The Pike's Peak gold rush was the boom in gold prospecting and mining in the Pike's Peak Country of western Kansas Territory and southwestern Nebraska Territory of the United States that began in July 1858 and lasted until roughly the creation of the Colorado Territory on February 28, 1861. An estimated 100,000 gold seekers took part in one of the greatest gold rushes in North American history.

Julian is a census-designated place (CDP) in San Diego County, California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,768, up from 1,502 at the time of the 2010 census.

A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, Greece, New Zealand, Brazil, Chile, South Africa, the United States, and Canada while smaller gold rushes took place elsewhere.
British Columbia gold rushes were important episodes in the history and settlement of European, Canadian and Chinese peoples in western Canada.
A. E. "Fred" Coleman was an American former slave credited with discovering gold in Julian, California and thus launching a gold rush in that area.

In the United States, gold mining has taken place continually since the discovery of gold at the Reed farm in North Carolina in 1799. The first documented occurrence of gold was in Virginia in 1782. Some minor gold production took place in North Carolina as early as 1793, but created no excitement. The discovery on the Reed farm in 1799 which was identified as gold in 1802 and subsequently mined marked the first commercial production.
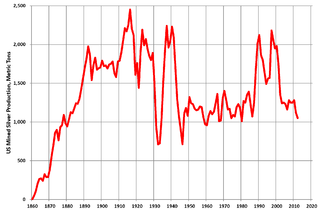
Silver mining in the United States began on a major scale with the discovery of the Comstock Lode in Nevada in 1858. The industry suffered greatly from the demonetization of silver in 1873 by the Coinage Act of 1873, known pejoratively as the "Crime of 73", but silver mining continues today.
Gold mining in Colorado, a state of the United States, has been an industry since 1858. It also played a key role in the establishment of the state of Colorado.

The Cuyamaca Mountains, locally the Cuyamacas, are a mountain range of the Peninsular Ranges System, in San Diego County, southern California. The mountain range runs roughly northwest to southeast. The Laguna Mountains are directly adjacent to the east, with Palomar Mountain and Hot Springs Mountain more distant to the north.
Orleans Flat was a historic mining town located on the San Juan Ridge about 20 miles northeast of Nevada City, California and about 5 miles northeast of North Bloomfield, California. The town was about 1 mile south of the Middle Yuba River at an elevation of about 4200 ft. To the west lay the mining towns of Moore's Flat and Woolsey's Flat, each about I mile apart. All three were settled around 1851 and their histories frequently intertwine. Collectively, they are sometimes referred to as "The Flats." All three were part of Eureka Township.
Banner is an unincorporated community in San Diego County, California. It lies at an elevation of 2743 feet. It is located on California State Route 78.
Belleville, California was a gold mining boomtown in the San Bernardino Mountains of San Bernardino County, California. The settlement grew up rapidly following the discovery of gold by William F. Holcomb in Holcomb Valley early 1860. Which helped the town challenge the seat of San Bernardino County. Belleville was named after Belle, the first child born in the new town. It was a busy mining town for ten years, it was virtually abandoned before the end of the 19th century. It is now a ghost town.

Confederate Gulch is a steeply incised gulch or valley on the west-facing slopes of the Big Belt Mountains in the U.S. state of Montana. Its small stream drains westward into Canyon Ferry Lake, on the upper Missouri River near present-day Townsend, Montana. In 1864, Confederate soldiers on parole during the American Civil War made a minor gold discovery in the gulch, but the discovery of the sensationally rich Montana Bar the following year—one of the richest placer strikes per acre ever made—led to other rich gold strikes up and down the gulch, and touched off a frantic boom period of placer gold mining in the area that extended through 1869. From 1866 to 1869, the gulch equaled or outstripped all other mining camps in the Montana Territory in gold production, producing an estimated $19–30 million worth of gold. For a time, Confederate Gulch was the largest community in Montana. In 1866, Montana had a total population of 28,000, and of these, about 10,000 (35%) were working in Confederate Gulch.
Remington Hill is a historic mining camp in Nevada County, California which prospered in the second half of the 19th century. It was named for Caleb Remington, a prominent local miner who lived mostly in neighboring Little York, where he died in 1865. It lay at an elevation of 4052 feet. It was situated around present Chalk Bluff Road about one mile south of Highway 20 and about 5.5 miles southeast of the town of Washington and 6 miles northeast of Dutch Flat, as the crow flies.
Sebastopol was a historic mining community located on the San Juan Ridge, about 13 miles north of Nevada City. It lay midway between Sweetland and North San Juan, around the intersection of modern Sweetland and School Roads, at an elevation of about 2000 feet.
Bonanza City is a ghost town, located 13 miles (21 km) southwest of Santa Fe in Santa Fe County, New Mexico, United States. The town was founded in 1880 as a mining town, following the discovery of gold and silver in the nearby Cerrillos Hills. It was abandoned sometime in the early 1900s. Later in the 20th century, The Bonanza Creek Movie Ranch, which contains a movie set depicting a late 19th century mining town, was built near the ruins of Bonanza City.
Branson City or Branson is a ghost town in San Diego County, California. It lies at an elevation of 3996 feet. It is located on State Highway 78 at its junction with Pine Hills Road, about one mile west of Julian.
Coleman Creek in San Diego County, California is a tributary of the San Diego River that arises at the top of the valley running southeasterly from Julian, at a saddle between two ridges of the Cuyamaca Mountains just south of Kentwood-In-The-Pines. From there, Coleman Creek descends northwesterly down the valley to Julian, where it turns west, descending its canyon northwesterly through the site of Branson City, past the mouth of its tributary Eastwood Creek on the north, passing through the south end of Spencer Valley, past the mouth of its tributary Baily Creek on the north, then descending northwest down Quanai Canyon to its confluence with the San Diego River.
Eastwood Creek in San Diego County, California, is a tributary of Coleman Creek that arises in the Cuyamaca Mountains, at the north face of the gold bearing mountain north of Julian. From the source Eastwood Creek descends northwesterly a short distance, then turns southwest down a canyon to its confluence with Coleman Creek, just below the site of Branson City.

Manchester was a mining town in the Los Burros Mining District in the southern Big Sur region of Monterey County, California from about 1875 to 1895. The town was reached by a 20 miles (32 km) road from King City to Jolon. From Jolon travelers could ride or take a stage or wagon to the Wagon Caves, followed by a difficult 14 miles (23 km) trail over the steep Santa Lucia Mountains to the site, about 4 miles (6.4 km) inland of Cape San Martin. Prospecting began in the area in the 1850s.