
Bergen-Belsen, or Belsen, was a Nazi concentration camp in what is today Lower Saxony in northern Germany, southwest of the town of Bergen near Celle. Originally established as a prisoner of war camp, in 1943, parts of it became a concentration camp. Initially this was an "exchange camp", where Jewish hostages were held with the intention of exchanging them for German prisoners of war held overseas. The camp was later expanded to hold Jews from other concentration camps.

Neuengamme was a network of Nazi concentration camps in Northern Germany that consisted of the main camp, Neuengamme, and more than 85 satellite camps. Established in 1938 near the village of Neuengamme in the Bergedorf district of Hamburg, the Neuengamme camp became the largest concentration camp in Northwest Germany. Over 100,000 prisoners came through Neuengamme and its subcamps, 24 of which were for women. The verified death toll is 42,900: 14,000 in the main camp, 12,800 in the subcamps, and 16,100 in the death marches and bombings during the final weeks of World War II. Following Germany's defeat in 1945, the British Army used the site as an internment camp for SS and other Nazi officials. In 1948, the British transferred the land to the Free Hanseatic City of Hamburg, which summarily demolished the camp's wooden barracks and built in its stead a prison cell block, converting the former concentration camp site into two state prisons operated by the Hamburg authorities from 1950 to 2004. Following protests by various groups of survivors and allies, the site now serves as a memorial. It is situated 15 km southeast of the centre of Hamburg.

Bad Ischl is a spa town in Austria. It lies in the southern part of Upper Austria, at the river Traun in the centre of the Salzkammergut region. The town consists of the Katastralgemeinden Ahorn, Bad Ischl, Haiden, Jainzen, Kaltenbach, Lauffen, Lindau, Pfandl, Perneck, Reiterndorf and Rettenbach. It is connected to the village of Strobl by the river Ischl, which drains from the Wolfgangsee, and to the Traunsee, into which the stream empties. It is home to the Kaiservilla, summer residence of Austro-Hungarian monarchs Emperor Franz Joseph I and Empress Elisabeth. In 2024, Bad Ischl will be one of the European Capitals of Culture – the third city in Austria after Graz (2003) and Linz (2009).

Displaced persons camps in post–World War II Europe were established in Germany, Austria, and Italy, primarily for refugees from Eastern Europe and for the former inmates of the Nazi German concentration camps. A "displaced persons camp" is a temporary facility for displaced persons, whether refugees or internally displaced persons. Two years after the end of World War II in Europe, some 850,000 people lived in displaced persons camps across Europe, among them Armenians, Czechoslovaks, Estonians, Greeks, Poles, Latvians, Lithuanians, Yugoslavs, Jews, Russians, Ukrainians, Hungarians, and Belarusians.

The entirety of Germany was occupied and administered by the Allies of World War II from the Berlin Declaration on 5 June 1945 to the establishment of West Germany on 23 May 1949. Unlike occupied Japan, Germany was stripped of its sovereignty and former state: after Nazi Germany surrendered on 8 May 1945, four countries representing the Allies asserted joint authority and sovereignty through the Allied Control Council (ACC) under the Berlin Declaration of 5 June 1945 that led to the fall of the German Reich. At first, Allied-occupied Germany was defined as all territories of Germany before the 1938 Nazi annexation of Austria; the Potsdam Agreement on 2 August 1945 defined the new eastern German border by giving Poland and the Soviet Union all regions of Germany east of the Oder–Neisse line and divided the remaining "Germany as a whole" into four occupation zones, each administered by one of the Allies.

Föhrenwald was one of the largest displaced persons camps in post-World War II Europe and the last to close, in 1957. It was located in the section now known as Waldram in Wolfratshausen in Bavaria, Germany.

