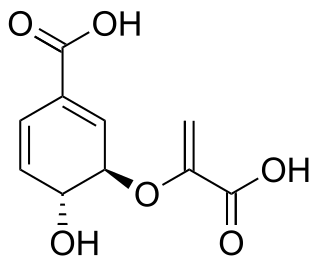
Chorismic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form chorismate, is an important biochemical intermediate in plants and microorganisms. It is a precursor for:
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, also known as p-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA), is a monohydroxybenzoic acid, a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water and chloroform but more soluble in polar organic solvents such as alcohols and acetone. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is primarily known as the basis for the preparation of its esters, known as parabens, which are used as preservatives in cosmetics and some ophthalmic solutions. It is isomeric with 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, known as salicylic acid, a precursor to aspirin, and with 3-hydroxybenzoic acid.

In biochemistry, mixed acid fermentation is the metabolic process by which a six-carbon sugar is converted into a complex and variable mixture of acids. It is an anaerobic (non-oxygen-requiring) fermentation reaction that is common in bacteria. It is characteristic for members of the Enterobacteriaceae, a large family of Gram-negative bacteria that includes E. coli.

Amino acid synthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids).

The transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the forward and the reverse.
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxybenzoate polyprenyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Isochorismate synthase ( EC 5.4.4.2) is an isomerase enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the biosynthesis of vitamin K2 (menaquinone) in Escherichia coli.

Cystathionine beta-lyase, also commonly referred to as CBL or β-cystathionase, is an enzyme that primarily catalyzes the following α,β-elimination reaction
4-amino-4-deoxychorismate lyase is an enzyme that participates in folate biosynthesis by catalyzing the production of PABA by the following reaction

The enzyme anthranilate synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme indole-3-glycerol-phosphate synthase (IGPS) (EC 4.1.1.48) catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an aminodeoxychorismate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.10) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme chorismate synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme ectoine synthase (EC ) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase (EC 2.2.1.7) is an enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway that catalyzes the chemical reaction
3-Deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate 7-phosphate (DAHP) synthase is the first enzyme in a series of metabolic reactions known as the shikimate pathway, which is responsible for the biosynthesis of the amino acids phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan. Since it is the first enzyme in the shikimate pathway, it controls the amount of carbon entering the pathway. Enzyme inhibition is the primary method of regulating the amount of carbon entering the pathway. Forms of this enzyme differ between organisms, but can be considered DAHP synthase based upon the reaction that is catalyzed by this enzyme.

In molecular biology this protein domain, refers to UbiD, which is found in prokaryotes, archaea and fungi, with two members in Archaeoglobus fulgidus. They are related to UbiD, a 3-octaprenyl-4-hydroxybenzoate carboxy-lyase from Escherichia coli that is involved in ubiquinone biosynthesis. The member from Helicobacter pylori has a C-terminal extension of just over 100 residues that is shared, in part, by the Aquifex aeolicus homologue.

Isochorismate pyruvate lyase is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing part of the pathway involved in the formation of salicylic acid. More specifically, IPL will use isochorismate as a substrate and convert it into salicylate and pyruvate. IPL is a PchB enzyme originating from the pchB gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
4-Hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate synthase (EC 4.3.3.7, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydropicolinate synthetase, dihydrodipicolinic acid synthase, L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing), dapA (gene)) is an enzyme with the systematic name L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing; (4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-(2S)-dipicolinate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction


















