
Keratin 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT9 gene.

Palmoplantar keratodermas are a heterogeneous group of skin disorders characterized by abnormal thickening (scleroderma) of the stratum corneum of the palms and soles.

Sézary disease, or Sézary syndrome, is a type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma that was first described by Albert Sézary. The affected T cells, known as Sézary's cells or Lutzner cells, have pathological quantities of mucopolysaccharides. Sézary disease is sometimes considered a late stage of mycosis fungoides with lymphadenopathy.
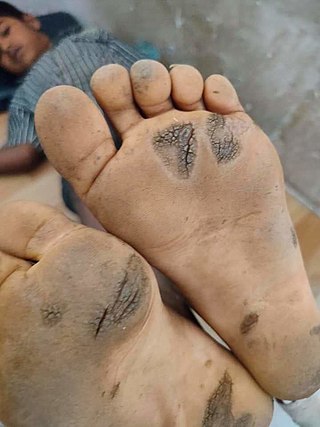
Keratoderma is a hornlike skin condition.

Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome (PLS), also known as palmoplantar keratoderma with periodontitis, is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder caused by a deficiency in cathepsin C.

Camisa disease is the variant form of Vohwinkel syndrome, characterized by ichthyosis and normal hearing.
Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia is a medical condition caused by mutations in a connexin gene, GJB6 or connexin-30, characterized by scalp hair that is wiry, brittle, and pale. It is often associated with patchy alopecia.
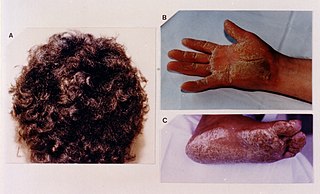
Naxos disease is a cutaneous condition characterized by a palmoplantar keratoderma. The prevalence of the syndrome is up to 1 in every 1000 people in the Greek islands.
Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome is an autosomal recessive condition with punctate symmetric palmoplantar keratoderma, with the keratoderma and fragility of the nails beginning around age 12. In addition to palmoplantar keratoderma, other symptoms include hypodontia, hypotrichosis, nail dystrophies, and eyelid cysts. Patients may also develop syringofibroadenoma and squamous cell carcinomas.
Keratoderma climactericum, also known as climacteric keratoderma, Haxthausen's disease, or acquired plantar keratoderma, is a skin condition characterized by hyperkeratosis of the palms and soles beginning at about the time of menopause.

Woolly hair autosomal recessive is a rare hereditary hair disorder characterized by sparse, short, curly hair.
Howel–Evans syndrome is an extremely rare condition involving thickening of the skin in the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet (hyperkeratosis). This familial disease is associated with a high lifetime risk of esophageal cancer. For this reason, it is sometimes known as tylosis with oesophageal cancer (TOC).

Bart–Pumphrey syndrome, also known as palmoplantar keratoderma with knuckle pads and leukonychia and deafness) is a cutaneous condition characterized by hyperkeratoses over the metacarpophalangeal, proximal and distal interphalangeal joints. It was characterized in 1967. It can be associated with GJB2.
Cerebral dysgenesis–neuropathy–ichthyosis–keratoderma syndrome is a neurocutaneous condition caused by mutation in the SNAP29 gene.

Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenita and sclerosing keratoderma syndrome is a rare cutaneous condition characterized by ichthyosis and keratoderma.
Hypotrichosis–acro-osteolysis–onychogryphosis–palmoplantar keratoderma–periodontitis syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by a prominent palmoplantar keratoderma.

Skin fragility-woolly hair-palmoplantar keratoderma syndrome is a very rare genetic disorder which is characterized by fragile skin which shows itself as blisters and erosion due to trauma that wouldn't typically cause those type of lesions, woolly hair with alopecia, nail dysplasia, widespread or local palmoplantar keratoderma associated with painful fissuring. Only 2 cases from two families have been described in medical literature.
Palmoplantar keratoderma with deafness, also known as Palmoplantar keratoderma-deafness syndrome is a rare genetic disorder which is characterized by either focal or diffuse early-onset palmoplantar keratoderma and sensorineural deafness. Transmission is autosomal dominant with incomplete penetrance.







