The Royal Australian Navy (RAN) is the naval branch of the Australian Defence Force. Following the Federation of Australia in 1901, the ships and resources of the separate colonial navies were integrated into a national force, called the Commonwealth Naval Forces. Originally intended for local defence, the navy was granted the title of 'Royal Australian Navy' in 1911, and became increasingly responsible for defence of the region.
Nickelodeon is an American pay television network which was launched on April 1, 1979 as the first cable channel for children. It is owned by Viacom through its Viacom Media Networks division's Nickelodeon Group unit and is based in New York City. It broadcasts usually from 7:00 a.m. to 9:00 p.m. on weekdays, Saturdays from 7:00 a.m. to 9:30 p.m., and Sundays from 7:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m.. It is primarily aimed at children and adolescents aged 2–17.

The 800 metres, or 800 meters, is a common track running event. It is the shortest common middle-distance running event. The 800 metres is run over two laps of the track and has been an Olympic event since the first games in 1896. During indoor track season the event is usually run on a 200-metre track, therefore requiring four laps.

The 400 metres, or 400 metre dash, is a sprinting event in track and field competitions. It has been featured in the athletics programme at the Summer Olympics since 1896 for men and since 1964 for women. On a standard outdoor running track, it is one lap around the track. Runners start in staggered positions and race in separate lanes for the entire course. In many countries, athletes previously competed in the 440 yard dash (402.336 m)—which is a quarter of a mile and was referred to as the 'quarter-mile'—instead of the 400 m (437.445 yards), though this distance is now obsolete.
A perennial candidate is a political candidate who frequently runs for an elected office. The term is not generally extended to incumbent politicians who successfully defend their seats repeatedly.

The 100 metres, or 100-metre dash, is a sprint race in track and field competitions. The shortest common outdoor running distance, it is one of the most popular and prestigious events in the sport of athletics. It has been contested at the Summer Olympics since 1896 for men and since 1928 for women.

The 200 metres is a sprint running event. On an outdoor race 400 m track, the race begins on the curve and ends on the home straight, so a combination of techniques are needed to successfully run the race. A slightly shorter race, called the stadion and run on a straight track, was the first recorded event at the ancient Olympic Games. The 200 m places more emphasis on speed endurance than shorter sprint distances as athletes predominantly rely on anaerobic energy system during the 200 m sprint. Similarly to other sprint distances, the 200 m begins from the starting blocks. When the sprinters adopt the 'set' position in the blocks they are able to adopt a more efficient starting posture and isometrically preload their muscles. This enables them to stride forwards more powerfully when the race begins and start faster.

The 4 × 400 metres relay or long relay is an athletics track event in which teams consist of four runners who each complete 400 metres or one lap. It is traditionally the final event of a track meet. At top class events, the first 500 metres is run in lanes. Start lines are thus staggered over a greater distance than in an individual 400 metres race; the runners then typically move to the inside of the track. The slightly longer 4 × 440 yards relay was a formerly run British and American event, until metrication was completed in the 1970s.

60 metres, or 60-meter dash, is a sprint event in track and field. It is a championship event for indoor championships, normally dominated by the best outdoor 100 metres runners. At outdoor venues it is a rare distance, at least for senior athletes. The format of the event is similar to other sprint distances. The sprinters follow three initial instructions: 'ready', instructing them to take up position in the starting blocks; 'set', instructing them to adopt a more efficient starting posture, which also isometrically preloads their muscles. This will enable them to start faster. The final instruction is the firing of the starter's pistol. Upon hearing this the sprinters stride forwards from the blocks.

The 1500 metres or 1,500-metre run is the foremost middle distance track event in athletics. The distance has been contested at the Summer Olympics since 1896 and the World Championships in Athletics since 1983. It is equivalent to 1.5 kilometers or approximately 15⁄16 miles.

