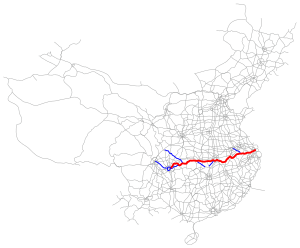
The Yangtze, Yangzi or Changjiang is the longest river in Eurasia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows 6,300 km (3,915 mi) in a generally easterly direction to the East China Sea. It is the fifth-largest primary river by discharge volume in the world. Its drainage basin comprises one-fifth of the land area of China, and is home to nearly one-third of the country's population.

Yichang, alternatively romanized as Ichang, is a prefecture-level city located in western Hubei province, China. It is the third largest city in the province after the capital, Wuhan and the prefecture-level city Xiangyang, by urban population. The Three Gorges Dam is located within its administrative area, in Yiling District.

Enshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture is located in the mountainous southwestern corner of Hubei province, People's Republic of China. It forms Hubei's southwestern "panhandle", bordering on Hunan in the south and Chongqing Municipality in the west and northwest. The Yangtze River crosses the prefecture's northeastern corner in Badong County.

Huanggang is a prefecture-level city in easternmost Hubei Province, China. It is situated to the north of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River and is bounded in the north by the Dabie Mountains and is named after Mount Huanggang. It borders Henan in the north, Anhui in the east and Jiangxi in the south.

Huangshi, alternatively romanized as Hwangshih, is a prefecture-level city in southeastern Hubei province, People's Republic of China. Its population was 2,469,079 inhabitants at the 2020 census; 1,567,108 of whom lived in the built-up area made up of 4 urban districts plus the city of Daye, now being part of the agglomeration.

The Yichang Yangtze River Highway Bridge is a suspension bridge that crosses the Yangtze River some 20 km downstream from the center city of Yichang, China. It is located within the prefecture-level city of Yichang, and carries the G50 Shanghai–Chongqing Expressway.

The Yichang–Wanzhou railway, or the Yiwan railway connects the cities of Yichang and Wanzhou via Lichuan, Hubei. It was completed in 2010 and forms part of the Shanghai–Wuhan–Chengdu passenger railway. Out of the line's total 377 km (234 mi) length, 288 km (179 mi) runs on bridges or in tunnels. According to the chief engineer, Zhang Mei, the line was the most difficult ever constructed in China. Operation started on 22 December 2010.

The Chongqing–Lichuan railway, or the Yuli railway is a railway connecting central Chongqing with the Hubei city of Lichuan. The 244 km (152 mi) long railway, connecting Chongqing North railway station with the Lichuan Station on the Yichang–Wanzhou railway, is a section of the Shanghai–Wuhan–Chengdu passenger railway, which extends to Wuhan, Nanjing, and Shanghai.

The Yangluo Yangtze River Bridge is a suspension bridge over the Yangtze River in Wuhan, Hubei, China. With a main span of 1,280 metres (4,200 ft), at its opening it was tied with the Golden Gate Bridge as the ninth longest suspension bridge in the world. The bridge carries the G70 Fuzhou–Yinchuan Expressway and G4201 Wuhan Ring Expressway over the Yangtze River and provides easy access to both sides of the river as part of a larger plan to promote development in the eastern portion of the city. Construction on the bridge began on November 4, 2003, and it opened to traffic on December 26, 2007.

Shanghai–Wuhan–Chengdu passenger-dedicated railway, is a fully completed higher-speed railway corridor in China. It is operated by CR Shanghai Group, CR Wuhan Group and CR Chengdu Group. The Chinese name of the railway line, Huhanrong, is a combination of the abbreviations for Shanghai, Wuhan, and Chengdu, three major cities along the line.

Nanjing–Tongling railway or Ningtong railway, is a single-track railroad in eastern China between Nanjing in Jiangsu Province and Tongling in Anhui Province. The line is 208 km (129 mi) long. Major towns along route include Nanjing, Maanshan, Wuhu and Tongling. With the opening of the parallel Nanjing–Anqing intercity railway in 2015, the line is mostly used for freight traffic.

