
The economy of Hong Kong is a highly developed free-market economy. It is characterised by low taxation, almost free port trade and a well-established international financial market. Its currency, called the Hong Kong dollar, is legally issued by three major international commercial banks, and is pegged to the US dollar. Interest rates are determined by the individual banks in Hong Kong to ensure that they are market driven. There is no officially recognised central banking system, although the Hong Kong Monetary Authority functions as a financial regulatory authority.

The renminbi, also known as the Chinese yuan, is the official currency of the People's Republic of China. The renminbi is issued by the People's Bank of China, the monetary authority of China. It is the world's fifth-most-traded currency as of April 2022.

The Four Asian Tigers are the developed Asian economies of Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan. Between the early 1950s and 1990s, they underwent rapid industrialization and maintained exceptionally high growth rates of more than 7 percent a year.

The Agricultural Bank of China (ABC), also known as AgBank, is a Chinese state-owned multinational banking and financial services corporation headquartered in Beijing, China. It is one of the "big four" banks in China, and the second largest bank in the world by total assets, behind the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China. ABC was founded on 10 July 1951, and has its headquarters in Dongcheng District, Beijing. It has branches throughout mainland China, Hong Kong, London, Tokyo, New York, Frankfurt, Sydney, Seoul, and Singapore.

The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong is a stock exchange based in Hong Kong. It is one of the largest stock exchanges in Asia and the 9th largest globally by market capitalization as of August 2024. The exchange plays a crucial role in connecting international investors with mainland Chinese companies, serving as a major platform for capital raising. Unlike mainland Chinese exchanges, it operates under Hong Kong’s distinct regulatory framework, which allows greater access to foreign investors.

CLP Group and its holding company, CLP Holdings Ltd, also known as China Light and Power Company, Limited, is an electricity company in Hong Kong. Incorporated in 1901 as China Light & Power Company Syndicate, its core business remains the generation, transmission, and retailing of electricity. It also has businesses in a number of Asian markets as well as EnergyAustralia in Australia. It is one of the two main electricity power generation companies in Hong Kong, the other being Hongkong Electric Company.

Ping An Insurance known also as Ping An of China, full name Ping An Insurance (Group) Company of China, Ltd. is a Chinese financial services holding company whose subsidiaries provide insurance, banking, asset management, financial services. The company was founded in 1988 and is headquartered in Shenzhen. "Ping An" literally means "safe and well". It is ranked as China’s 6th largest company.

The People's Insurance Company (Group) of China Limited, known as PICC Group or just PICC, is a Chinese listed insurer. The Chinese Central Government is the controlling shareholder.

The Stock Exchange of Thailand is the only stock exchange in Thailand. Founded on 30 April 1975, it is ASEAN's 3rd largest after Indonesia Stock Exchange and Singapore Exchange by market capitalization at US$489.95 billion as of November 2023. From 2015 to June 2020, it was the biggest IPO market in Southeast Asia in terms of accumulated raised fund at US$17.8 billion. It is also the region's most active bourse for 10 consecutive years with daily trading turnover normally exceeding US$2 billion.

The Shanghai Stock Exchange is a stock exchange based in the city of Shanghai, China. It is one of the three stock exchanges operating independently in mainland China, the others being the Beijing Stock Exchange and the Shenzhen Stock Exchange. The Shanghai Stock Exchange is the world's third largest stock market by market capitalization exceeding $6 trillion in July 2024. It is also Asia's biggest stock exchange. Unlike the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, the Shanghai Stock Exchange is still not entirely open to foreign investors and often affected by the decisions of the central government, due to capital account controls exercised by the Chinese mainland authorities.

Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited operates a range of equity, commodity, fixed income and currency markets through its wholly owned subsidiaries The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited (SEHK), Hong Kong Futures Exchange Limited (HKFE) and London Metal Exchange (LME).
The CSI 300 is a capitalization-weighted stock market index designed to replicate the performance of the top 300 stocks traded on the Shanghai Stock Exchange and the Shenzhen Stock Exchange. It has two sub-indexes: the CSI 100 Index and the CSI 200 Index. Over the years, it has been deemed the Chinese counterpart of the S&P 500 index and a better gauge of the Chinese stock market than the more traditional SSE Composite Index.
While beginning in the United States, the Great Recession spread to Asia rapidly and has affected much of the region.
The SZSE Component Index is an index of 500 stocks that are traded at the Shenzhen Stock Exchange (SZSE). It is the main stock market index of SZSE.
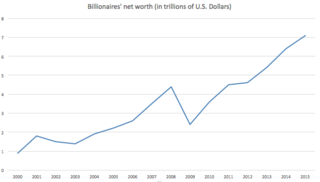
The World's Billionaires is an annual ranking of people who are billionaires, i.e., they are considered to have a net worth of US$1 billion or more, by the American business magazine Forbes. The list was first published in March 1987. The total net worth of each individual on the list is estimated and is cited in United States dollars, based on their documented assets and accounting for debt and other factors. Royalty and dictators whose wealth comes from their positions are excluded from these lists. This ranking is an index of the wealthiest documented individuals, excluding any ranking of those with wealth that is not able to be completely ascertained.
Since the late-2000s, the People's Republic of China (PRC) has sought to internationalize its official currency, the Renminbi (RMB). RMB internationalization accelerated in 2009 when China established the dim sum bond market and expanded Cross-Border Trade RMB Settlement Pilot Project, which helps establish pools of offshore RMB liquidity. The RMB was the 8th-most-traded currency in the world in 2013 and the 7th-most-traded in early 2014.
The 2015-2016 Chinese stock market turbulence began with the popping of a stock market bubble on 12 June 2015 and ended in early February 2016. A third of the value of A-shares on the Shanghai Stock Exchange was lost within one month of the event. Major aftershocks occurred around 27 July and 24 August's "Black Monday". By 8–9 July 2015, the Shanghai stock market had fallen 30 percent over three weeks as 1,400 companies, or more than half listed, filed for a trading halt in an attempt to prevent further losses. Values of Chinese stock markets continued to drop despite efforts by the government to reduce the fall. After three stable weeks the Shanghai index fell again by 8.48 percent on 24 August, marking the largest fall since 2007.
FTSE China A50 Index is a stock market index by FTSE Group, the components were chosen from Shanghai Stock Exchange and Shenzhen Stock Exchange, which issue A-share; B-share were not included.