The 110 metres hurdles, or 110-metre hurdles, is a hurdling track and field event for men. It is included in the athletics programme at the Summer Olympic Games. The female counterpart is the 100 metres hurdles. As part of a racing event, ten hurdles of 1.067 metres in height are evenly spaced along a straight course of 110 metres. They are positioned so that they will fall over if bumped into by the runner. Fallen hurdles do not carry a fixed time penalty for the runners, but they have a significant pull-over weight which slows down the run. Like the 100 metres sprint, the 110 metres hurdles begins in the starting blocks.

The 100 metres hurdles, or 100-meter hurdles, is a track and field event run mainly by women. For the race, ten hurdles of a height of 83.8 centimetres (33.0 in) are placed along a straight course of 100 metres (109.36 yd). The first hurdle is placed after a run-up of 13 metres from the starting line. The next 9 hurdles are set at a distance of 8.5 metres from each other, and the home stretch from the last hurdle to the finish line is 10.5 metres long. The hurdles are set up so that they will fall over if bumped into by the runner, but weighted so this is disadvantageous. Fallen hurdles do not count against runners provided that they do not run into them on purpose. Like the 100 metres sprint, the 100 m hurdles begins with athletes in starting blocks.

The 5000 metres or 5000-metre run is a common long-distance running event in track and field. It is one of the track events in the Olympic Games and the World Championships in Athletics, run over 12.5 laps of a standard track. The same distance in road running is called a 5K run. The 5000 m has been present on the Olympic programme since 1912 for men and since 1996 for women. Prior to 1996, women had competed in an Olympic 3000 metres race since 1984. The 5000 m has been held at each of the World Championships in Athletics in men's competition and since 1995 in women's.

The House Liberty Caucus is a congressional caucus consisting of conservative, libertarian and libertarian conservative Republican members of the United States House of Representatives. It hosts a bimonthly luncheon in Washington, D.C. The group was founded by Rep. Justin Amash of Michigan and joined by Republican members who wanted to "focus on specific issues like economic freedom, individual liberty, and following the Constitution". The caucus has also been characterized as "conservative with a libertarian emphasis" and associated with the Tea Party movement.

The 2012 United States House of Representatives elections in Washington were held on Tuesday, 6 November 2012, to elect the ten U.S. Representatives from the state, one from each of the state's ten congressional districts, a gain of one seat following the 2010 United States Census. The elections coincided with the elections of other federal and state offices, including a quadrennial presidential election, and a U.S. Senate election. The state certified the returns on 6 December 2012. Primary elections were held on 7 August 2012.

The 2012 San Francisco Board of Supervisors elections occurred on November 6, 2012. Six of the eleven seats of the San Francisco Board of Supervisors were contested in this election. One incumbent was termed out of office, four ran for reelection, and one ran for initial election after being appointed to the seat.
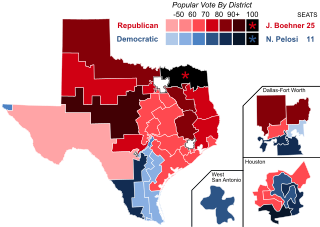
The 2014 United States House of Representatives elections in Texas were held on Tuesday, November 4, 2014 to elect the 36 U.S. Representatives from the state of Texas, one from each of the state's 36 congressional districts. The elections coincided with the elections of other federal and state offices, including a gubernatorial election and an election to the U.S. Senate.

The 2018 United States Senate elections were held on November 6, 2018. 33 of the 100 seats were contested in regular elections while two others were contested in special elections due to Senate vacancies in Minnesota and Mississippi. The winners were elected to six-year terms running from January 3, 2019, to January 3, 2025. Senate Democrats had 26 seats up for election while Senate Republicans had nine seats up for election.

A general election was held in the U.S. state of Vermont on November 8, 2016. All of Vermont's executive officers were up for election as well as Vermont's Class III Senate seat and at-large seat in the United States House of Representatives. Primary elections were held on August 9, 2016.

The 2012 San Diego City Attorney election occurred on Tuesday, June 12, 2012. Incumbent city attorney Jan Goldsmith ran unopposed and was reelected.