
The cownose ray is a species of Batoidea found throughout a large part of the western Atlantic and Caribbean, from New England to southern Brazil. These rays also belong to the order Myliobatiformes, a group that is shared by bat rays, manta rays, and eagle rays.

Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally, resulting in the species becoming increasingly underpopulated in that area. Overfishing can occur in water bodies of any sizes, such as ponds, wetlands, rivers, lakes or oceans, and can result in resource depletion, reduced biological growth rates and low biomass levels. Sustained overfishing can lead to critical depensation, where the fish population is no longer able to sustain itself. Some forms of overfishing, such as the overfishing of sharks, has led to the upset of entire marine ecosystems. Types of overfishing include growth overfishing, recruitment overfishing, and ecosystem overfishing.

The fishing industry includes any industry or activity that takes, cultures, processes, preserves, stores, transports, markets or sells fish or fish products. It is defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization as including recreational, subsistence and commercial fishing, as well as the related harvesting, processing, and marketing sectors. The commercial activity is aimed at the delivery of fish and other seafood products for human consumption or as input factors in other industrial processes. The livelihood of over 500 million people in developing countries depends directly or indirectly on fisheries and aquaculture.

The National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), informally known as NOAA Fisheries, is a United States federal agency within the U.S. Department of Commerce's National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) that is responsible for the stewardship of U.S. national marine resources. It conserves and manages fisheries to promote sustainability and prevent lost economic potential associated with overfishing, declining species, and degraded habitats.

Unsustainable fishing methods refers to the use of various fishing methods to capture or harvest fish at a rate that is unsustainable for fish populations. These methods facilitate destructive fishing practices that damage ocean ecosystems, resulting in overfishing.
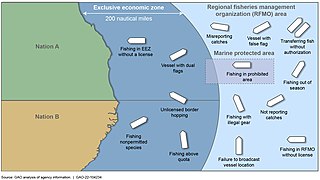
Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing (IUU) is an issue around the world. Fishing industry observers believe IUU occurs in most fisheries, and accounts for up to 30% of total catches in some important fisheries.

A factory ship, also known as a fish processing vessel, is a large ocean-going vessel with extensive on-board facilities for processing and freezing caught fish or whales. Modern factory ships are automated and enlarged versions of the earlier whalers, and their use for fishing has grown dramatically. Some factory ships are equipped to serve as a mother ship.

The giant guitarfish, also known as the whitespotted wedgefish, is a large species of guitarfish in the family Rhinidae. It is restricted to the Red Sea, Persian Gulf, and western Indian Ocean, but was formerly considered more widespread due to confusion with its relatives.

The sharpnose guitarfish also known as the granulated guitarfish is a species of ray in the Glaucostegidae family. They belong to the subclass Elsamobranchii which are cartilaginous fish that include sharks, rays, and skates as shown in their morphology. They have a flattened ray-like body and shark-like elongated snout. This species was first described by Georges Cuvier in 1829, and despite their appearance, they don’t pose any threat to humans.. As of April 2022, the IUNC has classified the sharpnose guitarfish as critically endangered.

The Brazilian cownose ray, also commonly called the Ticon cownose ray, is a species of fish in the family Rhinopteridae. Its range extends along the coast from the southern tip of Brazil to western Florida. Its natural habitats are shallow seas, estuarine waters, and intertidal flats.
This is a glossary of terms used in fisheries, fisheries management and fisheries science.

China has one-fifth of the world's population and accounts for one-third of the world's reported fish production as well as two-thirds of the world's reported aquaculture production. It is also a major importer of seafood and the country's seafood market is estimated to grow to a market size worth US$53.5 Billion by 2027.

As with other countries, the 200 nautical miles (370 km) exclusive economic zone (EEZ) off the coast of the United States gives its fishing industry special fishing rights. It covers 11.4 million square kilometres, which is the second largest zone in the world, exceeding the land area of the United States.

Lutjanus agennes, the African red snapper, Guinean snapper or African cubera snapper, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Lutjanidae, the snappers. It is native to the coastal Atlantic waters of Africa.

The coastline of the Russian Federation is the fourth longest in the world after the coastlines of Canada, Greenland, and Indonesia. The Russian fishing industry has an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of 7.6 million km2 including access to twelve seas in three oceans, together with the landlocked Caspian Sea and more than two million rivers.

The European pilchard is a species of ray-finned fish in the monotypic genus Sardina. The young of the species are among the many fish that are sometimes called sardines. This common species is found in the northeast Atlantic, the Mediterranean, and the Black Sea at depths of 10–100 m (33–328 ft). It reaches up to 27.5 cm (10.8 in) in length and mostly feeds on planktonic crustaceans. This schooling species is a batch spawner where each female lays 50,000–60,000 eggs.

The lunar fusilier, also known as the blue fusilier or moon fusilier, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a fusilier belonging to the family Caesionidae. It is widespread throughout the tropical waters of the Indo-West Pacific area.

African illegal fishing is the unlawful activity of obtaining fish and other aquatic species for various purposes in African waters. Fishing outside local, national, and international regulations causes the disturbance of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems in the countries of Africa. People living in local African communities may fish illegally in order to improve their income and lifestyle. On a larger scale, illegal fishing in Africa takes place when vessels from foreign countries are stationed on African waters without any legal documentation that allows fishing. Illegal fishing in Africa is one of the main causes of overfishing, and increases the spread of diseases. In Africa, the Chinese commercial fishing fleet is responsible for more illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing (IUU) fishing than that of any other nation.

Of the twelve species of billfish, there are six species of Billfish in the Indian Ocean.
The fishing industry in Thailand, in accordance with usage by The World Bank, the UN's Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and other multinational bodies, refers to and encompasses recreational fishing, aquaculture, and wild fisheries both onshore and offshore.



















