
Carex is a vast genus of over 2,000 species of grass-like plants in the family Cyperaceae, commonly known as sedges. Other members of the family Cyperaceae are also called sedges, however those of genus Carex may be called true sedges, and it is the most species-rich genus in the family. The study of Carex is known as caricology.

Carex spissa is a species of sedge known by the common name San Diego sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to the southwestern United States in California, Arizona, and New Mexico, and far northern Mexico. It grows in wet places such as seeps and streambanks, sometimes on serpentine soils. This sedge looks somewhat like a cattail. It produces angled stems easily exceeding a meter in height surrounded by leathery green to reddish leaves up to about 1.2 meters long. The inflorescence is up to 80 centimeters long, with many long reddish brown flower spikes, each holding up to 300 developing fruits.

Carex vesicaria is an essentially Holarctic species of sedge known as bladder sedge, inflated sedge, and blister sedge. It has been used to insulate footwear in Norway and among the Sami people, and for basketry in North America.

Carex fascicularis, commonly known as tassel sedge, is a species of sedge of the family Cyperaceae that is native to Australia, New Zealand and New Guinea.
Carex tereticaulis, also known as basket sedge, is a species of sedge of the family Cyperaceae that is native to southern parts of Western Australia, southern parts of South Australia, southern and eastern parts of New South Wales as well as north western and central Victoria and Tasmania. The Koori peoples know the plant as Poong'ort.

Carex magellanica, is a perennial Carex species native to North America, Europe and the subarctic Northern hemisphere. Although it is considered a stable species worldwide, it is listed as endangered in Connecticut.

Carex elata, is a species of tussock-forming, grass-like plant in the Cyperaceae family. It is native to all of Europe, the Atlas Mountains of Africa, Turkey, Iran and Central Asia.

Carex rupestris, called the curly sedge and rock sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the family Cyperaceae, native to temperate and subarctic North America, Greenland, Iceland, Europe, and Asia.
Carex microglochin, called the fewseeded bog sedge and bristle sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to temperate and subarctic North America, South America, Europe and Asia. It is uncertain which hemisphere it originated on before dispersing to the other.
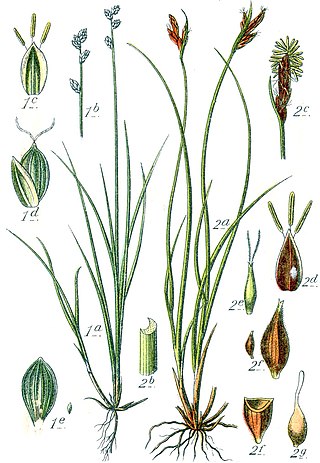
Carex loliacea is a species of flowering plant in the family Cyperaceae.

Carex radiata, the eastern star sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the family Cyperaceae, native to central and eastern North America. It is cultivated for its yellowish-green foliage and its relatively—for a sedge—showy flowers.

Carex alba, called the small white sedge, white-flowered sedge or just white sedge, is a species of sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is typically found in temperate forests of Eurasia, from the Pyrenees to the Russian Far East. It is the main host plant for the woodland brown butterfly, Lopinga achine.

Carex lessoniana, also commonly known as rautahi or cutty grass, is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to parts of New Zealand.

Carex congdonii is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to parts of California.

Carex gravida, also known as heavy-fruited sedge, heavy sedge or long-awned bracted sedge, is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to southern parts of Canada and parts of the United States.

Carex hendersonii, also known as Henderson's sedge or carex de Henderson, is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to western parts of North America.

Carex digitalis is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to south eastern parts of Canada as well as central and eastern parts of the United States.

Carex vestita, also commonly known as velvet sedge, is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to eastern parts of the United States.

Carex salina, also known as saltmarsh sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family, Cyperaceae. It is native to Eastern Canada, the UK, Norway, and parts of Northern Russia.

Carex prasina, the drooping sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the family Cyperaceae, native to eastern Canada, and the north-central and eastern United States. It is usually found growing in rich soils in deciduous forests, typically in wet places such as streamsides, seeps, springs and fens.



















