Related Research Articles

Congo may refer to:

Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Middle Africa is an analogous term used by the United Nations in its geoscheme for Africa and consists of the following countries: Angola, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Rwanda, and São Tomé and Príncipe. These eleven countries are members of the Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS). Six of those countries are also members of the Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa (CEMAC) and share a common currency, the Central African CFA franc.

The Kongo people are a Bantu ethnic group primarily defined as the speakers of Kikongo. Subgroups include the Beembe, Bwende, Vili, Sundi, Yombe, Dondo, Lari, and others.
Congolese or Kongolese may refer to:

The Hema people or Bahema (plural) are a Bantu ethnic group who are concentrated in parts of Ituri Province in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo.

The Bakole are a Bantu ethnic group of the Republic of Cameroon. They belong to the Sawa, or Cameroonian coastal peoples. The Bakole speak a language of the same name.

The Mongo people are an ethnic group who live in the equatorial forest of Central Africa. They are the largest ethnic group in the Democratic Republic of Congo, highly influential in its north region. The Mongo people are a diverse collection of sub-ethnic groups who are referred to as AnaMongo. The Mongo (Anamongo) subgroups include the Mongo, Batetela, Bakusu, Ekonda, Bolia, Nkundo, Lokele, Topoke, Iyadjima, Ngando, Ndengese, Sengele, Sakata, Mpama, Ntomba, Mbole. The Mongo (Anamongo) occupy 14 provinces particularly the province of Equateur,Tshopo, Tshuapa, Mongala, Kwilu, in Maï Ndombe, Kongo-Centrale, in Kasai, in Sankuru, Maniema, North Kivu and South Kivu, Tanganiyka (Katanga) and Ituri province. Their highest presence is in the province of Équateur and the northern parts of the Bandundu Province(Maï Ndombe).

The Republic of the Congo is a country located on the western coast of Central Africa to the west of the Congo River. It is bordered to the west by Gabon, to the northwest by Cameroon, to the northeast by the Central African Republic, to the southeast by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south by the Angolan exclave of Cabinda, and to the southwest by the Atlantic Ocean.
The Bangi language, or Bobangi, is a relative and main lexical source of Lingala spoken in central Africa. Dialects of the language are spoken on both sides of the Ubangi River and Congo River.
The Bangi–Ntomba languages are a group of Bantu languages spoken in the Democratic Republic of Congo and the Republic of the Congo. They are coded Zone C.30 in Guthrie's classification, and included the trade language Lingala, one of four national languages of the DRC and two of the RC.
The Lele, also known as Bashilele or Usilele, are a Bantu ethnic group closely related to the Kuba people in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. They traditionally live in the Kasai River region, but since the 1950s many have migrated to Kinshasa. There are currently about 30,000 Lele, of which 26,000 speak the Lele language.

The Twa are a group of indigenous Central African foragers tribes. These cultural groups were formerly called Pygmies by European writers, but the term is no longer preferred based on its cultural and geographic inaccuracy, as well as being seen as pejorative. Cultural groups are being reclassified by themselves based on their function in society, lineage, and land ties.
The Kele people are a Bantu ethnic group of about 160,000 people, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. They mainly live on the south bank of the Congo River between Kisangani and Isangi. The Kele are a subgroup of The Mongo people.
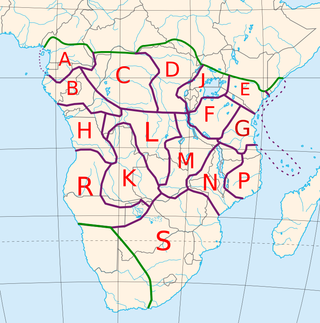
The Bantu peoples are an ethnolinguistic grouping of approximately 400 distinct native African ethnic groups who speak Bantu languages. The languages are native to 24 countries spread over a vast area from Central Africa to Southeast Africa and into Southern Africa.

The African Pygmies are a group of ethnicities native to Central Africa, mostly the Congo Basin, traditionally subsisting on a forager and hunter-gatherer lifestyle. They are divided into three roughly geographic groups:
Mpama (Pama) is a Bantu language of Kasai, Democratic Republic of Congo. It is spoken by the Mpama people.
Mpama can refer to:
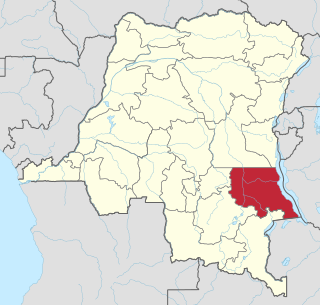
The Batwa–Luba clashes were a series of clashes in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) between the Pygmy Batwa people, and the Luba people that began in 2013 and ended in 2018.
Nyemba may refer to:
References
- ↑ James Stuart Olson: The Peoples of Africa: An Ethnohistorical Dictionary, Greenwood Publishing Group, 1996 ISBN 0313279187, p. 407