
Penguins are a group of aquatic flightless birds from the family Spheniscidae of the order Sphenisciformes. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is found north of the Equator. Highly adapted for life in the ocean water, penguins have countershaded dark and white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch with their bills and swallow whole while swimming. A penguin has a spiny tongue and powerful jaws to grip slippery prey.

Vegavis is a genus of extinct bird that lived in Antarctica during the Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous. The type species is Vegavis iaai. Vegavis was initially considered to be a member of Anseriformes within Galloanserae, but this claim has not been supported by some recent studies.

Plotopteridae is an extinct family of flightless seabirds with uncertain placement, generally considered as member of order Suliformes. They exhibited remarkable convergent evolution with the penguins, particularly with the now extinct giant penguins. That they lived in the North Pacific, the other side of the world from the penguins, has led to them being described at times as the Northern Hemisphere's penguins, though they were not closely related. More recent studies have shown, however, that the shoulder-girdle, forelimb and sternum of plotopterids differ significantly from those of penguins, so comparisons in terms of function may not be entirely accurate. Plotopterids are regarded as closely related to Anhingidae (darters) and Phalacrocoracidae (cormorants). On the other hand, there is a theory that this group may have a common ancestor with penguins due to the similarity of forelimb and brain morphology. However, the endocast morphology of stem group Sphenisciformes differs from both Plotopteridae and modern penguins.
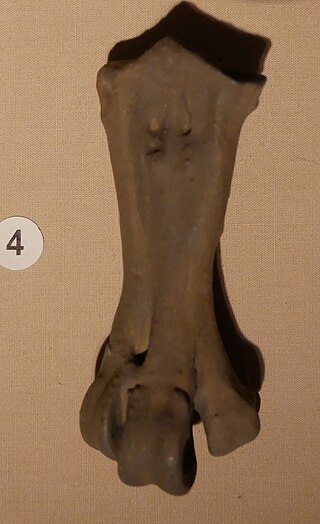
Waimanu is a genus of early penguin which lived during the Paleocene, soon after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, around 62–60 million years ago. It was about the size of an emperor penguin. It is one of the most important bird fossils for understanding the origin and evolution of birds because of the time period it comes from, and the position of penguins near the base of the bird family tree.
Archaeospheniscus lopdelli was the largest species of the extinct penguin genus Archaeospheniscus, standing about 90–120 cm (35–47 in) high, or somewhat less than the extant emperor penguin. It is only known from bones of a single individual which was found in the Late Oligocene Kokoamu Greensand Formation at Duntroon, New Zealand. Bones apparently belonging to this species are now also known from the Late Eocene La Meseta Formation on Seymour Island, Antarctica.

Palaeeudyptes antarcticus, also referred to as the narrow-flippered penguin, is the type species of the extinct penguin genus Palaeeudyptes. It was a huge species, albeit probably with a large size variation. Although the size range can only be loosely estimated, the birds seem to have stood between 43 and 55 inches high in life, placing this species and its congener Palaeeudyptes marplesi among the largest penguin species known. It was the last known Palaeeudyptes species, and although the exact time when it lived is not precisely determined, it may have evolved from P. marplesi, or they might even have been a single species which slightly decreased in size over time.
Palaeeudyptes gunnari is an extinct species of the extinct penguin genus Palaeeudyptes. It was a bit smaller than its congener Palaeeudyptes antarcticus of New Zealand, standing between 110 and 125 cm high, approximately the size of the emperor penguin. It is known from dozens of fossil bones from Middle or Late Eocene strata of the La Meseta Formation on Seymour Island, Antarctica. Initially, it was described as a separate genus, Eosphaeniscus. However, this was based on a single weathered and broken tarsometatarsus. Better material recovered later showed that the species belongs into the present genus.
Palaeeudyptes klekowskii is an extinct species of the penguin genus Palaeeudyptes. It was previously thought to have been approximately the size of its congener Palaeeudyptes antarcticus, somewhat larger than the modern emperor penguin, but a 2014 study showed it was in fact almost twice as tall, earning it the nickname “Mega Penguin”. Its maximum length is estimated to be up to 2 meters (6.6 ft) and maximum body mass up to 116 kg (256 lb). Knowledge of it comes from an extensive collection of fossil bones from the Late Eocene of the La Meseta Formation on Seymour Island, Antarctica. P. klekowskii was at first not recognized as a distinct species, and despite the coexistence of two so closely related species of similar size as Palaeeudyptes gunnari and P. klekowskii seeming somewhat improbable, the amount of fossil material suggests that the two species are indeed diagnosably different.

