Related Research Articles

The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is the largest country of sub-Saharan Africa, occupying some 2,344,858 square kilometres (905,355 sq mi). Most of the country lies within the vast hollow of the Congo River basin. The vast, low-lying central area is a plateau-shaped basin sloping toward the west, covered by tropical rainforest and criss-crossed by rivers. The forest center is surrounded by mountainous terraces in the west, plateaus merging into savannas in the south and southwest. Dense grasslands extend beyond the Congo River in the north. High mountains of the Ruwenzori Range are found on the eastern borders with Rwanda and Uganda.

The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world by discharge volume, following the Amazon and Ganges rivers. It is the world's deepest recorded river, with measured depths of around 220 m (720 ft). The Congo–Lualaba–Luvua–Luapula–Chambeshi River system has an overall length of 4,700 km (2,900 mi), which makes it the world's ninth-longest river. The Chambeshi is a tributary of the Lualaba River, and Lualaba is the name of the Congo River upstream of Boyoma Falls, extending for 1,800 km (1,100 mi).

The Zambezi is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers 1,390,000 km2 (540,000 sq mi), slightly less than half of the Nile's. The 2,574 km (1,599 mi) river rises in Zambia and flows through eastern Angola, along the north-eastern border of Namibia and the northern border of Botswana, then along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe to Mozambique, where it crosses the country to empty into the Indian Ocean.

Kisangani is the capital of Tshopo Province, located on the Congo River in the eastern part of the central Congo Basin in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is the country's fifth-most populous urban area, with an estimated population of 1,602,144 as of 2016, and the largest of the cities in the tropical woodlands of the Congo.

The East Region occupies the southeastern portion of the Republic of Cameroon. It is bordered to the east by the Central African Republic, to the south by Congo, to the north by the Adamawa Region, and to the west by the Centre and South Regions. With 109,002 km2 of territory, it is the largest region in the nation as well as the most sparsely populated. Historically, the peoples of the East have been settled in Cameroonian territory for longer than any other of the country's many ethnic groups, the first inhabitants being the Baka pygmies.

The 1,576 kilometres (979 mi) long Kafue River is the longest river lying wholly within Zambia. Its water is used for irrigation and for generating hydroelectric power. It is the largest tributary of the Zambezi, and of Zambia's principal rivers, it is the most central and the most urban. More than 50% of Zambia's population live in the Kafue River Basin and of these around 65% are urban.
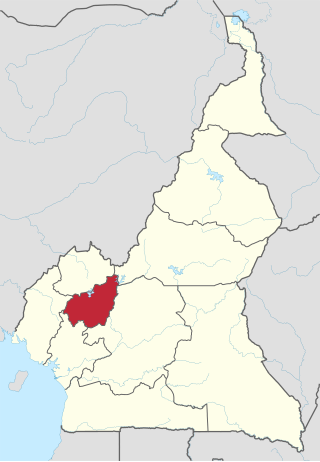
The West Region is 14,000 km2 of territory located in the central-western portion of the Republic of Cameroon. It borders the Northwest Region to the northwest, the Adamawa Region to the northeast, the Centre Region to the southeast, the Littoral Region to the southwest, and the Southwest Region to the west. The West Region is the smallest of Cameroon's ten regions in area, yet it has the highest population density.

Basankusu is a town in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is the main town and administrative centre of the Basankusu Territory. In 2004, it had an estimated population of 23,764. It has a gravel airstrip, covered and open markets, a hospital, and three cellphone networks, the first of which was installed in 2006. The town is also known as a centre for bonobo conservation efforts. Despite such developments, most inhabitants live at a subsistence level: hunting, fishing, keeping chickens and keeping a vegetable plot. In 2010, the workers at the local palm plantation would earn an average monthly salary of $40, most others would have much less.

Benin is predominantly a rural society, and agriculture in Benin supports more than 70% of the population. Agriculture contributes around 35% of the country's gross domestic product (GDP) and 80% of export income. While the Government of Benin (GOB) aims to diversify its agricultural production, Benin remains underdeveloped, and its economy is underpinned by subsistence agriculture. Approximately 93% of total agricultural production goes into food production. The proportion of the population living in poverty is about 35.2%, with more rural households in poverty (38.4%) than urban households (29.8%). 36% of households depend solely upon agricultural (crop) production for income, and another 30% depend on crop production, livestock, or fishing for income.

Walikale Territory is a territory located within the Congolese province of North Kivu, in the eastern regions of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The headquarters are in the town of Walikale. The locality is situated between Bukavu and Lubutu on DR Congo National Road No. 3 in the valley of the river Lowa, 135 km to the west of Goma.

Kasoa, formerly known as Odupongkpehe, is a peri-urban town in the Awutu Senya East Municipal District of the Central region of Ghana.

The Calabar River in Cross River State, Nigeria flows from the north past the city of Calabar, joining the larger Cross River about 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) to the south. The river at Calabar forms a natural harbor deep enough for vessels with a draft of 6 metres (20 ft).

The Topoke people are an ethnic group that live in the Isangi Territory south of the Congo River, downstream from Kisangani in the Tshopo Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. They speak the Poke language, in the Soko–Kele languages group of Bantu languages.
Yangambi is a town in Isangi territory of Tshopo province, Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Isangi is a town in the Tshopo Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, headquarters of Isangi Territory.
Costa Rican agriculture plays a profound part in the country's gross domestic product (GDP). It makes up about 6.5% of Costa Rica's GDP, and 14% of the labor force. Depending upon location and altitude, many regions differ in agricultural crops and techniques. The main exports include: bananas, pineapples, coffee, sugar, rice, vegetables, tropical fruits, ornamental plants, corn, potatoes and palm oil.

The Ndjili River is a river that flows from the south through the capital city of Kinshasa in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, where it joins the Congo River. It separates the districts of Tshangu and Mont Amba. The river gives its name to the Ndjili commune and to the Ndjili International Airport.

Tumba-Ngiri-Maindombe is the largest Wetland of International Importance in the world as recognized by the Ramsar Convention. The site covers an area of 65,696 square kilometres (25,365 sq mi) in the region around Lake Tumba in the western Congo Basin in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). This is more than twice the size of Belgium or Maryland.

The National Institute for Agronomic Study of the Belgian Congo was a research facility established in Yangambi in the Belgian Congo, operating from 1933 to 1962.

The Likouala-aux-Herbes is a river in the Republic of the Congo. It is a tributary of the Sangha River, which in turn is a tributary of the Congo River. It gives its name to the Likouala Department.
References
- ↑ "Lombo". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2011-10-09.
- ↑ Tshibaka 1992, p. 15.
- 1 2 Tshibaka 1992, pp. 16–17.
- ↑ "Spear blade currency". National Museum of African Art. Retrieved 2011-10-09.