
Gobiidae or gobies is a family of bony fish in the order Gobiiformes, one of the largest fish families comprising more than 2,000 species in more than 200 genera. Most of gobiid fish are relatively small, typically less than 10 cm (3.9 in) in length, and the family includes some of the smallest vertebrates in the world, such as Trimmatom nanus and Pandaka pygmaea, Trimmatom nanus are under 1 cm long when fully grown, then Pandaka pygmaea standard length are 9 mm (0.35 in), maximum known standard length are 11 mm (0.43 in). Some large gobies can reach over 30 cm (0.98 ft) in length, but that is exceptional. Generally, they are benthic or bottom-dwellers. Although few are important as food fish for humans, they are of great significance as prey species for other commercially important fish such as cod, haddock, sea bass and flatfish. Several gobiids are also of interest as aquarium fish, such as the dartfish of the genus Ptereleotris. Phylogenetic relationships of gobiids have been studied using molecular data.
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem found in and around a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms—aquatic life—that are dependent on each other and on their environment. The two main types of aquatic ecosystems are marine ecosystems and freshwater ecosystems. Freshwater ecosystems may be lentic ; lotic ; and wetlands.

Dalhousie Springs, also known as Witjira-Dalhousie Springs, is a group of over 60 natural artesian springs located in Witjira National Park on the western fringe of the Simpson Desert, 180 kilometres northeast of Oodnadatta in northern South Australia. They are about 250 kilometres (160 mi) southeast of Alice Springs.

The Old World silversides are a family, Atherinidae, of fish in the order Atheriniformes. Atherinidae are abundant and considered bony fish (teleost) that are widespread globally, living in rivers, estuaries, and coastal waters. They occur worldwide in tropical and temperate waters. About two-thirds of the species are marine, and the remainder live in fresh water. The 74 species are in 13 genera. The genus Craterocephalus is the most diverse with 25 species. Four genera are monotypic.

The delta smelt is an endangered slender-bodied smelt, about 5 to 7 cm long, in the family Osmeridae. Endemic to the upper Sacramento-San Joaquin Estuary of California, it mainly inhabits the freshwater-saltwater mixing zone of the estuary, except during its spawning season, when it migrates upstream to fresh water following winter "first flush" flow events. It functions as an indicator species for the overall health of the Delta's ecosystem. Delta Smelt are usually found at temperatures of less than 25 °C and prefer temperatures of around 20 °C. They are euryhaline but occur mostly at salinities of 0–7 practical salinity units.

Mudskippers are any of the 23 extant species of amphibious fish from the subfamily Oxudercinae of the goby family Oxudercidae. They are known for their unusual body shapes, preferences for semiaquatic habitats, limited terrestrial locomotion and jumping, and the ability to survive prolonged periods of time both in and out of water.

Upland and lowland are conditional descriptions of a plain based on elevation above sea level. In studies of the ecology of freshwater rivers, habitats are classified as upland or lowland.

The Australian smelt is a small, pelagic silvery freshwater fish found in large numbers in waters of the south eastern Australian mainland.
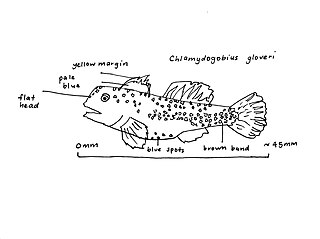
The Dalhousie goby is a species of goby endemic to Australia where it lives in the Dalhousie Springs. This species can reach a standard length of 4.5 centimetres (1.8 in). It feeds on small molluscs, crustaceans and other odds and ends like most other gobies.
Chlamydogobius micropterus, the Elizabeth Springs goby, is a species of goby endemic to Elizabeth Springs in the Shire of Diamantina, Queensland, Australia where it occurs in shallow, marshy pools. This species can reach a length of 3 centimetres (1.2 in) SL.

