
The Hypocreales are an order of fungi within the class Sordariomycetes. In 2008, it was estimated that it contained some 237 genera, and 2647 species in seven families. Since then, a considerable number of further taxa have been identified, including an additional family, the Stachybotryaceae. Wijayawardene et al. in 2020 added more families and genera to the order. According to the Catalog of Life, As of April 2021 the Hypocreales contains 6 families, 137 genera, and 1411 species. Hyde et al. (2020a) listed 14 families under Hypocreales, while, Wijayawardene et al. (2022) accepted 15 families in the order, where Cylindriaceae was additionally added. Earlier, Hyde et al. (2020a) had placed Cylindriaceae in class Xylariomycetidae. Samarakoon et al. (2022) agreed. Hence, Cylindriaceae should have been excluded from Hypocreales and placed in Xylariomycetidae. Xiao et al. (2022) recently introduced a new family Polycephalomycetaceae to Hypocreales.

Neurospora is a genus of Ascomycete fungi. The genus name, meaning "nerve spore" refers to the characteristic striations on the spores that resemble axons.

The order Sordariales is one of the most diverse taxonomic groups within the Sordariomycetes.
The Melanommataceae are a family of fungi in the order Pleosporales. Taxa are widespread in temperate and subtropical regions, and are saprobic on wood and bark.
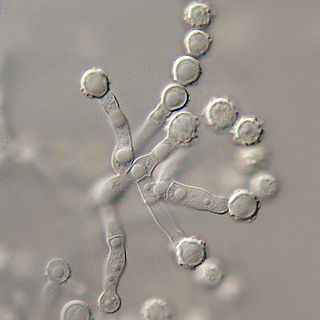
Microascus is a genus of fungi in the family Microascaceae.
Montagnula is a genus of fungi in the family Didymosphaeriaceae. The genus, circumscribed by mycologist Augusto Napoleone Berlese in 1896, contains an estimated 24 species in 2008, but is probably polyphyletic as currently circumscribed. It was originally placed in family Montagnulaceae, before that family was dissolved and it was later placed in family Didymosphaeriaceae, with 34 species.
Delitschia is a genus of fungi in the family Delitschiaceae.
Jugulospora is a genus of fungi that was placed within the Lasiosphaeriaceae family, It was then moved into the Neoschizotheciaceae family. This was thought to be a monotypic genus, containing the single species Jugulospora rotula, until more species were found.
Triangularia is a genus of fungi in the family Podosporaceae.
Zopfiella is a genus of fungi within the Lasiosphaeriaceae family.
Thielavia is a genus of fungi in the family Chaetomiaceae. Circumscribed by German botanist Friedrich Wilhelm Zopf in 1876, Thielavia is a teleomorph of Myceliophthora. Collectively, the genus is widely distributed, and according to a 2008 estimate, contained 31 species. Thielavia heterothallica and T. terrestris can cause infections in humans.
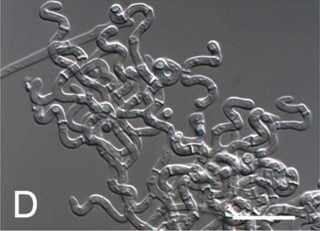
Arachnomyces is a genus of cleistothecial ascomycete fungi described in 1902, of which the anamorph (asexual) stage is the genus Onychocola. Although morphologically similar to members of other families, the fungus now belongs to its own monotypic family Arachnomycetaceae, which is the only family in the monotypic order Arachnomycetales.
Sphaerodes is a genus of fungi within the Coronophorales order but it has not been placed within a family.
Neocosmospora is a genus of fungi in the family Nectriaceae.
Dothiora is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Dothioraceae.
Epicoccum is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Didymellaceae.
Oidiodendron is a genus of fungi in the family Myxotrichaceae. It has 26 species. The genus was circumscribed by Norwegian forester Håkon Robak in 1932, with Oidiodendron fuscum assigned as the type species. The species is now known as Oidiodendron tenuissimum.
Conioscypha is a genus of terrestrial and freshwater fungi in the monotypic family Conioscyphaceae and the monotypic order Conioscyphales. They are found on decayed wood, leaves, or bamboo stems. Except for Conioscypha japonica which was isolated from dog skin fragments and hair in 2017.

Neocamarosporium is a genus of ascomycete fungi, as accepted by Wijayawardene et al. 2020. The species are typically halotolerant, being commonly found in saline environments like in saline water, hypersaline soils and especially in association with halophytes.







