
Panama is a country located in Caribbean, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, between Colombia and Costa Rica. Panama is located on the narrow and low Isthmus of Panama.

Dacite is a volcanic rock formed by rapid solidification of lava that is high in silica and low in alkali metal oxides. It has a fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic texture and is intermediate in composition between andesite and rhyolite. It is composed predominantly of plagioclase feldspar and quartz.

The Volcán Barú is an active stratovolcano and the tallest mountain in Panama, at 3,475 metres (11,401 ft) high. It lies about 35 km (22 mi) off the border of Costa Rica. It is also the twelfth highest peak in Central America.

The Central American Volcanic Arc is a chain of volcanoes which extends parallel to the Pacific coastline of the Central American Isthmus, from Mexico to Panama. This volcanic arc, which has a length of 1,100 kilometers (680 mi) is formed by an active subduction zone, with the Cocos plate subducting underneath the Caribbean plate, the North American plate and the Panama plate. Volcanic activity is recorded in the Central American region since the Permian. Numerous volcanoes are spread throughout various Central American countries; many have been active in the geologic past, varying in intensity of their activity according to different factors.

Cerro Galán is a caldera in the Catamarca Province of Argentina. It is one of the largest exposed calderas in the world and forms part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, one of the three volcanic belts found in South America. One of several major caldera systems in the Central Volcanic Zone, the mountain is grouped into the Altiplano–Puna volcanic complex.

Cerro Macá is a stratovolcano located to the north of the Aisén Fjord and to the east of the Moraleda Channel, in the Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region of Chile. This glacier-covered volcano lies along the regional Liquiñe-Ofqui Fault Zone.

La Yeguada is a massive stratovolcano located in Veraguas Province, Panama, north of the Azuero Peninsula.

Adakites are volcanic rocks of intermediate to felsic composition that have geochemical characteristics of magma originally thought to have formed by partial melting of altered basalt that is subducted below volcanic arcs. Most magmas derived in subduction zones come from the mantle above the subducting plate when hydrous fluids are released from minerals that break down in the metamorphosed basalt, rise into the mantle, and initiate partial melting. However, Defant and Drummond recognized that when young oceanic crust is subducted, adakites are typically produced in the arc. They postulated that when young oceanic crust is subducted it is "warmer" than crust that is typically subducted. The warmer crust enables melting of the metamorphosed subducted basalt rather than the mantle above. Experimental work by several researchers has verified the geochemical characteristics of "slab melts" and the contention that melts can form from young and therefore warmer crust in subduction zones.
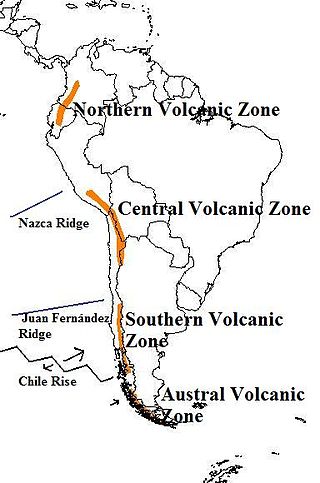
The Andean Volcanic Belt is a major volcanic belt along the Andean cordillera in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. It is formed as a result of subduction of the Nazca plate and Antarctic plate underneath the South American plate. The belt is subdivided into four main volcanic zones which are separated by volcanic gaps. The volcanoes of the belt are diverse in terms of activity style, products, and morphology. While some differences can be explained by which volcanic zone a volcano belongs to, there are significant differences within volcanic zones and even between neighboring volcanoes. Despite being a type location for calc-alkalic and subduction volcanism, the Andean Volcanic Belt has a broad range of volcano-tectonic settings, as it has rift systems and extensional zones, transpressional faults, subduction of mid-ocean ridges and seamount chains as well as a large range of crustal thicknesses and magma ascent paths and different amounts of crustal assimilations.

Cordón de Puntas Negras is a 500 km2 (193 sq mi) volcanic chain located east of the Salar de Atacama in Chile's Antofagasta Region.

El Valle de Antón, generally called El Valle, or Anton's Valley in English, is a town of 7,600 in the Coclé province of Panama.

Cay is a stratovolcano in the South Volcanic Zone of the Andes in Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region, Chile. The volcano is located 15 km northeast of the larger Maca Volcano and about 230 km of the Chile Trench at the intersection of NW-SE and NE-SW faults of the Liquiñe-Ofqui Fault Zone.

The Luzon Volcanic Arc is a chain of volcanoes in a north–south line across the Luzon Strait from Taiwan to Luzon. The name "Luzon Volcanic Arc" was first proposed by Carl Bowin et al. to describe a series of Miocene to recent volcanoes due to eastward subduction along the Manila Trench for approximately 1,200 km from the Coastal Range in Taiwan south to southern Mindoro in the Philippines. Islands that form part of the arc are the Eastern Coastal Range of Taiwan, Green Island, Taiwan, Orchid Island, Kaotai Rock, Mavudis or Y'ami Island, Mabudis, Siayan Island, Itbayat Island, Diogo Island, Batan Island, Unnamed volcano Ibuhos, Sabtang Island, Babuyan, Didicas, and Camiguin de Babuyanes. At the south end it terminates on Luzon. The geochemistry of a number of volcanoes along the arc have been measured. There are five distinct geochemical domains within the arc. The geochemistry of the segments verified that the volcanoes are all subduction related. Isotopes and trace elements show unique geochemical characteristics in the north. Geochemical variations northward were due to the subduction of sediments derived from the erosion of continental crust from China and Taiwan.
Cerro Chascon-Runtu Jarita is a complex of lava domes located inside, but probably unrelated to, the Pastos Grandes caldera. It is part of the more recent phase of activity of the Altiplano-Puna volcanic complex.

Sairecabur is a volcano located on the frontier between Bolivia and Chile. It is part of the Andean Central Volcanic Zone. Sairecabur proper is 5,971 m (19,590 ft) high; other mountains in the range are 5,722 m (18,773 ft) high Curiquinca, 5,819 m (19,091 ft) high Escalante and 5,748 m (18,858 ft) high Cerro Colorado, all of which have erupted a number of lava flows. Also in close proximity to Sairecabur lie the volcanic centres Licancabur, Putana and Juriques.

La Reforma is a Plio-Pleistocene caldera on the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico. It is part of eleven volcanoes in Baja California, which formed with the Gulf of California during the Miocene, about ten million years ago. Previously, a volcanic arc had existed on the peninsula. The caldera's basement consists of granites and monzonites, formed between the Cretaceous and the Middle Miocene.
Tastil volcanic complex is a volcanic group in Argentina.
The geology of Costa Rica is part of the Panama Microplate, which is slowly moving north relative to the stable Caribbean Plate.

Tocorpuri is a volcano in Chile, close to the border with Bolivia. Its peak height is most recently given as 5,808 metres (19,055 ft) and it features a 1.3 kilometres (0.81 mi) wide summit crater. The volcano consists mainly of lava flows and pyroclastic deposits and is subdivided into two separate edifices. Just west of Tocorpuri, the La Torta lava dome is a 200 metres (660 ft) high flat-topped structure. The volcanoes are formed by andesitic, dacitic and rhyolitic rocks.

Cerro Overo is a volcanic crater in Chile. It lies at the foot of Chiliques volcano and close to Laguna Lejía, over ignimbrites of Pliocene age erupted by the La Pacana volcano. It is 480 by 580 metres wide and 72 metres (236 ft) deep and formed through combined explosive-effusive eruptions. The lavas are of lower crustal provenience and are among the least silicic in the region.




















