
The Cryptobranchidae are a family of large salamanders that are fully aquatic. The family includes some of the largest living amphibians. They are native to China, Japan, and the eastern United States. Giant salamanders constitute one of two living families—the other being the Asiatic salamanders belonging to the family Hynobiidae—within the Cryptobranchoidea, one of two main divisions of living salamanders.

The family Proteidae is a group of aquatic salamanders found today in the Balkan Peninsula and North America. The range of the genus Necturus runs from southern central Canada, through the midwestern United States, east to North Carolina and south to Georgia and Mississippi. The range of the olm, the only extant member of the genus Proteus, is limited to the Western Balkans. The fossil record of the family extends back to the Late Cretaceous, with Paranecturus being known from the Maastrichtian of North America, and Bishara from the Santonian-Campanian of Central Asia.

Karaurus is an extinct genus of stem-group salamander (Caudata) from the Middle to Late Jurassic (Callovian–Kimmeridgian) Karabastau Formation of Kazakhstan. It is one of the oldest salamanders known.

The Albanerpetontidae are an extinct family of small amphibians, native to the Northern Hemisphere during the Mesozoic and Cenozoic. The only members of the order Allocaudata, they are thought to be allied with living amphibians belonging to Lissamphibia. Despite a superficially salamander-like bodyform, their anatomy is strongly divergent from modern amphibians in numerous aspects. The fossil record of albanerpetontids spans over 160 million years from the Middle Jurassic to the beginning of the Pleistocene, about 2.13–2 million years ago.

Chunerpeton tianyiensis is an extinct species of salamander from the Late Jurassic Daohugou Beds in Ningcheng County, Nei Mongol, China. It is the only species classified under the genus Chunerpeton, which means "early creeping animal". It was a small animal measuring 18 cm in length. It was neotenic, with the retention of external gills into adulthood. In the original description it was placed in Cryptobranchidae, which contains modern giant salamanders. A redescription published in 2020 found it to be a stem-group caudatan outside the crown group of modern salamanders. A 2021 study found it to be a member of Cryptobranchoidea outside of Cryptobranchidae. In 2022 a more extensive analysis, with greater character and taxon sampling, recovered Chunerpeton tianyiense as a stem-group caudatan, outside the crown group of modern salamanders, and associated with Beiyanerpeton jianpingensis and Qinglongtriton gangouensis.
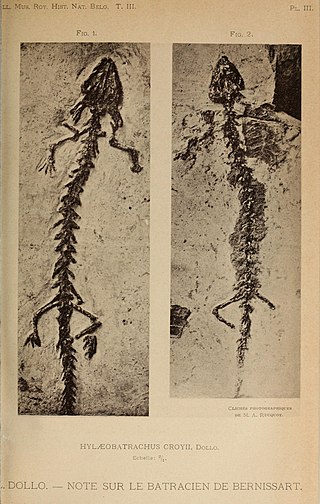
Hylaeobatrachus is an extinct genus of prehistoric salamander, known from the Early Cretaceous of Europe. The type species H. croyii is known from the Sainte-Barbe Clays Formation at the Iguanodon locality of Belgium, and was described by Louis Dollo. An unnamed Hylaeobatrachus-like taxon has also been reported from Las Hoyas, Spain. Both localities are of Barremian age. Hylaeobatrachus belongs to the crown group of modern salamanders, though its exact relationship with modern salamander groups is uncertain. It was neotenic, llike some modern salamanders.
Horezmia is an extinct genus of Mesozoic salamanders. The fossils have been found in Russia. It is comparable to modern advanced salamanders, though its phylogenetic placement within Salamandroidea is uncertain.
Kokartus is an extinct genus of prehistoric stem-group salamander (Caudata) from the Middle Jurassic Balabansai Formation of Kyrgyzstan.

Kansajsuchus is an extinct genus of paralligatorid mesoeucrocodylian. It is based on PIN 2399/301, a right premaxilla, one of the bones of the tip of the snout. This specimen was found in rocks of the lower Santonian-age Upper Cretaceous Yalovach Svita of Kansai, in the Fergana Basin of Tajikistan. Additional fossils including vertebrae and bony armor have been assigned to this genus. It would have been a large animal, estimated at between 5–7 metres (16–23 ft) long. Kansajsuchus was described in 1975 by Mikhail Efimov. The type species is Kansajsuchus extensus.

Turanosuchus is an extinct genus of paralligatorid crocodyliform. It is based on PIN 2229/507, a partial lower jaw consisting of the area where the two halves of the lower jaw meet. This specimen was found in rocks of the lower Santonian-age Upper Cretaceous Bostobe Svita of Shakh-Shakh, southern Kazakhstan. Turanosuchus was described in 1988 by Mikhail Efimov. The type species is T. aralensis. Halliday et al. (2015) revised the material attributed to T. aralensis and concluded that it represents non-diagnostic neosuchian material, and as such the genus was considered to be a nomen dubium.
The Ialovachsk or Yalovach Formation is a geologic formation in Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan dating to the Santonian age of the Cretaceous period.
Nesovtriton is an extinct genus of cryptobranchoid salamander known from the Late Cretaceous of Bissekty Formation, in Uzbekistan. It was first named by Pavel P. Skutschas in 2009 and the type species is Nesovtriton mynbulakensis.

The Karauridae are a family of stem-group salamanders (Caudata) that are known from the Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous in Central Asia, Northern Asia and Western Europe. The family includes four members: Karaurus from the Middle-Late Jurassic Karabastau Formation of Kazakhstan, Kokartus from the Middle Jurassic Balabansai Formation of Kyrgyzstan, Marmorerpeton from the Middle Jurassic Forest Marble Formation of England and Kilmaluag Formation of Scotland, and Kuzbassia from the Early Cretaceous (Aptian) Ilek Formation. The members are some of the oldest known salamanders. The family is united by several morphological characters, including sculptured skull roof bones. Like some modern salamanders, karaurids were neotenic. Members of the family likely fed via suction feeding on small fish and invertebrates. The Early Cretaceous Siberian Kulgeriherpeton has been suggested to be a karaurid by some authors.
The Ilek Formation is a Lower Cretaceous geologic formation in Western Siberia. Many different fossils have been recovered from the formation. It overlies the Late Jurassic Tyazhin Formation and underlies the Albian Kiya Formation.
The Moskvoretskaya Formation is a Middle Jurassic geologic formation in the European part of Russia. It consists of continental claystones, siltstones and sandstones deposited in karstified segments of underlying Middle Carboniferous limestone, that would have formed underground aquifers.

The Batylykh Formation is a geological formation in Yakutia, Russia. It is of an uncertain Early Cretaceous age, probably dating between the Berriasian and the Barremian. It is the oldest unit of the 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) thick Sangar Series within the Vilyuy syneclise. The mudstones, sandstones and shales of the formation were deposited in a fluvial to lacustrine environment.
This list of fossil amphibians described in 2018 is a list of new taxa of fossil amphibians that were described during the year 2018, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to amphibian paleontology that occurred in 2018.
This list of fossil amphibians described in 2020 is a list of new taxa of fossil amphibians that were described during the year 2020, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to amphibian paleontology that occurred in 2020.

Kiyacursor is an extinct genus of noasaurid theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Ilek Formation of Russia. The genus contains a single species, K. longipes, known from a partial skeleton. Kiyacursor represents the first Early Cretaceous ceratosaur discovered in Asia, as well as the second non-avian theropod named from Russia, after Kileskus in 2010.









