
Dihydrofolate reductase, or DHFR, is an enzyme that reduces dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid, using NADPH as an electron donor, which can be converted to the kinds of tetrahydrofolate cofactors used in 1-carbon transfer chemistry. In humans, the DHFR enzyme is encoded by the DHFR gene. It is found in the q14.1 region of chromosome 5.
Thioredoxin reductases are enzymes that reduce thioredoxin (Trx). Two classes of thioredoxin reductase have been identified: one class in bacteria and some eukaryotes and one in animals. In bacteria TrxR also catalyzes the reduction of glutaredoxin like proteins known as NrdH. Both classes are flavoproteins which function as homodimers. Each monomer contains a FAD prosthetic group, a NADPH binding domain, and an active site containing a redox-active disulfide bond.
Siderophores (Greek: "iron carrier") are small, high-affinity iron-chelating compounds that are secreted by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. They help the organism accumulate iron. Although a widening range of siderophore functions is now being appreciated, siderophores are among the strongest (highest affinity) Fe3+ binding agents known. Phytosiderophores are siderophores produced by plants.

Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) (EC 1.1.1.42) and (EC 1.1.1.41) is an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate, producing alpha-ketoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate) and CO2. This is a two-step process, which involves oxidation of isocitrate (a secondary alcohol) to oxalosuccinate (a ketone), followed by the decarboxylation of the carboxyl group beta to the ketone, forming alpha-ketoglutarate. In humans, IDH exists in three isoforms: IDH3 catalyzes the third step of the citric acid cycle while converting NAD+ to NADH in the mitochondria. The isoforms IDH1 and IDH2 catalyze the same reaction outside the context of the citric acid cycle and use NADP+ as a cofactor instead of NAD+. They localize to the cytosol as well as the mitochondrion and peroxisome.

2,4 Dienoyl-CoA reductase also known as DECR1 is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the DECR1 gene which resides on chromosome 8. This enzyme catalyzes the following reactions

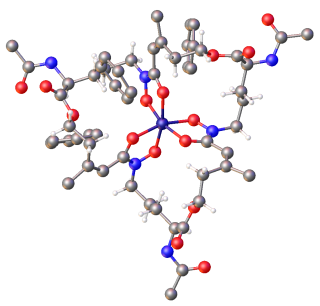
Enterobactin is a high affinity siderophore that acquires iron for microbial systems. It is primarily found in Gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium.

RyhB RNA is a 90 nucleotide RNA that down-regulates a set of iron-storage and iron-using proteins when iron is limiting; it is itself negatively regulated by the ferric uptake repressor protein, Fur.

In enzymology, a shikimate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.25) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a GDP-L-fucose synthase (EC 1.1.1.271) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2,5-didehydrogluconate reductase (EC 1.1.1.274) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybenzoate dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.1.28) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
A glutamyl-tRNA reductase (EC 1.2.1.70) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Flavin reductase a class of enzymes. There are a variety of flavin reductases, which bind free flavins and through hydrogen bonding, catalyze the reduction of these molecules to a reduced flavin. Riboflavin, or vitamin B, and flavin mononucleotide are two of the most well known flavins in the body and are used in a variety of processes which include metabolism of fat and ketones and the reduction of methemoglobin in erythrocytes. Flavin reductases are similar and often confused for ferric reductases because of their similar catalytic mechanism and structures.
In enzymology, an FMN reductase (EC 1.5.1.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nitrite reductase [NAD(P)H] (EC 1.7.1.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
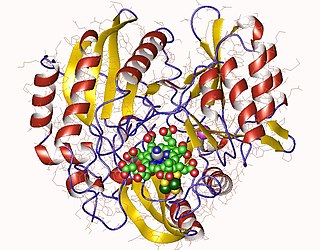
Sulfite reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.8.1.2, sulfite (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) reductase, NADPH-sulfite reductase, NADPH-dependent sulfite reductase, H2S-NADP oxidoreductase, sulfite reductase (NADPH2)) is an enzyme with systematic name hydrogen-sulfide:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalises the following chemical reaction

Aerobactin is a bacterial iron chelating agent (siderophore) found in E. coli. It is a virulence factor enabling E. coli to sequester iron in iron-poor environments such as the urinary tract.

Yersiniabactin (Ybt) is a siderophore found in the pathogenic bacteria Yersinia pestis, Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, and Yersinia enterocolitica, as well as several strains of enterobacteria including enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica. Siderophores, compounds of low molecular mass with high affinities for ferric iron, are important virulence factors in pathogenic bacteria. Iron—an essential element for life used for such cellular processes as respiration and DNA replication—is extensively chelated by host proteins like lactoferrin and ferritin; thus, the pathogen produces molecules with an even higher affinity for Fe3+ than these proteins in order to acquire sufficient iron for growth. As a part of such an iron-uptake system, yersiniabactin plays an important role in pathogenicity of Y. pestis, Y. pseudotuberculosis, and Y. entercolitica.
FMN reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.5.1.38, FRP, flavin reductase P, SsuE) is an enzyme with systematic name FMNH2:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
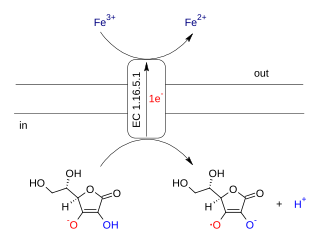
Ascorbate ferrireductase (transmembrane) (EC 1.16.5.1, cytochrome b561) is an enzyme with systematic name Fe(III):ascorbate oxidorectuctase (electron-translocating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction











