
The Qinghai–Tibet railway or Qingzang railway, is a high-elevation railway line in China between Xining, Qinghai Province, and Lhasa, Tibet. With over 960 km (600 mi) of track being more than 4,000 m (13,123 ft) above sea level, it is the highest railway line in the world.

The Beijing–Harbin Expressway, designated as G1 and commonly abbreviated as Jingha Expressway (京哈高速) is an expressway linking the cities of Beijing and Harbin, Heilongjiang.

China National Highway 109 connects Beijing with Lhasa. It runs westwards from Beijing via Datong, Yinchuan and Xining to Golmud before turning southwest to Lhasa. The portion of the highway from Xining to Lhasa is known as the Qinghai-Tibet Highway. The total length of the route is 3,901 km.

Ulanqab or Ulan Chab is a region administered as a prefecture-level city in south-central Inner Mongolia, China. Its administrative centre is in Jining District, which was formerly a county-level city. It was established as a prefecture-level city on 1 December 2003, formed from the former Ulanqab League. The Ulanqab Stadium is located in the city.

Golmud, also known by various other romanizations, is a county-level city in the Haixi Mongol and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture of Qinghai Province, China. It is now the second-largest city in Qinghai and the third largest in the Tibetan Plateau. The population in 2020 is 221,863.
The Lanzhou–Qinghai railway, abbreviated as the Lanqing railway was built as the first step of an ambitious plan set by the People's Republic of China to connect Tibet with the rest of China by railway. LanQing railway, designed in 1956 and built from May 1958 to September 1959, runs 188 Kilometers long, connecting Lanzhou, the capital city of Gansu province, and Xining, the capital city of Qinghai province.

Lan–Yin Mandarin (Lanyin) is a branch of Mandarin Chinese traditionally spoken throughout Gansu province and in the northern part of Ningxia. In recent decades it has expanded into northern Xinjiang. It forms part of Northwestern Mandarin. It has also been grouped together with Central Plains Mandarin. The name is a compound of the capitals of the two former provinces where it dominates, Lanzhou and Yinchuan, which are also two of its principal subdialects.

The Qingdao–Yinchuan Expressway, designated as G20 and commonly referred to as the Qingyin Expressway is an expressway that connects the cities of Qingdao, Shandong, China, and Yinchuan, Ningxia. It is 1,600 km (990 mi) in length.
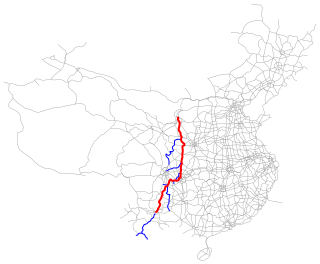
The Yinchuan–Kunming Expressway, designated as G85 and commonly referred to as the Yinkun Expressway is an expressway in China that connects the cities of Yinchuan, Ningxia and Kunming, Yunnan. It is 2,332 km (1,449 mi) in length. The full length was completed and opened for traffic in 2024.
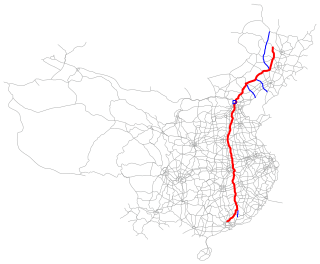
The Daqing–Guangzhou Expressway (大庆-广州高速公路), designated as G45 and commonly referred to as the Daguang Expressway (大广高速公路) is an expressway that connects the cities of Daqing, Heilongjiang, and Guangzhou, Guangdong in China. When fully complete, it will be 3,550 km (2,210 mi) in length.

The Fuzhou–Yinchuan Expressway, designated as G70 and commonly referred to as the Fuyin Expressway is an expressway that connects the cities of Fuzhou, Fujian, China, and Yinchuan, Ningxia. It is 2,397.55 km (1,489.77 mi) in length.

The G3011 Liuyuan–Golmud Expressway, commonly referred to as the Liuge Expressway, is a planned expressway in China that will connect Liuyuan, a town in Guazhou County, Jiuquan, Gansu, and Golmud, Haixi Mongol and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Qinghai.
The history of the administrative divisions of China after 1949 refers to the administrative divisions under the People's Republic of China. In 1949, the communist forces initially held scattered fragments of China at the start of the Chinese Civil War. By late 1949, they controlled the majority of mainland China, forcing the Republic of China government to relocate to Taiwan.
The Yinchuan Ring Expressway, designated as G2004, is an expressway in Ningxia, Northern China orbiting the city of Yinchuan. This expressway is a branch of G6 Beijing–Lhasa Expressway.
China Railway Qingzang Group, officially abbreviated as CR Qingzang or CR-Qingzang, also known as CR Qinghai-Tibet and CRQT, formerly, Qinghai-Tibet Railway Company or Qingzang Railway Company, is a subsidiary under the jurisdiction of the China Railway. The company was founded in 2002 and reincorporated in 2017.
Dabaozi is a town in Chengbei District of Xining, Qinghai, China. As of the 2017 census it has a population of 21,000 and an area of 45 square kilometres (17 sq mi).
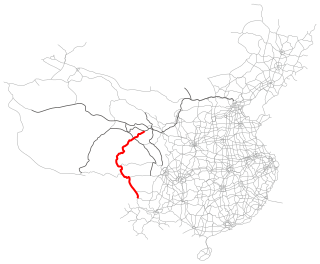
The G0613 Xining–Lijiang Expressway, also referred to as the Xili Expressway, is an under construction expressway in China that connects Xining, Qinghai to Lijiang, Yunnan.
The 62 Aid Projects to Tibet are the sixty-two projects of the People's Republic of China in support of the construction of Tibet, as determined by the Third Symposium on Tibet Work convened by the Central Government in 1994. These projects involved agriculture, animal husbandry and forestry, transportation, energy, post and telecommunications, and communications, with a cumulative total investment of over RMB 4.86 billion. These projects have been fully completed and put into operation.


















