
The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately 1,127,711.92 km2 (435,412.01 sq mi) and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated population as of the second quarter of 2024 is 44,920. Yellowknife is the capital, most populous community, and only city in the territory; its population was 20,340 as of the 2021 census. It became the territorial capital in 1967, following recommendations by the Carrothers Commission.

The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea lane between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Arctic Archipelago of Canada. The eastern route along the Arctic coasts of Norway and Siberia is accordingly called the Northeast Passage (NEP). The various islands of the archipelago are separated from one another and from Mainland Canada by a series of Arctic waterways collectively known as the Northwest Passages, Northwestern Passages or the Canadian Internal Waters.

Victoria Island is a large island in the Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth-largest island in the world, and at 217,291 km2 (83,897 sq mi)1 in area, it is Canada's second-largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (111,390 km2 [43,010 sq mi]), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain (209,331 km2 [80,823 sq mi]) but smaller than Honshu (225,800 km2 [87,200 sq mi]). The western third of the island lies in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region. The population of 2,168 is divided between two settlements, the larger of which is Cambridge Bay (Nunavut) and the other Ulukhaktok.

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland.

Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada, variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut. This area covers about 48 per cent of Canada's total land area, but has less than 0.5 per cent of Canada's population.

Melville Island is an uninhabited member of the Queen Elizabeth Islands of the Arctic Archipelago. With an area of 42,149 km2 (16,274 sq mi), it is the 33rd largest island in the world and Canada's eighth largest island.

The Queen Elizabeth Islands are the northernmost cluster of islands in Canada's Arctic Archipelago, split between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories in Northern Canada. The Queen Elizabeth Islands contain approximately 14% of the global glacier and ice cap area. The southern islands are called the Parry Islands or Parry Archipelago.
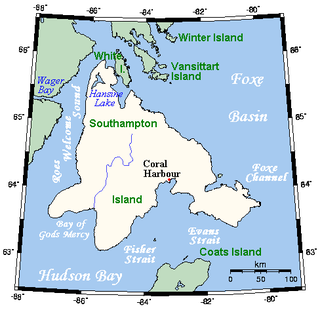
Southampton Island is a large island at the entrance to Hudson Bay at Foxe Basin. One of the larger members of the Arctic Archipelago, Southampton Island is part of the Kivalliq Region in Nunavut, Canada. The area of the island is stated as 41,214 km2 (15,913 sq mi) by Statistics Canada. It is the 34th largest island in the world and Canada's ninth largest island. The only settlement on Southampton Island is Coral Harbour, called Salliq in Inuktitut.

A member of the Arctic Archipelago, Prince Patrick Island is the westernmost of the Queen Elizabeth Islands in the Northwest Territories of Canada, lying northwest of Melville Island. The area of Prince Patrick Island is 15,848 km2 (6,119 sq mi), making it the 55th largest island in the world and Canada's 14th largest island. It has historically been icebound all year, making it one of the least accessible parts of Canada. Located at the entrance of the M'Clure Strait, Prince Patrick Island is uninhabited.

Amundsen Gulf is a gulf located mainly in the Inuvik Region, Northwest Territories, Canada with a small section in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut. It lies between Banks Island and Victoria Island and the mainland. It is approximately 250 mi (400 km) in length and about 93 mi (150 km) across where it meets the Beaufort Sea.

Cambridge Bay is a hamlet located on Victoria Island in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is the largest settlement on Victoria Island. Cambridge Bay is named for Prince Adolphus, Duke of Cambridge, while the traditional Inuinnaqtun name for the area is Ikaluktutiak or Iqaluktuuttiaq meaning "good fishing place".

The British Arctic Territories were a region of British North America, composed of islands to the north of continental North America. They are now known as the Arctic Archipelago.

The history of the Northwest Territories covers the period from thousands of years ago to the present day. Prior to European colonization, the lands that encompass present-day Northwest Territories were inhabited for millennia by several First Nations. European explorers and fur traders began to explore the region since the late-16th century. By the 17th century, the British laid claim to both the North-Western Territory and Rupert's Land; and granted the Hudson's Bay Company a commercial fur trade monopoly over the latter region.

Nunavut is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, which provided this territory to the Inuit for self-government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland was admitted in 1949.

The Arctic Archipelago Marine Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a marine ecozone in the Canadian Arctic, encompassing Hudson Bay, James Bay, the internal waters and some shores of the islands in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, and the shores of the territories, northern Ontario and western Quebec. Early exploration of these waters by Europeans were conducted to find a passage to the Orient, now referred to as the Northwest Passage.
Griffith Island lies within the Arctic Archipelago in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of northern Canada's territory of Nunavut. It is one of the mid-channel islands in the western sector of Barrow Strait.
Marie Bay is a fjord on the Northwest tip of Melville Island. Marie Bay lies on the part of Melville Island that is in the Northwest Territories while the eastern part of the island is in Nunavut.
The Arctic policy of Canada includes both the foreign policy of Canada in regard to the Arctic region and Canada's domestic policy towards its Arctic territories. This includes the devolution of powers to the territories. Canada's Arctic policy includes the plans and provisions of these regional governments. It encompasses the exercise of sovereignty, social and economic development, the protection of the environment, and the improving and devolving of governance.
Purchase Bay is a fjord in the Arctic Archipelago, on the western side of Melville Island, Northwest Territories, Canada. It is approximately 65 km (40 mi) long. It was named for the engineer of HMS Intrepid, Thomas Purchase, during the Belcher expedition