Bergen-Belsen displaced persons camp was a displaced persons (DP) camp for refugees after World War II, in Lower Saxony in northwestern Germany, southwest of the town of Bergen near Celle. It was in operation from the summer of 1945 until September 1950. For a time, Belsen DP camp was the largest Jewish DP camp in Germany and the only one in the British occupation zone with an exclusively Jewish population. The camp was under British authority and overseen by the United Nations Relief and Rehabilitation Administration (UNRRA) with camp directors that included Simon Bloomberg. Today, the camp is a Bundeswehr barracks, having been a British Army base until 2015.
Sh'erit ha-Pletah is a Hebrew term for Jewish Holocaust survivors living in Displaced Persons (DP) camps, and the organisations they created to act on their behalf with the Allied authorities. These were active between 27 May 1945 and 1950–51, when the last DP camps closed.
Feldafing displaced persons camp in Bavaria was the first DP camp exclusively for use by liberated Jewish concentration camp prisoners. It was later used by Jewish refugees from the Russian-controlled Jewish areas. The camp was located in Feldafing's Höhenberg area and beyond.
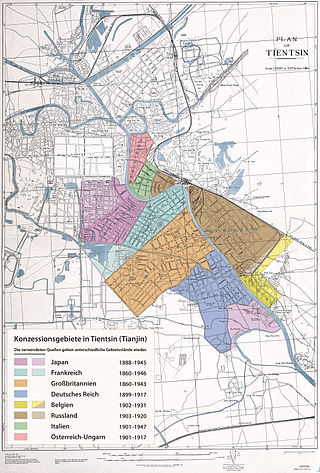
The foreign concessions in Tianjin were concession territories ceded by Qing China to a number of European countries, the United States and Japan within the city of Tianjin. There were altogether nine foreign concessions in old Tianjin on the eve of World War II. These concessions also contributed to the rapid development of Tianjin from the early to mid-20th century. The first foreign concessions in Tianjin were granted in 1860. By 1943, all the foreign concessions, except the Japanese concession, had ceased to exist de facto.
Holocaust survivors are people who survived the Holocaust, defined as the persecution and attempted annihilation of the Jews by Nazi Germany and its allies before and during World War II in Europe and North Africa. There is no universally accepted definition of the term, and it has been applied variously to Jews who survived the war in German-occupied Europe or other Axis territories, as well as to those who fled to Allied and neutral countries before or during the war. In some cases, non-Jews who also experienced collective persecution under the Nazi regime are considered Holocaust survivors as well. The definition has evolved over time.

Bagnoli is a western seaside quarter of Naples, Italy, well beyond the confines of the original city. It is beyond Cape Posillipo and, thus, looking on the coast of the Bay of Pozzuoli.
The Baltic University in Exile was established in the displaced persons camps in Germany to educate refugees from Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania in the aftermath of the Second World War.
Scouting has been active in displaced persons camps and in the lives of refugees since World War I. During and after World War II, until the early 1950s, Scouting and Guiding flourished in these camps. These Scout and Girl Guide groups often provided postal delivery and other basic services in displaced persons camps. This working system was duplicated dozens of times around the world. In the present, Scouting and Guiding once again provide services and relief in camps throughout war-torn Africa.

USS General W. M. Black (AP-135) was a General G. O. Squier-class transport ship for the U.S. Navy in World War II. The ship was crewed by the U.S. Coast Guard until decommissioning. She was named in honor of U.S. Army general William Murray Black. She was transferred to the U.S. Army as USAT General W. M. Black in 1946. On 1 March 1950 she was transferred to the Military Sea Transportation Service (MSTS) as USNS General W. M. Black (T-AP-135). She was later sold for commercial operation under the name SS Green Forest, before being scrapped in 1980.
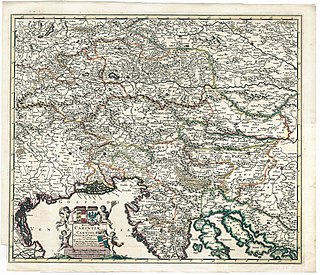
World War II in the Slovene Lands started in April 1941 and lasted until May 1945. The Slovene Lands were in a unique situation during World War II in Europe. In addition to being trisected, a fate which also befell Greece, Drava Banovina was the only region that experienced a further step—absorption and annexation into neighboring Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, and Hungary. The Slovene-settled territory was divided largely between Nazi Germany and the Kingdom of Italy, with smaller territories occupied and annexed by Hungary and the Independent State of Croatia.

The Austro-Hungarian Armed Forces occupied Serbia from late 1915 until the end of World War I. Austria-Hungary's declaration of war against Serbia on 28 July 1914 marked the beginning of the war. After three unsuccessful Austro-Hungarian offensives between August and December 1914, a combined Austro-Hungarian and German offensive breached the Serbian front from the north and west in October 1915, while Bulgaria attacked from the east. By January 1916, all of Serbia had been occupied by the Central Powers.

Hirsch Schwartzberg was a Jewish leader of Holocaust survivors under the American occupation of Berlin.

Petersberg Citadel in Erfurt, central Germany, is one of the largest and best-preserved town fortresses in Europe. The citadel was built on Petersberg hill, in the north-western part of the old town centre from 1665, when Erfurt was governed by the Electorate of Mainz. It is surrounded by over two kilometres of stone walls and is 36 hectares in size.
Germany has an embassy in Minsk. Belarus has an embassy in Berlin, a consulate general in Munich, and two honorary consulates in Cottbus and Hamburg.













