Parts of this article (those related to documentation) need to be updated.(January 2020) |
 |
|---|
| Constitution |
| |
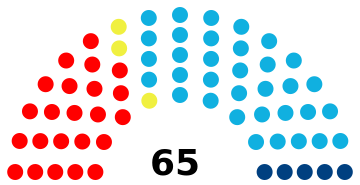
Timor-Leste (formerly East Timor) elects on national level a head of state, the president, and a legislature. The president is elected for a five-year term by the people. The National Parliament (Portuguese: Parlamenta Nacional) has 65 members.