
Eriocraniidae is a family of moths restricted to the Holarctic region, with six extant genera. These small, metallic moths are usually day-flying, emerging fairly early in the northern temperate spring. They have a proboscis with which they drink water or sap. The larvae are leaf miners on Fagales, principally the trees birch (Betula) and oak (Quercus), but a few on Salicales and Rosales.

Dyseriocrania subpurpurella is a diurnal moth from the family Eriocraniidae, found in most of Europe. The moth was first named by the English entomologist, Adrian Hardy Haworth in 1828.

Eriocrania semipurpurella is a moth of the family Eriocraniidae, found from Europe to Japan and in North America. It was first described by James Francis Stephens in 1835. The species closely resembles Eriocrania sangii and the larvae of both species mine the leaves of birch.

Agonopterix ocellana is a species of moth of the family Depressariidae. It is found in Europe and was first described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1775.

Prays fraxinella, also known as the ash bud moth, is a moth of the family Plutellidae found in Europe. The larvae are leaf miners, feeding on the leaves and buds of ash trees.

Eriocrania sangii, the large birch purple, is a moth of the family Eriocraniidae found in Europe and described by John Henry Wood in 1891. The moth can be found flying in sunshine around birch trees and the larvae feed on birch leaves.

Eriocrania cicatricella is a moth of the family Eriocraniidae found in Europe. It was first described by Johan Wilhelm Zetterstedt in 1839. The larvae mine the leaves of birch.

Eriocrania sparrmannella also known as the mottled purple is a moth of the family Eriocraniidae, found in Europe and Japan. It was first described by the French entomologist, Louis Augustin Guillaume Bosc in 1791. The specific name honours the Swedish naturalist Anders Erikson Sparrman. The larvae mine the leaves of birch.

Eriocrania unimaculella is a moth of the family Eriocraniidae found in Europe. It was first described by the Swedish naturalist Johan Wilhelm Zetterstedt in 1839. The larvae feed inside the leaves of birch, making a mine.

Eriocrania chrysolepidella is a moth of the family Eriocraniidae found in Europe. It was first described by the German entomologist, Philipp Christoph Zeller in 1851. The larvae mine the leaves of hazel and hornbeam.

Parornix anglicella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae found in Asia and Europe. It was described in 1850, by the English entomologist Henry Tibbats Stainton, from a specimen from Lewisham, Kent.

Eriocrania is a Palearctic genus of moth of the family Eriocraniidae. The moths are diurnal, flying in sunshine, and the larvae are leaf miners, forming blotches in leaves.

Stigmella confusella is a moth of the family Nepticulidae. It is found from Fennoscandia to the Pyrenees, Alps and Bulgaria and from Ireland to central Russia.

Stigmella microtheriella, the Hazel leaf miner moth, is a moth of the family Nepticulidae. It is found in Asia, Europe and New Zealand. The larvae mine the leaves of hazel and hornbeams. It was described by the English entomologist, Henry Tibbats Stainton in 1854 from a type specimen found in England.

Stigmella lapponica is a moth of the family Nepticulidae found in Asia, Europe and North America. It was first described by the German entomologist, Maximilian Ferdinand Wocke in 1862. The larvae mine the leaves of birch.

Stigmella plagicolella is a moth of the family Nepticulidae described by Henry Tibbats Stainton in 1854. It is found in all of Europe and the Near East.
Stigmella sorbi is a moth of the family Nepticulidae, described by Henry Tibbats Stainton in 1861. It is found in most of Europe, east to the eastern part of the Palearctic realm.

Stigmella salicis is a moth of the family Nepticulidae which is found in Europe. It was first described by the English entomologist, Henry Stainton in 1854. The type locality is from England.

Enteucha acetosae, the pygmy sorrel moth, is a moth of the family Nepticulidae found in Europe. It is one of the smallest moths in the world with some having a wingspan of only 3mm. The larvae mine the leaves of docks, leaving bright red tissue around the mines.
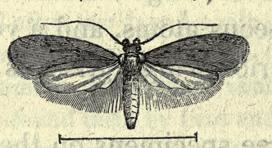
Agonopterix rotundella is a moth of the family Depressariidae and is found in most of Europe. It was first described from moths found in Surrey, England by the entomologist John Douglas in 1846.



