The Pelagornithidae, commonly called pelagornithids, pseudodontorns, bony-toothed birds, false-toothed birds or pseudotooth birds, are a prehistoric family of large seabirds. Their fossil remains have been found all over the world in rocks dating between the Early Paleocene and the Pliocene-Pleistocene boundary.
Australornis is a genus of extinct seabird discovered in New Zealand. It lived in the Paleocene epoch, 60.5 to 61.6 million years ago (Ma). The type species name originates from australis, Latin for "southern", and ornis, the Greek word for "bird", and lovei commemorates Leigh Love, an amateur paleontologist who discovered it.
Tereingaornis moisleyi, also referred to as Moisley's penguin, is a genus and species of extinct penguin from the Middle Pliocene of New Zealand. It was slightly smaller than the extant Fiordland crested penguin. It was described by Ron Scarlett in 1983 from fossil material found by William Moisley near Te Reinga Falls on the Wairoa River, in the Hawke's Bay Region of the North Island. Another specimen was found later at Waihi Beach, Hāwera, on the South Taranaki Bight. The genus name Tereingaornis combines the name of the type locality with the Greek ornis ("bird"); the specific epithet honours the discoverer of the fossil.

Kumimanu is an extinct genus of giant penguin, which lived around 56 to 60 million years ago. The type species is K. biceae, which arose after the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs. Fossils were found in New Zealand, and the discovery was announced in December 2017. A second species, Kumimanu fordycei, was named in February 2023.

Muriwaimanu is an extinct genus of early penguin from the Paleocene Waipara Greensand of New Zealand. Only the type species M. tuatahi is known.
Sequiwaimanu is an extinct genus of early penguin from the Waipara Greensand of New Zealand. The type species, S. rosieae, was named and described by Gerald Mayr in 2018.
Kupoupou is an extinct genus of bird from the Paleocene-aged Takatika Grit of the Chatham Islands, New Zealand which is believed to be the oldest penguin genus known to date. The type species, K. stilwelli, was named and described by Blokland et al. in 2019.
The Waipara Greensand is a geological rock unit found in Canterbury, New Zealand. It dates from just after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, the Selandian and Thanetian, around 62–58 million years ago in the Palaeocene. It is well known for its fossils, particularly for containing the oldest penguins (Sphenisciformes) and also containing shark and fish fossils.

Tonsala is an extinct genus of Plotopteridae, a family of flightless seabird similar in biology with penguins, but more closely related to modern cormorants. The genus is known from terrains dated from the Late Oligocene of the State of Washington and Japan.

Klallamornis is an extinct genus of Plotopteridae, a family of large, flightless birds related to modern cormorants, darters, gannets, and boobies. This genus included the largest North American plotopterids. Its remains can be found in Late Eocene to Late Oligocene rocks from the Makah Formation, the overlying Pysht Formation and the Lincoln Creek Formation of the State of Washington. During its existence, Klallamornis was the largest plotopterid on the North American continent. The first fossil remains attributed to the taxon were collected in 1983, although the genus wasn't described until 2016.
Protodontopteryx is a genus of pelagornithid that lived in New Zealand roughly 62 million years ago, during the early Paleocene epoch. It contains one species, Protodontopteryx ruthae. Protodontopteryx is the smallest, oldest, and most basal pelagornithid discovered.












