
Calystegia is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the bindweed family Convolvulaceae. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution in temperate and subtropical regions, but with half of the species endemic to California. They are annual or herbaceous perennial twining vines growing 1–5 m tall, with spirally arranged leaves. The flowers are trumpet-shaped, 3–10 cm diameter, white or pink, with a sometimes inflated basal epicalyx.

Fallopia convolvulus, the black-bindweed or wild buckwheat, is a fast-growing annual flowering plant in the family Polygonaceae native throughout Europe, Asia and northern Africa.

Calystegia sepium is a species of flowering plant in the family Convolvulaceae. It has a subcosmopolitan distribution throughout temperate regions of the North and South hemispheres.

Dioscorea communis or Tamus communis is a species of flowering plant in the yam family Dioscoreaceae and is commonly known as black bryony, lady's-seal or black bindweed.

Malva moschata, the musk mallow or musk-mallow, is a species of flowering plant in the family Malvaceae, native to Europe and southwestern Asia, from Spain north to the British Isles and Poland, and east to southern Russia and Turkey. Growing to 60 cm (24 in) tall, it is a herbaceous perennial with hairy stems and foliage, and pink saucer-shaped flowers in summer.

Convolvulus arvensis, or field bindweed, is a species of bindweed in the Convolvulaceae native to Europe and Asia. It is a rhizomatous and climbing or creeping herbaceous perennial plant with stems growing to 0.5–2 metres (1.6–6.6 ft) in length. It is usually found at ground level with small white and pink flowers.

Sagina subulata (, the heath pearlwort, Irish-moss, awl-leaf pearlwort or Scottish moss, is a species of flowering plant in the pink and carnation family Caryophyllaceae. It is native to Europe, from Iceland south to Spain, and east to southern Sweden and Romania. It occurs on dry sandy or gravelly soils.

Rosa chinensis, known commonly as the China rose, Chinese rose, or Bengal rose, is a member of the genus Rosa native to Southwest China in Guizhou, Hubei, and Sichuan Provinces. The first publication of Rosa chinensis was in 1768 by Nikolaus Joseph von Jacquin in Observationum Botanicarum, 3, p. 7 & plate 55.

Calystegia soldanella is a species of bindweed known by various common names such as sea bindweed, seashore false bindweed, shore bindweed, shore convolvulus and beach morning glory.

Stellaria neglecta, greater chickweed, is an annual to short-lived herbaceous perennial flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae. It is native to Europe and Asia, where it grows in hedges and woodland margins on neutral to slightly acid, damp soils, and is widespread but rarely abundant. It has been introduced to North America, where it has been spreading in recent decades.

Stachys arvensis is a species of flowering plant in the mint family known by the common names field woundwort and staggerweed. It is native to Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa. It is known on other continents as an introduced species and widespread weed.

Calystegia affinis is a critically endangered species of climbing or creeping vine in the plant family Convolvulaceae. It is endemic to Lord Howe Island and Norfolk Island. In 2003 only about 45 mature plants were known, with about 40 of those on Norfolk Island.

Hypericum humifusum is a prostrate flowering plant in the St. John's wort family Hypericaceae commonly known as trailing St John's-wort. It is found in Western Europe.
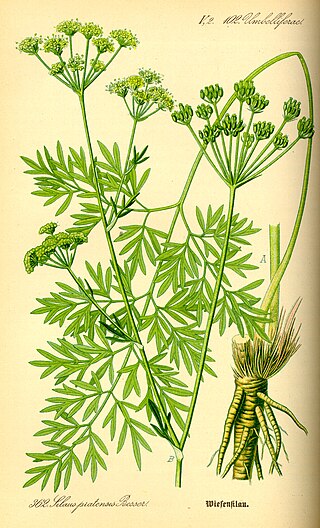
Silaum silaus, commonly known as pepper-saxifrage, is a perennial plant in the family Apiaceae (Umbelliferae) found across south-eastern, central, and western Europe, including the British Isles. It grows in damp grasslands on neutral soils.

Baeckea imbricata, commonly known as heath myrtle, is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a shrub with elliptical to egg-shaped or round leaves and small white flowers with five to twelve stamens.

Helleborus viridis, commonly called green hellebore, is a species of flowering plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae, native to Central and Western Europe, including southern England. All parts of the plant are poisonous.

Hewittia malabarica is a flowering plant in the monotypic genus HewittiaWight & Arn., belonging to the family Convolvulaceae and widespread throughout tropical Africa, Asia, and Polynesia. It is a climbing or prostrate perennial herb with slender stems and flowers that are pale yellow, cream, or white with a purple center, and large leaves that can be used as a cooked vegetable or used in folk medicine with the roots. The stems can be used to make ropes.

Fumaria purpurea, known as purple ramping-fumitory, is an annual flowering herbaceous plant in the poppy family which is endemic to the British Isles.

Oenanthe lachenalii, parsley water-dropwort, is a flowering plant in the carrot family, which is native to Europe and parts of North Africa. It is a declining plant of coastal wetlands.

Oenanthe silaifolia, narrow-leaved water-dropwort, is a flowering plant in the carrot family, which is native to Europe and adjacent parts of Asia and North Africa. It is an uncommon plant of water-meadows and wetlands.

























