Related Research Articles

Digital television (DTV) is the transmission of television signals using digital encoding, in contrast to the earlier analog television technology which used analog signals. At the time of its development it was considered an innovative advancement and represented the first significant evolution in television technology since color television in the 1950s. Modern digital television is transmitted in high-definition television (HDTV) with greater resolution than analog TV. It typically uses a widescreen aspect ratio in contrast to the narrower format (4:3) of analog TV. It makes more economical use of scarce radio spectrum space; it can transmit up to seven channels in the same bandwidth as a single analog channel, and provides many new features that analog television cannot. A transition from analog to digital broadcasting began around 2000. Different digital television broadcasting standards have been adopted in different parts of the world; below are the more widely used standards:

Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) is a cordless telephony standard maintained by ETSI. It originated in Europe, where it is the common standard, replacing earlier standards, such as CT1 and CT2. Since the DECT-2020 standard, it also includes IoT communication.

Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB) is a digital radio standard for broadcasting digital audio radio services in many countries around the world, defined, supported, marketed and promoted by the WorldDAB organisation. The standard is dominant in Europe and is also used in Australia, and in parts of Africa and Asia; as of 2022, 55 countries are actively running DAB broadcasts.

Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is a set of international open standards for digital television. DVB standards are maintained by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and are published by a Joint Technical Committee (JTC) of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) and European Broadcasting Union (EBU).
Digital Video Broadcasting – Satellite (DVB-S) is the original DVB standard for satellite television and dates from 1995, in its first release, while development lasted from 1993 to 1997. The first commercial applications were by Star TV in Asia and Galaxy in Australia, enabling digitally broadcast, satellite-delivered television to the public. According to ETSI,
DVB-S was the first DVB standard for satellite, defining the framing structure, channel coding and modulation for 11/12 GHz satellite services.
Digital Video Broadcasting - Cable (DVB-C) is the DVB European consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital television over cable. This system transmits an MPEG-2 or MPEG-4 family digital audio/digital video stream, using a QAM modulation with channel coding. The standard was first published by the ETSI in 1994, and subsequently became the most widely used transmission system for digital cable television in Europe, Asia and South America. It is deployed worldwide in systems ranging from the larger cable television networks (CATV) down to smaller satellite master antenna TV (SMATV) systems.
Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting is a Japanese broadcasting standard for digital television (DTV) and digital radio.
Digital radio is the use of digital technology to transmit or receive across the radio spectrum. Digital transmission by radio waves includes digital broadcasting, and especially digital audio radio services.

Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite - Second Generation (DVB-S2) is a digital television broadcast standard that has been designed as a successor for the popular DVB-S system. It was developed in 2003 by the Digital Video Broadcasting Project, an international industry consortium, and ratified by ETSI in March 2005. The standard is based on, and improves upon DVB-S and the electronic news-gathering system, used by mobile units for sending sounds and images from remote locations worldwide back to their home television stations.
DVB-H is one of three prevalent mobile TV formats. It is a technical specification for bringing broadcast services to mobile handsets. DVB-H was formally adopted as ETSI standard EN 302 304 in November 2004. The DVB-H specification can be downloaded from the official DVB-H website. From March 2008, DVB-H was officially endorsed by the European Union as the "preferred technology for terrestrial mobile broadcasting".
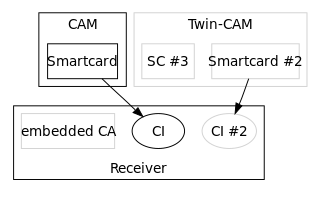
In Digital Video Broadcasting, the Common Interface is a technology which allows decryption of pay TV channels. Pay TV stations want to choose which encryption method to use. The Common Interface allows TV manufacturers to support many different pay TV stations, by allowing to plug in exchangeable conditional-access modules (CAM) for various encryption schemes.
Globally Executable MHP (GEM) is a DVB specification of a Java based middleware for TV broadcast receivers, IPTV terminals and Blu-ray players. GEM is an ETSI standard and an ITU "Recommendation”. GEM defines a set of common functionalities which are independent from the signaling and protocols of a specific transmission network and enables to write interoperable Java applications for TV. GEM is not intended to be directly implemented, but rather forms the basis for broader specifications targeting a particular network infrastructure or class of device. GEM defines profiles for different device classes (targets) – these define the set of available features of GEM for this device class. Currently GEM defines targets for broadcast, packaged media (Blu-Ray) and IPTV. Combinations of these targets can be combined into a hybrid GEM platform, which enables to build devices with multiple network interfaces, such as a combined broadcast/IPTV set-top box.
Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Services (MBMS) is a point-to-multipoint interface specification for existing 3GPP cellular networks, which is designed to provide efficient delivery of broadcast and multicast services, both within a cell as well as within the core network. For broadcast transmission across multiple cells, it defines transmission via single-frequency network configurations. The specification is referred to as Evolved Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Services (eMBMS) when transmissions are delivered through an LTE network. eMBMS is also known as LTE Broadcast.

