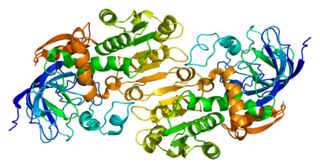
Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADH) (EC 1.1.1.1) are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to NADH. In humans and many other animals, they serve to break down alcohols that are otherwise toxic, and they also participate in the generation of useful aldehyde, ketone, or alcohol groups during the biosynthesis of various metabolites. In yeast, plants, and many bacteria, some alcohol dehydrogenases catalyze the opposite reaction as part of fermentation to ensure a constant supply of NAD+.

Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ), also called methoxatin, is a redox cofactor and antioxidant. Produced by bacteria, it is found in soil and foods such as kiwifruit, as well as human breast milk. Enzymes using PQQ as a redox cofactor are called quinoproteins and play a variety of redox roles. Quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase is used as a glucose sensor in bacteria. PQQ stimulates growth in bacteria. Eukaryote targets, including mammalian lactate dehydrogenase, are of more interest to health. It is suggested that PQQ taken as a dietary supplement could promote mitochondrial biogenesis via this pathway as well as PGC-1α.
Carbohydrate dehydrogenases are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the conversion from a carbohydrate to an aldehyde, lactone, or ketose.

Aldehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH2 gene located on chromosome 12. This protein belongs to the aldehyde dehydrogenase family of enzymes. Aldehyde dehydrogenase is the second enzyme of the major oxidative pathway of alcohol metabolism. Two major liver isoforms of aldehyde dehydrogenase, cytosolic and mitochondrial, can be distinguished by their electrophoretic mobilities, kinetic properties, and subcellular localizations.
In enzymology, a cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.195) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an alcohol oxidase (EC 1.1.3.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucose 1-dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a malate dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.1.5.4), formerly malate dehydrogenase (acceptor) (EC 1.1.99.16), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a polyvinyl-alcohol dehydrogenase (acceptor) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a polyvinyl-alcohol oxidase (EC 1.1.3.30) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.6.5.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
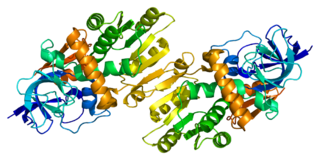
Quinone oxidoreductase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CRYZ gene.
Polyvinyl alcohol dehydrogenase (cytochrome) (EC 1.1.2.6, PVA dehydrogenase, PVADH) is an enzyme with systematic name polyvinyl alcohol:ferricytochrome-c oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Alcohol dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.1.5.5, type III ADH, membrane associated quinohaemoprotein alcohol dehydrogenase) is an enzyme with systematic name alcohol:quinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

NADH:ubiquinone reductase (non-electrogenic) (EC 1.6.5.9, NDH-2, ubiquinone reductase, coenzyme Q reductase, dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-coenzyme Q reductase, DPNH-coenzyme Q reductase, DPNH-ubiquinone reductase, NADH-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase, NADH-coenzyme Q reductase, NADH-CoQ oxidoreductase, NADH-CoQ reductase) is an enzyme with systematic name NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
NADH dehydrogenase is an enzyme that converts nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) from its reduced form (NADH) to its oxidized form (NAD+). Members of the NADH dehydrogenase family and analogues are commonly systematically named using the format NADH:acceptor oxidoreductase. The chemical reaction these enzymes catalyze is generally represented with the following equation:
Alcohol dehydrogenases are enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones.







