, are a Bantu ethnic group in Uganda. They are among the 65 ethnic societies of Uganda. Gwere is the root word, and the people are referred to as Bagwere (endonym) or Mugwere (singular). According to the 2002 Census of Uganda, 23.6% of Bagwere are Roman Catholic, 46.8% are Anglican, 23.9% are Muslim and 3.1% are Pentecostal.

The Lugbara are a Central Sudanic ethnic group who live primarily in the West Nile region of Uganda, in the adjoining area of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) with a few living in South Sudan. They speak the Lugbara language, a Central Sudanic language similar to the language spoken by the Madi, with whom they also share many cultural similarities.

Khonds are an indigenous Adivasi tribal community in India. Traditionally hunter-gatherers, they are divided into the hill-dwelling Khonds and plain-dwelling Khonds for census purposes, but the Khonds themselves identify by their specific clans. Khonds usually hold large tracts of fertile land, but still practice hunting, gathering, and slash-and-burn agriculture in the forests as a symbol of their connection to, and as an assertion of their ownership of the forests wherein they dwell. Khonds speak the Kui language and write it in the Odia script.
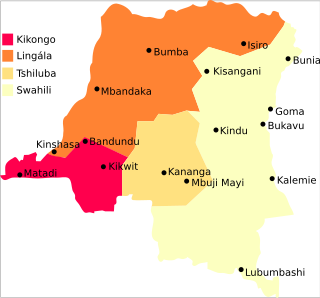
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a multilingual country where an estimated total of 242 languages are spoken. Ethnologue lists 215 living languages. The official language, since the colonial period, is French, one of the languages of Belgium. Four other languages, three of them Bantu based, have the status of national language: Kikongo-Kituba, Lingala, Swahili and Tshiluba.

Rwenzururu is a subnational kingdom in western Uganda, located in the Rwenzori Mountains on the border with the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It includes the districts of Bundibugyo, Kasese and Ntoroko. Rwenzururu is also the name given to the region the kingdom is located in.

The Xhosa people, or Xhosa-speaking people are a Bantu ethnic group native to South Africa. They are the second largest ethnic group in South Africa and are native speakers of the isiXhosa language.

The Konjo, BaKonzo, or Konzo, are a Bantu ethnic group located in the Rwenzori region of Southwest Uganda in districts that include; Kasese, Bundibugyo, Bunyangabu and Ntoroko districts.
Suri is a collective name for three ethnic groups mainly living in Suri woreda, in southwestern Ethiopia. They share many similarities politically, territorially, culturally and economically but speak different languages. They all speak South East Surmic languages within the Nilo-Saharan language family, which includes the Mun, Majang, and Me'en people's languages.

South Sudan is home to around 60 indigenous ethnic groups and 80 linguistic partitions among a 2021 population of around 11 million. Historically, most ethnic groups were lacking in formal Western political institutions, with land held by the community and elders acting as problem solvers and adjudicators. Today, most ethnic groups still embrace a cattle culture in which livestock is the main measure of wealth and used for bride wealth.
The Songora or Shongora are a traditionally pastoralist people of the Great Lakes region of Central Africa located in Western Region, Uganda and Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. They have distinctive customs and speak Rusongora, a Bantu language that is similar to Runyankole and Runyoro. The Basongora population in Uganda was reported at numbering 15,897 people in the 2014 census. Although various community estimates put their population at around 40,000 and 50,000 people. Some Basongora also live in Eastern Congo.
Yenga is an Amba village in western Uganda, Bundibugyo District, on the border with the Congo. It lies in the rift valley between Lake Albert and Lake Edward above the Semliki River. The village is within the borders of the Semuliki National Park. To the south of the village are the foothills of the Rwenzori Mountains. While Yenga is only 24 kilometres (15 mi) from the district capital of Bundibugyo, the nearest town of substance is Fort Portal. Yenga is located in lowland tropical rainforest, much like the Ituri Rainforest across the river.
The Baruuli or Baluuli, are a Bantu ethnic group native to Bunyoro-Kitara, a subnational kingdom within Uganda. They stay in an area called Buruuli. They share a common ancestry with the Banyala.
The Bafumbira, are a Bantu ethnic group from Kisoro District in South Western Uganda. They are of three indigenous groups: Bahutu, Batutsi and Batwa.

Violence erupted on 26 November 2016 in the town of Kasese, the capital of the Ugandan Kingdom of Rwenzururu, when Ugandan police raided the government offices of the Rwenzururu kingdom, killing eight Rwenzururian royal guards and arresting two others. According to the government of Uganda, the raid was in response to militant attacks on police posts in the region two weeks earlier, allegedly perpetrated by the royal guards.
The Rwenzururu movement was an armed secessionist movement active in southwest Uganda, in the subnational kingdom of Tooro. The group was made up of Konjo and Amba fighters and was led by Isaya Mukirania. It disbanded in 1982 following successful peace negotiations with the Ugandan government.
References
- ↑ "2014 Uganda Population and Housing Census – Main Report" (PDF). Uganda Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- 1 2 "Amba: A language of Uganda", Ethnologue (accessed 20 August 2009)
- 1 2 Prunier, Gérard (2009). Africa's World War: Congo, the Rwandan Genocide, and the Making of a Continental Catastrophe. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-537420-9., 82-83
- ↑ "Uganda: Welcome Rwenzururu", editorial by the New Vision , 31 March 2008
- ↑ Rubongoya, Joshua B. (January 1995). "The Bakonjo‐Baamba and Uganda: Colonial and postcolonial integration and ethnocide". Studies in Conflict & Terrorism. 18 (2): 75–92. doi:10.1080/10576109508435970. ISSN 1057-610X.
- ↑ "The People, Settlements and Tribes in Uganda". Saso Gorilla Trips. 2018-03-09. Retrieved 2024-02-03.
- ↑ Arens, William (1979). The Man-Eating Myth: Anthropology and Anthropophagy (first ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. p. 154. ISBN 9780195025064.