Yan'an Elevated Road is an elevated expressway in the city of Shanghai, China. It runs along Yan'an Road in its entirety, continuing from the east terminus of G50 Shanghai-Chongqing Expressway at Huqingping Interchange to just beyond the old building of Shanghai Natural History Museum, at which point it ends and rejoins Yan'an Road on the surface. Traffic is then partly directed underground to the Bund Tunnel. Motorists continuing east can cross the Huangpu River using the East Yan'an Road Tunnel to Pudong.

The Shenyang–Haikou Expressway, designated as G15 and commonly referred to as the Shenhai Expressway is an expressway in China that connects the cities of Shenyang, Liaoning, and Haikou, Hainan. When fully complete, it will be 3,710 km (2,310 mi) in length. One of its oldest portions is the Shenyang–Dalian Expressway, or Shenda Expressway is a 400 km (250 mi) expressway that connects Shenyang and Dalian, the two largest cities of China's Liaoning province.

The Shanghai–Chengdu Expressway, designated as G42 and commonly referred to as the Hurong Expressway is an east–west bound expressway that connects the eastern metropolis of Shanghai to Chengdu, the capital city of Sichuan. The expressway passes through six provinces and serves major cities such as Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Nanjing, Hefei, Wuhan, and Yichang. The eastern terminus of G42 is at the Wuning Road Interchange of Shanghai Middle Ring Road. At its western terminus, the expressway intersects the East 3rd Ring Road and connects East Erxianqiao Road in Chenghua District, Chengdu. The expressway spans 1,960 km (1,220 mi) in length.
The G4211 Nanjing–Wuhu Expressway, commonly referred to as the Ningwu Expressway, is a north-south bound expressway that connects Nanjing, the capital city of Jiangsu and Wuhu, Anhui in China. It is an auxiliary route of G42 Shanghai–Chengdu Expressway that connects the parallel G42 and G50 Shanghai-Chongqing Expressway. The expressway spans a length of 75 km (47 mi), passes two provinces and serves the cities of Nanjing, Jiangsu; Ma'anshan, Anhui; and Wuhu, Anhui. The north terminus of G4211 is at Tianbao Bridge in Yuhuatai District, Nanjing, and the south terminus connects to G50 and G5011 Wuhu-Hefei Expressway via a cloverleaf interchange in Wuhu. G4211 is a four-lane limited access tollway for its entire length.

The Edong Yangtze River Bridge is a cable-stayed bridge across the Yangtze River in Hubei Province in eastern China. The bridge connects Huangshi and Xishui County and forms part of the G45 Daqing–Guangzhou Expressway and the G50 Shanghai–Chongqing Expressway. Construction of the bridge started in 2008 and it was completed in 2010. With a main span of 926 m (3,038 ft) it is currently the fourth longest cable-stayed bridge in the world.

Anqing Yangtze River Bridge is a cable-stayed bridge spanning 1,040 metres (3,410 ft) over the Yangtze River at Anqing, Anhui Province in eastern China. The bridge is 31.2 metres (102 ft) wide and carries four lanes of traffic on the G50 Shanghai–Chongqing Expressway between Anqing north of the river and Dongzhi County in Chizhou prefecture to the south. The bridge opened on December 27, 2004 and was the 35th bridge across the Yangtze River between Yibin and Shanghai. The bridge required investment of ¥1.3174 billion.

The Wuhan Junshan Yangtze River Bridge is a large cable-stayed bridge over the Yangtze River. The bridge carries 6 lanes of traffic between the Caidian District and the Jiangxia District of Wuhan, Hubei. A concurrency of expressways go over the bridge: The G4 Beijing–Hong Kong and Macau Expressway, the G50 Shanghai–Chongqing Expressway, and the G4201 Wuhan Ring Expressway. The bridge, which was opened in 2001, is one of the largest cable-stayed bridges in the world.

The Jiujiang Yangtze River Expressway Bridge, also known as the Second Jiujiang Bridge, is a cable-stayed bridge over the Yangtze River between Huangmei, Huanggang, in Hubei province and Jiujiang, in Jiangxi province. The bridge carries six lanes of traffic on the G70 Fuzhou–Yinchuan Expressway and is the second Yangtze River crossing in Jiujiang. Construction of the bridge started on September 27, 2009, and the bridge was completed on October 28, 2013.