Geography and demography
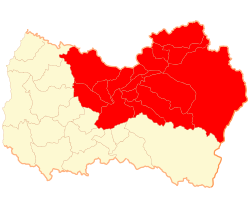
According to the 2002 census by the National Statistics Institute (INE), the province spans an area of 7,384.2 km2 (2,851 sq mi) [1] and had a population of 542,901 inhabitants (271,226 men and 271,675 women), giving it a population density of 73.5/km2 (190/sq mi). It is the fifth most populated province in the country. Between the 1992 and 2002 censuses, the population grew by 13.8% (65,871 persons). [1]
Cachapoal Valley wine region
Located 85 km (53 mi) south of Santiago, the Cachapoal Valley is a wine-growing area in Cachapoal in the O`Higgins Region of central Chile, to the north of the Rapel Valley. [4] It is located between the heights of Paine to the north and Pelequén to the south and between the Andes to the west and the smaller coastal range to the east. The valley takes its name from the Cachapoal River that flows through Rapel Valley along with its tributaries, the Claro and Cortaderal Rivers. All these watercourses flow into Lake Rapel.
The climate of the valley is temperate and consistently Mediterranean, sheltered by the coastal range from the cooling influences of the Pacific Ocean.
Most of Cachapoal's noteworthy wineries and vineyards are located toward the east of the region, in the foothills of the Andes, away from the warmer valley floor. This is an area for Cabernet Sauvignon vines, whereas closer to the coast the ocean breezes flow through the coastal range, and there are more Carménère vines.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.