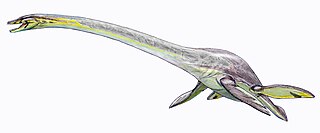
Plesiosauroidea is an extinct clade of carnivorous marine reptiles. They have the snake-like longest neck to body ratio of any reptile. Plesiosauroids are known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. After their discovery, some plesiosauroids were said to have resembled "a snake threaded through the shell of a turtle", although they had no shell.

Plesiosaurus is a genus of extinct, large marine sauropterygian reptile that lived during the Early Jurassic. It is known by nearly complete skeletons from the Lias of England. It is distinguishable by its small head, long and slender neck, broad turtle-like body, a short tail, and two pairs of large, elongated paddles. It lends its name to the order Plesiosauria, of which it is an early, but fairly typical member. It contains only one species, the type, Plesiosaurus dolichodeirus. Other species once assigned to this genus, including P. brachypterygius, P. guilielmiimperatoris, and P. tournemirensis have been reassigned to new genera, such as Hydrorion, Seeleyosaurus and Microcleidus.

Elasmosaurus is a genus of plesiosaur that lived in North America during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous period, at about 80.6 to 77 million years ago. The first specimen was discovered in 1867 near Fort Wallace, Kansas, US, and was sent to the American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope, who named it E. platyurus in 1868. The generic name means "thin-plate reptile", and the specific name means "flat-tailed". Cope originally reconstructed the skeleton of Elasmosaurus with the skull at the end of the tail, an error which was made light of by the paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh, and became part of their "Bone Wars" rivalry. Only one incomplete Elasmosaurus skeleton is definitely known, consisting of a fragmentary skull, the spine, and now lost pectoral and pelvic girdles, and a single species is recognized today; other species are now considered invalid or have been moved to other genera. A fragmentary elasmosaurid specimen from Germany may belong to this genus.

The Plesiosauria or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia.

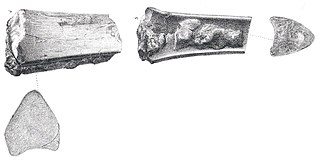
Valdoraptor is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous. Its fossils were found in England. It is known only from bones of the feet. The holotype, BMNH R2559, was found near Cuckfield in layers of the Tunbridge Wells Sand Formation dating from the late Valanginian. The specimen is damaged lacking parts of the upper and lower ends. It has a conserved length of 215 millimetres (8.5 in) and an estimated length of 240 millimetres (9.4 in). This genus is paleontologically significant for being the first ornithomimosaur specimen known from England and represents the earliest record of ornithomimosaurs.

Ornithopsis is a genus of sauropod dinosaur, from the Early Cretaceous of England and possibly Germany. The type species, which is the only species seen as valid today, is O. hulkei, which is only known from fragmentary remains.

Elasmosauridae is an extinct family of plesiosaurs, often called elasmosaurs. They had the longest necks of the plesiosaurs and existed from the Hauterivian to the Maastrichtian stages of the Cretaceous, and represented one of the two groups of plesiosaurs present at the end of the Cretaceous alongside Polycotylidae.
Ornithostoma is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur that lived during the Early Cretaceous period of Europe, around 110 million years ago. Ornithostoma was once thought to have been a senior synonym of the pteranodontid Pteranodon due to its toothless anatomy and prior naming.

Suchosaurus is a spinosaurid dinosaur from Cretaceous England and Portugal, originally believed to be a genus of crocodile. The type material, consisting of teeth, was used by British palaeontologist Richard Owen to name the species S. cultridens in 1841. Later in 1897, French palaeontologist Henri-Émile Sauvage named a second species, S. girardi, based on two fragments from the mandible and one tooth discovered in Portugal. Suchosaurus is possibly a senior synonym of the contemporary spinosaurid Baryonyx, but is usually considered a dubious name due to the paucity of its remains, and is considered an indeterminate baryonychine. In the Wadhurst Clay Formation of what is now southern England, Suchosaurus lived alongside other dinosaurs, as well as plesiosaurs, mammals, and crocodyliforms.

Brachauchenius is an extinct genus of pliosaurs that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what are now North America and North Africa. Only one species is known, B. lucasi, initially described by Samuel Wendell Williston in 1903 from a partial fossil skeleton discovered in a quarry in Kansas, United States. Many other fossil specimens attributed to the species were subsequently discovered, including an individual from Morocco whose presence was made official in 2016. Many contemporary pliosaur specimens were formerly attributed to Brachauchenius, but have since been reidentified as belonging to other genera or are recognized as indeterminate.

Styxosaurus is a genus of plesiosaur of the family Elasmosauridae. Styxosaurus lived during the Campanian age of the Cretaceous period. Three species are known: S. snowii, S. browni, and S. rezaci.

Colymbosaurus is a genus of cryptoclidid plesiosaur from the Late Jurassic (Callovian-Tithonian) of the UK and Svalbard, Norway. There are two currently recognized species, C. megadeirus and C. svalbardensis.

Polyptychodon is a genus of pliosaurid found in Middle-Late Cretaceous marine deposits in southern England, France and Argentina. It has been considered a nomen dubium in a 2016 review.

Aristonectes is an extinct genus of large elasmosaurid plesiosaurs that lived during the Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous. Two species are known, A. parvidens and A. quiriquinensis, whose fossil remains were discovered in what are now Patagonia and Antarctica. Throughout the 20th century, Aristonectes was a difficult animal for scientists to analyze due to poor fossil preparation, its relationships to other genera were uncertain. After subsequent revisions and discoveries carried out from the beginning of the 21st century, Aristonectes is now recognised as the type genus of the subfamily Aristonectinae, a lineage of elasmosaurids characterized by an enlarged skull and a reduced length of the neck.
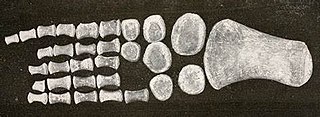
Ogmodirus is an extinct genus of plesiosaur found in the Cenomanian-Turonian Greenhorn Limestone of Kansas. The type species, O. martini, was named by Samuel Wendell Williston and Roy Lee Moodie in 1913.

Cimoliasaurus was a plesiosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of the eastern United States, with fossils known from New Jersey, North Carolina, and Maryland.

Polycotylus is a genus of plesiosaur within the family Polycotylidae. The type species is P. latippinis and was named by American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope in 1869. Eleven other species have been identified. The name means 'much-cupped vertebrae', referring to the shape of the vertebrae. It lived in the Western Interior Seaway of North America toward the end of the Cretaceous. One fossil preserves an adult with a single large fetus inside of it, indicating that Polycotylus gave live birth, an unusual adaptation among reptiles.
Eurycleidus is an extinct genus of large-bodied rhomaleosaurid known from the Early Jurassic period of the United Kingdom. It contains a single species, E. arcuatus.

Eretmosaurus is an extinct genus of plesiosaur from the Early and Middle Jurassic of England and Russia. Two species are known: E. rugosus and E. dubius.

This timeline of plesiosaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, taxonomic revisions, and cultural portrayals of plesiosaurs, an order of marine reptiles that flourished during the Mesozoic Era. The first scientifically documented plesiosaur fossils were discovered during the early 19th century by Mary Anning. Plesiosaurs were actually discovered and described before dinosaurs. They were also among the first animals to be featured in artistic reconstructions of the ancient world, and therefore among the earliest prehistoric creatures to attract the attention of the lay public. Plesiosaurs were originally thought to be a kind of primitive transitional form between marine life and terrestrial reptiles. However, now plesiosaurs are recognized as highly derived marine reptiles descended from terrestrial ancestors.


