The Gobiiformes are an order of fish that includes the gobies and their relatives. The order, which was previously considered a suborder of Perciformes, is made up of about 2,211 species that are divided between seven families. Phylogenetic relationships of the Gobiiformes have been elucidated using molecular data. Gobiiforms are primarily small species that live in marine water, but roughly 10% of these species inhabit fresh water. This order is composed chiefly of benthic or burrowing species; like many other benthic fishes, most gobiiforms do not have a gas bladder or any other means of controlling their buoyancy in water, so they must spend most of their time on or near the bottom. Gobiiformes means "goby-like".
Brachygobius nunus, the Golden banded goby, is a species of bumblebee goby, a small genus of gobies that takes its common name from their round bodies, big heads, and their overall yellow to golden coloration interrupted by four brown to black vertical stripes reminiscent of the striped pattern of a bumblebee. They have also been figuratively described as "buzzing" from one surface to another inside the aquarium. Like other members of its genus, it is popular as an aquarium fish.

Tarpon are fish of the genus Megalops. They are the only members of the family Megalopidae. Of the two species, one is native to the Atlantic, and the other to the Indo-Pacific Oceans.

The desert pupfish is a rare species of bony fish in the family Cyprinodontidae. It is a small fish, typically less than 7.62 cm (3 in) in length. Males are generally larger than females, and have bright-blue coloration, while females and juveniles are silvery or tan. A notable attribute of the desert pupfish is their ability to survive in environments of extreme salinity, pH, and temperature, and low oxygen content. The desert pupfish mates in a characteristic fashion, wherein compatible males and females will come in contact and collectively jerk in an s-shape. Each jerk typically produces a single egg that is fertilized by the male and deposited in his territory. Breeding behavior includes aggressive arena-breeding and more docile consort-pair breeding.

The eastern mosquitofish was introduced to Australia in 1925, and had spread from the northeast coasts to New South Wales, southern Australia, and parts of Western Australia by 1934. By the 21st century, known populations of wild mosquitofish had occurred in every state and territory except the Northern Territory, found in swamps, lakes, billabongs, thermal springs, salt lakes, and ornamental ponds. Mosquitofish are considered a noxious pest, especially in New South Wales and Queensland, and it is illegal to release them into the wild or transport them live into any of the states or territories. Mosquitofish were introduced by military and local councils to control mosquito populations; however, there has been no evidence that Gambusia has had any effect in controlling mosquito populations or mosquito-borne diseases. Studies have shown that Gambusia can suffer mortalities if fed only on mosquito larvae, and survivors show poor growth and maturation. Gambusia typically eat zooplankton, beetles, mayflies, caddis flies, mites and other invertebrates; mosquito larvae make up only a small portion of their diet.

Species Descriptions

The Shimofuri goby is found in fresh and brackish waters. However, it is most abundant in low-salinity environments. The fish has typical features consistent with the family Gobiidae and grows to a maximum of 12 centimeters. These characteristics include two pelvic fins united from a conical sucking disk, a spiny anterior and a soft posterior dorsal fin, and eyes near the top of the head. These fins typically have 6-7 spines and 11-14 rays with orange tints on the edges. The Tridentiger bifasciatus has a flat wide head and is highly variable in color, but generally light or dark brown with midlateral spots and minuscule white spots on the head.

The Gulf killifish is one of the largest members of the genus Fundulus; it is capable of growing up to 7 inches (18 cm) in length, whereas the majority of other Fundulus reach a maximum length of 4 inches (10 cm). Therefore, F. grandis is among the largest minnows preyed upon by many sport fish, such as flounder, speckled trout, and red drum. Fundulus derives from the Latin meaning "bottom," and grandis means "large". The Gulf killifish is native to the Gulf of Mexico from Texas to Florida and the eastern coast of Florida and the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean. Threats to the survival of the Gulf killifish include extreme changes in salinity, changes in temperatures, and toxic events such as the hypoxic dead zone in Louisiana and the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. The Gulf killifish is currently being used to test the effects of oil and oil dispersants on the physiology of marine species affected by these substances. This is significant to conservation biology, because with the continued extraction of oil and other natural resources from North American waters, it has become increasingly important to understand the risks and consequences in worst-case scenarios, such as the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, and the lasting effects on the marine ecosystem.

Elizabeth Springs is a heritage-listed artesian springs in Diamantina Lakes, Shire of Diamantina, Queensland, Australia. It is one of the springs of the Great Artesian Basin (GAB). It was added to the Australian National Heritage List on 4 August 2009.
















