
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual to hold public office. Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated since the 17th century. Elections may fill offices in the legislature, sometimes in the executive and judiciary, and for regional and local government. This process is also used in many other private and business organizations, from clubs to voluntary associations and corporations.

The 2000 United States presidential election was the 54th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 7, 2000. Republican candidate George W. Bush, the Governor of Texas and the eldest son of the 41st President George H. W. Bush, won the election by defeating Democratic nominee Al Gore, the incumbent vice president. It was the fourth of five presidential elections in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote, and is considered one of the closest elections in US history.

The United States Electoral College is a body of electors established by the United States Constitution, constituted every four years for the sole purpose of electing the president and vice president of the United States. The Electoral College consists of 538 electors, and an absolute majority of 270 electoral votes is required to win an election. Pursuant to Article II, Section 1, Clause 2, the legislature of each state determines the manner by which its electors are chosen. Each state's number of electors is equal to the combined total of the state's membership in the Senate and House of Representatives; currently there are 100 senators and 435 representatives. Additionally, the Twenty-third Amendment provides that the District of Columbia (D.C.) is entitled to a number of electors no greater than that of the least populous state.

The Bharatiya Janata Party is one of the two major political parties in India, along with the Indian National Congress. As of 2018, it is the country's largest political party in terms of representation in the national parliament and state assemblies, and it is the world's largest party in terms of primary membership. BJP is a right-wing party, and its policy has historically reflected Hindu nationalist positions. It has close ideological and organisational links to the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh.
The incumbent is the current holder of an office. This term is usually used in reference to elections, in which races can often be defined as being between an incumbent and non-incumbent(s). For example, in the Hungarian presidential election, 2017, János Áder was the incumbent, because he had been the president in the term before the term for which the election sought to determine the president. A race without an incumbent is referred to as an open seat.

Elections in the United States are held for government officials at the federal, state, and local levels. At the federal level, the nation's head of state, the President, is elected indirectly by the people of each state, through an Electoral College. Today, these electors almost always vote with the popular vote of their state. All members of the federal legislature, the Congress, are directly elected by the people of each state. There are many elected offices at state level, each state having at least an elective Governor and legislature. There are also elected offices at the local level, in counties, cities, towns, townships, boroughs, and villages. According to a study by political scientist Jennifer Lawless, there were 519,682 elected officials in the United States as of 2012.
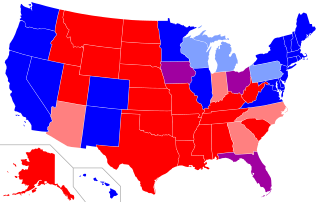
Since the 2000 United States presidential election, red states and blue states have referred to states of the United States whose voters predominantly choose either the Republican Party (red) or Democratic Party (blue) presidential candidates. Since then, the use of the term has been expanded to differentiate between states being perceived as liberal and those perceived as conservative. Examining patterns within states reveals that the reversal of the two parties' geographic bases has happened at the state level, but it is more complicated locally, with urban/rural divides associated with many of the largest changes.
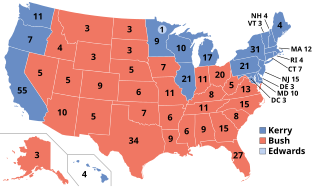
The 2004 United States presidential election, the 55th quadrennial presidential election, was held on Tuesday, November 2, 2004. Incumbent Republican President George W. Bush defeated Democratic nominee John Kerry, a United States Senator from Massachusetts.
India is a federation with a parliamentary system governed under the Constitution of India, which defines the power distribution between the union, or central, government and the states.
An independent or nonpartisan politician is an individual politician not affiliated with any political party. There are numerous reasons why someone may stand for office as an independent.

India held general elections to the 15th Lok Sabha in five phases between 16 April 2009 and 13 May 2009. With an electorate of 714 million, it was the largest democratic election in the world till the Indian General Elections 2014 held from 7 April 2014.

The Indian general election, 2014 was held to constitute the 16th Lok Sabha, electing members of parliament for all 543 parliamentary constituencies. Running in nine phases from 7 April to 12 May 2014, it was the longest election in the country's history. According to the Election Commission of India, 814.5 million people were eligible to vote, with an increase of 100 million voters since the last general election in 2009, making it the largest ever election in the world. Around 23.1 million or 2.7% of the total eligible voters were aged 18–19 years. A total of 8,251 candidates contested for the 543 Lok Sabha seats. The average election turnout over all nine phases was around 66.38%, the highest ever in the history of Indian general elections.

The 2012 United States presidential election was the 57th quadrennial American presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 6, 2012. The Democratic nominee, President Barack Obama, and his running mate, Vice President Joe Biden, were elected to a second term. They defeated the Republican ticket of former Governor Mitt Romney of Massachusetts and Representative Paul Ryan of Wisconsin.

The 2016 United States presidential election was the 58th quadrennial American presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. The Republican ticket of businessman Donald Trump and Indiana Governor Mike Pence defeated the Democratic ticket of former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton and U.S. Senator from Virginia Tim Kaine, despite losing the popular vote. Trump took office as the 45th President, and Pence as the 48th Vice President, on January 20, 2017.

The election of president and vice president of the United States is an indirect election in which citizens of the United States who are registered to vote in one of the 50 U.S. states or in Washington, D.C. cast ballots not directly for those offices, but instead for members of the U.S. Electoral College, known as electors. These electors then in turn cast direct votes, known as electoral votes, for president, and for vice president. The candidate who receives an absolute majority of electoral votes is then elected to that office. If no candidate receives an absolute majority of the votes for President, the House of Representatives chooses the winner; if no one receives an absolute majority of the votes for Vice President, then the Senate chooses the winner.

The 2015 Canadian federal election was held on October 19, 2015, to elect members to the House of Commons of the 42nd Canadian Parliament. The writs of election for the 2015 election were issued by Governor General David Johnston on August 4. The ensuing campaign was one of the longest in Canadian history. It was also the first time since the 1979 election that a Prime Minister attempted to remain in office into a fourth consecutive Parliament and the first time since the 1980 election that someone attempted to win a fourth term of any kind as Prime Minister.

The 2019 Indian general election is scheduled to be held in 7 phases from 11 April 2019 to 19 May 2019 to constitute the 17th Lok Sabha. The counting of votes will be conducted on 23 May 2019 and on the same day the results will be declared.

The 2017 United Kingdom general election took place on Thursday 8 June 2017, having been called just under two months earlier by Prime Minister Theresa May on 18 April 2017 after it was discussed in cabinet. Each of the 650 constituencies elected one Member of Parliament (MP) to the House of Commons. The governing Conservative Party remained the largest single party in the House of Commons but lost its majority, resulting in the formation of a minority government with a confidence-and-supply arrangement with the Democratic Unionist Party (DUP) of Northern Ireland.

The Election Commission of India is an autonomous constitutional authority responsible for administering election processes in India. The body administers elections to the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha and state Legislative Assemblies and Legislative Council in India, and the offices of the President and Vice President in the country. The Election Commission operates under the authority of Constitution per Article 324, and subsequently enacted Representation of the People Act. The commission has the powers under the Constitution, to act in an appropriate manner when the enacted laws make insufficient provisions to deal with a given situation in the conduct of an election. Being a constitutional authority, Election Commission is amongst the few institutions which function with both autonomy and freedom, along with the country’s higher judiciary, the Union Public Service Commission and the Comptroller and Auditor General of India.



















