
Parrotfish are a group of fish species traditionally regarded as a family (Scaridae), but now often treated as a subfamily (Scarinae) or tribe (Scarini) of the wrasses (Labridae). With roughly 95 species, this group's largest species richness is in the Indo-Pacific. They are found in coral reefs, rocky coasts, and seagrass beds, and can play a significant role in bioerosion.

The giant grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus), also known as the Queensland groper (grouper), brindle grouper or mottled-brown sea bass, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It has a wide Indo-Pacific distribution and is one of the largest extant species of bony fish.

Ephippidae is a family of percomorph fishes, the spadefishes, in the order Moroniformes. These fishes are found in the tropical and temperate oceans of the world, except for the central Pacific.

The green humphead parrotfish is the largest species of parrotfish, growing to lengths of 1.5 m (4.9 ft) and weighing up to 75 kg (165 lb).

Sparisoma is a genus of parrotfishes native to warmer parts of the Atlantic. FishBase recognizes 15 species in this genus, including S. rocha described from Trindade Island in 2010 and S. choati described from the East Atlantic in 2012. They are the most important grazers of algae in the Caribbean Sea, especially since sea urchins, especially Diadema, the other prominent consumers of algae, have been reduced in many places by a recent epidemic.

The marbled parrotfish, also known as the seagrass parrotfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a parrotfish from the family Scaridae and is the only known member of the genus Leptoscarus. It has a wide Indo-Pacific distribution and is also found in the southeastern Atlantic Ocean. It is a coastal species found in beds of sea grass and seaweed.

Cetoscarus bicolor, also known as the bicolour parrotfish or bumphead parrotfish, is a species of fish belonging to the family Scaridae. It is found only in the Red Sea.

Jansen's wrasse is a species of ray-finned fish, a wrasse from the family Labridae which is native to the Indian Ocean and Pacific Ocean. In the south-western Pacific Ocean it is replaced by sibling species black-barred wrasse. It can be found in the aquarium trade.

The rusty parrotfish is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a parrotfish belonging to the family Scaridae. It is associated with reefs in the north western Indian Ocean and the Red Sea.

Chlorurus bowersi, Bower's parrotfish or the orange-blotch parrotfish, is a species of ray-finned fish, a parrotfish from the family Scaridae. It is found in the Western Pacific Ocean from the Ryukyu Islands of Japan in the north to Java, Papua and the Philippines in the south, and east to Micronesia. This species is found in reef flats and fronts in sheltered areas or where there is moderate exposure to the currents or waves. This is a relatively small parrotfish generally found in pairs which excavates burrows. It feeds on filamentous algae. Chlorurus bowersi was first formally described as Callyodon bowersi in 1909 by the American ichthyologist John Otterbein Snyder (1867-1943) and the type locality was given as Naha, Okinawa, Japan.

Chlorurus sordidus, known commonly as the daisy parrotfish or bullethead parrotfish, is a species of marine fish in the family Scaridae.

Scorpaenopsis diabolus, the false stonefish, false scorpionfish or the devil scorpionfish, is a species of venomous marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes. It has venomous spines and lives in the tropical Indian and Pacific Oceans as well as in the Red Sea. It is a bottom-dwelling predator that relies on its camouflage to catch passing prey.

Hipposcarus harid, the Longnose parrotfish or Candelamoa parrotfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a parrotfish from the family Scaridae found on coral reefs of Indian Ocean and the Red Sea.

Scarus altipinnis, the filament-finned parrotfish, high-fin parrotfish or mini-fin parrotfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a parrotfish from the family Scaridae. It occurs in the tropical and subtropical Western Pacific Ocean.

Chlorurus microrhinos, the blunt-head parrotfish or steephead parrotfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a parrotfish from the family Scaridae. It is found in the Indo-Pacific region.

Calotomus zonarchus, commonly known as yellowbar parrotfish, is a species of parrotfish native to the waters of the Hawaiian Islands.
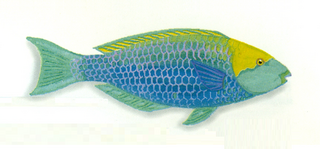
Scarus prasiognathos, the Singapore parrotfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a parrotfish, in the family Scaridae. It is native to the eastern Indian and western Pacific Oceans, where it lives in coral reefs.
Pseudojuloides cerasinus, the smalltail wrasse or the pencil wrasse, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a wrasse from the family Labridae. It is found in the tropical Pacific Ocean and was previously considered to have a much wider distribution but the recognition of new species has reduced this wide range.

Chlorurus gibbus, the heavybeak parrotfish, gibbus parrotfish or Red Sea steephead parrotfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a parrotfish from the family Scaridae. It is found in the Red Sea.

Scarus psittacus, the common parrotfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a parrotfish, in the family Scaridae. Other common names for this species include the palenose parrotfish, Batavian parrotfish and the rosy-cheek parrotfish. It has a wide distribution in the Indo-Pacific region where it is associated with coral reefs. This species is utilised as food. It is the type species of the genus Scarus.






















