
Perciformes, also called the Acanthopteri, is an order or superorder of ray-finned fish in the clade Percomorpha. Perciformes means "perch-like". Among the well-known members of this group are perch and darters (Percidae), sea bass and groupers (Serranidae).

Osteoglossidae is a family of large-sized freshwater fish, which includes the arowanas. They are commonly known as bonytongues. The family has been regarded as containing two extant subfamilies Arapaiminae and Osteoglossinae, with a total of five living genera, but these are regarded as valid families in Eschmeyer's Catalog of Fishes The extinct Phareodontinae are known from worldwide during the Late Cretaceous and Paleogene; they are generally considered to be crown group osteoglossids that are more closely related to one of the extant osteoglossid subfamilies than the other, though their exact position varies.

Enchodus is an extinct genus of aulopiform ray-finned fish related to lancetfish and lizardfish. Species of Enchodus flourished during the Late Cretaceous, where they were a widespread component of marine ecosystems worldwide, and there is some evidence that they may have survived to the Paleocene or Eocene; however, this may just represent reworked Cretaceous material.
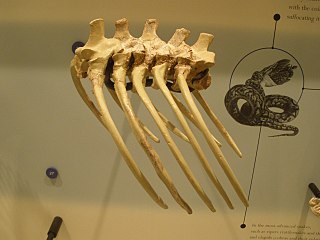
Madtsoiidae is an extinct family of mostly Gondwanan snakes with a fossil record extending from early Cenomanian to late Pleistocene strata located in South America, Africa, India, Australia and Southern Europe. Madtsoiidae include very primitive snakes, which like extant boas and pythons would likely dispatch their prey by constriction. Genera include some of the longest snakes known such as Vasuki, measuring at least 11–15 metres (36–49 ft) long, and the Australian Wonambi and Yurlunggur. As a grouping of basal forms the composition and even the validity of Madtsoiidae is in a state of flux as new pertinent finds are described, with more recent evidence suggesting that it is paraphyletic as previously defined.

Albulidae is a family of fish, commonly known as the bonefishes, that are popular as game fish in Florida, select locations in the South Pacific and the Bahamas and elsewhere. The family is small, with 11 species in 3 genera. Presently, the bonefishes are in their own order: Albuliformes. The families Halosauridae and Notacanthidae were previously classified in this order, but are now, according to FishBase, given their own order Notacanthiformes. The largest bonefish caught in the Western Hemisphere is a 16-pound, 3 ounce example caught off Islamorada, Florida, on March 19, 2007.

Gasteroclupea is a genus of prehistoric ellimmichthyiform fish that is distantly related to modern anchovies and herrings. It contains one species, G. branisai. It inhabited freshwater or estuarine habitats across South America during the Campanian and Maastrichtian stages of the Late Cretaceous period, and it briefly survived beyond the K-Pg boundary into the Danian stage of the Paleocene, making it among the few genera from its order to survive into the Cenozoic. Fossils of the genus have been found in the Yacoraite Formation of Argentina, the Chaunaca Formation, Santa Lucía Formation, and El Molino Formation of Bolivia, and the Navay Formation in Venezuela.

Coriops is an extinct genus of freshwater osteoglossomorph fish, possibly a hiodontiform, with a single species known from the Late Cretaceous of western North America.

Rhombodus is a prehistoric genus of ray belonging to the family Rhombodontidae.
Cyranichthys is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish known from the Late Cretaceous of central Africa and western Europe. It was a member of Dercetidae, a group of elongated aulopiforms.
Casierius is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish that lived during the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous epoch. It was a relative of the modern bonefish in the extinct family Phyllodontidae, although some authorities consider it either a true albulid or a very early eel. It contains a single species, C. heckeli, known from the Glen Rose Formation near Hood County, Texas.

Coelodus is an extinct genus of marine and possibly freshwater pycnodont fish. It contains only one definitive species, C. saturnusHeckel, 1854, from the Late Cretaceous of Slovenia. Other species from the Late Jurassic to the Eocene have also been attributed to this genus based on isolated dental elements, but their assignment to Coelodus is uncertain, and this genus likely represents a non-monophyletic wastebasket taxon. A potential diagnostic trait is a prearticular tooth row with three regular highly elongated teeth.

Cylindracanthus is an extinct, enigmatic genus of marine ray-finned fish with fossils known throughout North America, Europe, Asia and Africa from the Late Cretaceous to the late Eocene, with potential Oligocene records and a possible Miocene record also known. It is exclusively known from its distinctive partial remains, which are long cylindrical bony spines that are usually considered rostrum fragments, as well as some associated teeth. These spines are abundant & widespread throughout this timespan, and are useful indicators of a nearshore marine environment, but the taxonomic identity of the fish is still highly uncertain and debated.
Egertonia is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine and estuarine ray-finned fish known from the Late Cretaceous to the middle Eocene. It contains one known species, E. isodonta, although indeterminate remains potentially referable to other species are also known. It was a member of the Phyllodontidae, an extinct family of elopomorph fish with crushing tooth plates, which are the primary remains found of the genus.

The Benue Trough is a major geological structure underlying a large part of Nigeria and extending about 1,000 km northeast from the Bight of Benin to Lake Chad. It is part of the broader West and Central African Rift System.
Deccanolestes is a scansorial, basal Euarchontan from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) and Paleocene Intertrappean Beds of Andhra Pradesh, India. It may be closely related to Sahnitherium. Deccanolestes has been referred to Palaeoryctidae in the past, but recent evidence has shown that it is either the most basal Euarchontan, as the earliest known Adapisoriculid, or as a stem-afrotherian.

Dwardius is an extinct genus of cardabiodontid sharks which existed during the Cretaceous period in what is now Australia, England, France, and India. It was described by Mikael Siverson in 1999, as a new genus for the species Cretalamna woodwardi, which had been described by J. Hermann in 1977. Another species, D. siversoni, was described from the middle Albian of northeastern France by V.I. Zhelezko in 2000; the species epithet honours the author of the genus. A new species, D. sudindicus, was described by Charlie J. Underwood, Anjali Goswami, G.V.R. Prasad, Omkar Verma, and John J. Flynn in 2011, from the Cretaceous Karai Formation of India.

The Oulad Abdoun Basin is a phosphate sedimentary basin located in Morocco, near the city of Khouribga. It is the largest in Morocco, comprising 44% of Morocco's phosphate reserves, and at least 26.8 billion tons of phosphate. It is also known as an important site for vertebrate fossils, with deposits ranging from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Turonian) to the Eocene epoch (Ypresian), a period of about 25 million years.

Coniophis is an extinct genus of snakes from the late Cretaceous period. The type species, Coniophis precedes, was about 7 cm long and had snake-like teeth and body form, with a skull and a largely lizard-like bone structure. It probably ate small vertebrates. The fossil remains of Coniophis were first discovered at the end of the 19th century in the Lance Formation of the US state of Wyoming, and were described in 1892 by Othniel Charles Marsh. For the genus Coniophis, a number of other species have been described. Their affiliation is, however, poorly secured, mostly based on vertebrae descriptions from only a few fossils.
The Kallamedu Formation is a Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) geologic formation located in the Ariyalur district of Tamil Nadu, India that forms part of the Ariyalur Group. It dates to the Maastrichtian of the Late Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains and petrified wood samples are among the known fossils recovered from this formation.