MediaFLO was a technology developed by Qualcomm for transmitting audio, video and data to portable devices such as mobile phones and personal televisions, used for mobile television. In the United States, the service powered by this technology was branded as FLO TV.
S-DMB (Satellite-DMB) was a hybrid version of the Digital Multimedia Broadcasting. The S-DMB used the S band (2170-2200 MHz) of IMT-2000. and delivered around 18 channels at 128 kbit/s in 15 MHz. It incorporated a high power geostationary satellite, the MBSat 1. For outdoor and light indoor coverage is integrated with a terrestrial repeater network for indoor coverage in urban areas.
Mobile television is television watched on a small handheld or mobile device, typically developed for that purpose. It includes service delivered via mobile phone networks, received free-to-air via terrestrial television stations, or via satellite broadcast. Regular broadcast standards or special mobile TV transmission formats can be used. Additional features include downloading TV programs and podcasts from the Internet and storing programming for later viewing.
IP over DVB implies that Internet Protocol datagrams are distributed using some digital television system, for example DVB-H, DVB-SH, DVB-T, DVB-S, DVB-C or their successors like DVB-T2, DVB-S2, and DVB-C2. This may take the form of IP over MPEG, where the datagrams are transferred over the MPEG transport stream, or the datagrams may be carried in the DVB baseband frames directly, as in GSE.
DVB-RCS provides a method by which the DVB-S platform can become a bi-directional, asymmetric data path using wireless between broadcasters and customers. It is a specification for an interactive on-demand multimedia satellite communication system formulated in 1999 by the DVB consortium. Without this method, various degrees of interactivity can be offered, without implying any return channel back from the user to the service provider: Data Carrousel or Electronic Programs Guides (EPG) are examples of such enhanced TV services which make use of “local interactivity”, without any return path from customer to provider.
Generic Stream Encapsulation, or GSE for short, is a Data link layer protocol defined by DVB. GSE provides means to carry packet oriented protocols such as IP on top of uni-directional physical layers such as DVB-S2, DVB-T2 and DVB-C2.

Digital multimedia broadcasting (DMB) is a digital radio transmission technology developed in South Korea as part of the national IT project for sending multimedia such as TV, radio and datacasting to mobile devices such as mobile phones, laptops and GPS navigation systems. This technology, sometimes known as mobile TV, should not be confused with Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB) which was developed as a research project for the European Union.
References
- ↑ ETSI TR 102 525 v1.1.1 (2006-09) Satellite Earth Stations and Systems (SES); Satellite Digital Radio (SDR) service; Functionalities, architecture and technologies
- ↑ "WORLDSPACE(R) Satellite Radio Signs Fraunhofer IIS to Develop 'Blueprint' for European Satellite Radio Receivers". Archived from the original on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2009-10-28.
- ↑ "ONDAS Media: Helping to Set the Standards for Satellite Digital Radio in Europe (Ondas Media)". Archived from the original on 2010-07-08. Retrieved 2009-10-28.