
Trilobites are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last extant trilobites finally disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 251.9 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described.

Redlichiida is an order of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. Species assigned to the order Redlichiida are among the first trilobites to appear in the fossil record, about halfway during the Lower Cambrian. Due to the difficulty to relate sediments in different areas, there remains some discussion, but among the earliest are Fallotaspis, and Lemdadella, both belonging to this order. The first representatives of the orders Corynexochida and Ptychopariida also appear very early on and may prove to be even earlier than any redlichiid species. In terms of anatomical comparison, the earliest redlichiid species are probably ancestral to all other trilobite orders and share many primitive characters. The last redlichiid trilobites died out before the end of the Middle Cambrian.

Phacopidae is a family of phacopid trilobites that ranges from the Lower Ordovician to the Upper Devonian, with representatives in all paleocontinents.

Paradoxides is a genus of large to very large trilobite found throughout the world during the Middle Cambrian period. One record-breaking specimen of Paradoxides davidis, described by John William Salter in 1863, is 37 cm (15 in). The cephalon was semicircular with free cheeks ending in long, narrow, recurved spines. Eyes were crescent shaped providing an almost 360° view, but only in the horizontal plane. Its elongate thorax was composed of 19–21 segments and adorned with longish, recurved pleural spines. Its pygidium was comparatively small. Paradoxides is a characteristic Middle-Cambrian trilobite of the 'Atlantic' (Avalonian) fauna. Avalonian rocks were deposited near a small continent called Avalonia in the Paleozoic Iapetus Ocean. Avalonian beds are now in a narrow strip along the East Coast of North America, and in Europe.
Agnostus is a genus of agnostid trilobites, belonging to the family Agnostidae, that lived during the late Middle Cambrian – early Upper Cambrian. It is the type genus of the family Agnostidae and is subdivided into two subgenera, Agnostus and Homagnostus.

Dikelocephalus is a genus of very large trilobites of up to 50 cm (20 in) long, that lived during the last 3 million years of the Cambrian (Sunwaptan). Their fossils are commonly found as disarticulated sclerites, in the upper Mississippi Valley and in Canada (Alberta). The exoskeleton is rounded anteriorly, with the thorax and sides of the tailshield slightly tapering to about 2⁄3× of the width across the base of the spines at the back of the headshield. At the side corners of the pygidium there may be triangular or hooked spines, pointing backwards, while between the spines the posterior margin is at a 30-75° angle with the lateral margin, gently convex or nearly straight. If pygidial spines are lacking, the margin is gradually rounded. The thorax has 12 segments.

Analox Rasetti, 1966 is a genus of Eodiscinid trilobites belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida It lived during the Botomian stage. It can easily be distinguished from other trilobites by the two furrows that extend forwards and sidewards from the front of the glabella.

Meteoraspis is an extinct genus of ptychopariid trilobites of the family Tricrepicephalidae. The various species lived from 501 to 497 million years ago during the Dresbachian faunal stage of the late Cambrian Period. Fossils of Meteoraspis are characteristic of Late Cambrian strata in North America, though they are found in Late Cambrian strata elsewhere in the world, such as M. nevensis from Victoria Land, Antarctica.
Acadagnostus is a genus of trilobite from the Middle Cambrian, with 7 species currently recognized. The type species A. acadicus has the widest distribution known from any peronopsid and has been found in North America, Greenland, England, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Central Asia, the Altai Mountains, the Siberian shield, China, and Australia.

Ellipsocephalus Zenker, 1833, is a genus of blind Cambrian trilobite, comprising benthic species inhabiting deep, poorly lit or aphotic habitats. E. hoffi is a common trilobite mainly from central Europe.

Alokistocaridae is a family of ptychopariid trilobites that lived from the Botomian epoch of the Early Cambrian until the Late Cambrian. Alokistocarids were particle feeders and left small furrows which are occasionally preserved. Their remains are found worldwide. Elrathia kingii, one of the most collected trilobites in the world, is a typical alokistocarid.

Ptychoparia is a genus of ptychopariid trilobites, and is the type genus of the family Ptychopariidae, and the order Ptychopariida.

Odontochile is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, family Dalmanitidae.

Eodiscina is trilobite suborder. The Eodiscina first developed near the end of the Lower Cambrian period and became extinct at the end of the Middle Cambrian. Species are tiny to small, and have a thorax of two or three segments. Eodiscina includes six families classified under one superfamily, Eodiscoidea.
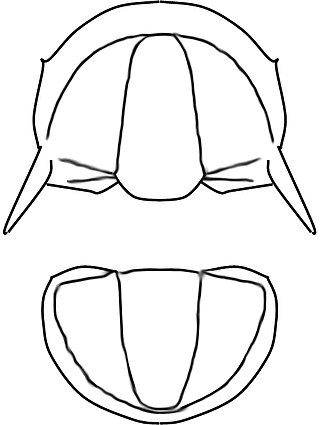
Litometopus is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the Botomian stage.
Diplorrhina Hawle and Corda (1847) is a genus of trilobite belonging to Order Agnostida. It lived during the early Middle Cambrian in what are now the Czech Republic and the North Siberian plateau. as in members of the family Peronopsidae it lacks a preglabellar furrow. Both cephalon and pygidium lack spines. It is difficult to distinguish Diplorrhina from many other peronopsids.
ConocephalitesBarrande, 1852, is a disused name for a genus of trilobite, of which the species have now been reassigned to other genera. The name was introduced as a replacement for ConocephalusZenker, 1833, which was unavailable since Thunberg used it in 1815 for a genus of conehead bushcricket. Barrande however was unaware that Conocoryphe had already been proposed by Hawle and Corda in 1847.

Tricrepicephalus is an extinct genus of ptychopariid trilobites of the family Tricrepicephalidae with species of average size. Its species lived from 501 to 497 million years ago during the Dresbachian faunal stage of the late Cambrian Period. Fossils of Tricrepicephalus are widespread in Late Cambrian deposits in North America, but is also known from one location in South America. Tricrepicephalus has an inverted egg-shaped exoskeleton, with three characteristic pits in the fold that parallels the margin of the headshield just in front of the central raised area. The articulating middle part of the body has 12 segments and the tailshield carries two long, tubular, curved pygidial spines that are reminiscent of earwig's pincers that rise backwards from the plain of the body at approximately 30°.

The Paradoxidoidea Hawle & Corda 1847, are a superfamily of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. They occurred during the late Lower Cambrian (Toyonian) and disappeared at the end of the Middle Cambrian.

Viaphacops is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, family Phacopidae, that lived during the Middle Devonian, and is known from North and South America, Asia.

















