
Thrips are minute, slender insects with fringed wings and unique asymmetrical mouthparts. Entomologists have described approximately 7,700 species. They fly only weakly and their feathery wings are unsuitable for conventional flight; instead, thrips exploit an unusual mechanism, clap and fling, to create lift using an unsteady circulation pattern with transient vortices near the wings.

The Thripidae are the most speciose family of thrips, with over 290 genera representing just over two thousand species. They can be distinguished from other thrips by a saw-like ovipositor curving downwards, narrow wings with two veins, and antennae of six to ten antennomeres with stiletto-like forked sense cones on antennal segments III and IV.

Franklinothrips is a genus of thrips with pantropical distribution.

Orthotospovirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses, in the family Tospoviridae of the order Bunyavirales, which infects plants. Tospoviruses take their name from the species Tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus (TSWV) which was discovered in Australia in 1919. TSWV remained the only known member of the family until the early 1990s when genetic characterisation of plant viruses became more common. There are now at least twenty species in the genus with more being discovered on a regular basis. Member viruses infect over eight hundred plant species from 82 different families.

The Thripinae are a subfamily of thrips, insects of the order Thysanoptera. The Thripinae belong to the common thrips family Thripidae and include around 1,400 species in 150 genera. A 2012 molecular phylogeny found that the Thripinae was paraphyletic; further work will be needed to clarify the relationships within the group.
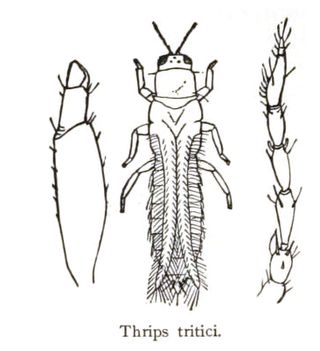
Frankliniella tritici, the eastern flower thrips, is a species of thrips in the genus Frankliniella. F. tritici inhabits blossom, such as dandelion flowers. They can directly damage plants, grasses and trees, in addition to commercial crops, and as a vector for tospoviruses, a form of plant virus, it particularly affects small fruit production in the United States, including strawberries, grapes, blueberries and blackberries. It can also affect alfalfa, oats, beans and asparagus crops. The species features strap-like wings edged with long hairs, a design which increases aerodynamic efficiency in very small arthropods; the reduced drag means the insect uses less energy. They extract nutrients directly from individual plant cells, and may also digest cells of fungi in the leaf litter.

Haplothrips is a genus of thrips in the family Phlaeothripidae. It is found worldwide and contains about 240 extant species.
Frankliniella schultzei, the common blossom thrips or cotton thrips, is a species of thrips in the family Thripidae. It is found in many parts of the world and is an important pest insect in agriculture.
Gynaikothrips is a genus of tube-tailed thrips in the family Phlaeothripidae. There are more than 30 described species in Gynaikothrips.

Panchaetothripinae is a subfamily of thrips in the family Thripidae, first described in 1912 by Richard Siddoway Bagnall. There are about 11 genera and more than 50 described species in Panchaetothripinae.
Adurothrips is a genus of thrips in the family Phlaeothripidae, first described by Laurence Mound in 1994. There is just one species in this genus: Adurothrips atopus. The species is wingless and breeds in leaf litter in New South Wales, Queensland and South Australia.

Holothrips is a genus of thrips in the family Phlaeothripidae, first described in 1911 by Heinrich Hugo Karny. The type species is Holothrips ingens.
Octurothrips is a genus of thrips in the family Phlaeothripidae, first described by Hermann Priesner in 1931. There is just one species in this genus: Octurothrips pulcher.
Parabaphothrips is a genus of thrips in the family Phlaeothripidae, first described by Dudley Moulton in 1949. There is just one species in this genus: Parabaphothrips coffeae found in Africa.

Xyela is a genus of sawflies, belonging to the family Xyelidae.

Anaphothrips is a genus of thrips belonging to the family Thripidae.
Chirothrips is a genus of insects belonging to the family Thripidae.

Hypulus is a genus of beetles belonging to the family Melandryidae. The species of this genus are found in Europe and North America
Megalurothrips is a genus of thrips belonging to the family Thripidae.
Retithrips is a genus of thrips in the family Thripidae, first described in 1910 by Paul Marchal. These thrips are leaf-feeding.












