
Silene is a genus of flowering plants in the family Caryophyllaceae. Containing nearly 900 species, it is the largest genus in the family. Common names include campion and catchfly. Many Silene species are widely distributed, particularly in the northern hemisphere.
Hildburghausen is a district in Thuringia, Germany. It is bounded by the district of Schmalkalden-Meiningen, the city of Suhl, the districts of Ilm-Kreis, Saalfeld-Rudolstadt and Sonneberg, and the state of Bavaria. Located roughly halfway between the mountain chains of the Rhön and the Thuringian Forest, the district is densely forested and covered by hilly countryside. Its territory is similar to that of the former Ernestine duchy, Saxe-Hildburghausen.

The Urticaceae are a family, the nettle family, of flowering plants. The family name comes from the genus Urtica. The Urticaceae include a number of well-known and useful plants, including nettles in the genus Urtica, ramie, māmaki, and ajlai.

The Wasserkuppe is a mountain within the German state of Hesse. It is a large plateau formation at an elevation of 950 metres (3,120 ft) and is the highest peak in the Rhön Mountains. Great advances in sailplane development took place on the mountain during the interwar period, driven by annual contests. Near the summit there is still an airfield used by gliding clubs and pilots of light aircraft.

The Rhön Mountains are a group of low mountains in central Germany, located around the border area where the states of Hesse, Bavaria and Thuringia come together. These mountains, which are at the extreme southeast end of the East Hesse Highlands, are partly a result of ancient volcanic activity. They are separated from the Vogelsberg Mountains by the river Fulda and its valley. The highest mountain in the Rhön is the Wasserkuppe, which is in Hesse. The Rhön Mountains are a popular tourist destination and walking area.
Rhön-Grabfeld is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Hassberge, Schweinfurt and Bad Kissingen, and the states of Hesse and Thuringia.

Ostrya is a genus of eight to 10 small deciduous trees belonging to the birch family Betulaceae. Common names include hop-hornbeam and hophornbeam. It may also be called ironwood, a name shared with a number of other plants.

Teucrium is a cosmopolitan genus of flowering plants in the mint family Lamiaceae, commonly known as germanders. Plants in this genus are perennial herbs or shrubs, with branches that are more or less square in cross-section, leaves arranged in opposite pairs, and flowers arranged in thyrses, the corolla with mostly white to cream-coloured, lobed petals.

Bischofsheim in der Rhön is a town in the district Rhön-Grabfeld, in Bavaria, Germany. It is situated in the Rhön Mountains, 29 km southeast of Fulda.

Distylium (winter-hazel) is a genus of about 18 species of evergreen shrubs and trees in the witch hazel family, Hamamelidaceae, native to eastern and southeastern Asia.

The Kreuzberg is one of the Rhön Mountains in southern Germany. With about 928 m (3,045 ft) high it is the highest elevation of the Bavarian part of the Rhön, in the province of Lower Franconia. The Kreuzberg — also referred to as the "sacred mountain of the Franconians" — is near the town of Bischofsheim in der Rhön in the district Rhön-Grabfeld.

Heustreu is a municipality in the district of Rhön-Grabfeld in Lower Franconia in Germany. It lies on the river Streu.
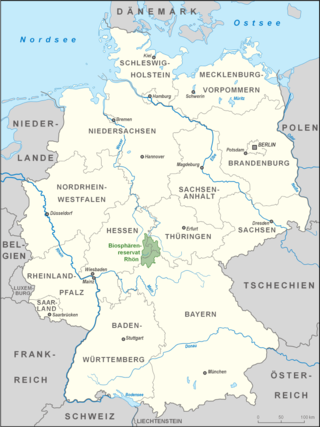
The Rhön Biosphere Reserve includes the entire central area of the Rhön Mountains, a low mountain range in the German states of Hesse, Bavaria and Thuringia.

Cannabaceae is a small family of flowering plants, known as the hemp family. As now circumscribed, the family includes about 170 species grouped in about 11 genera, including Cannabis (hemp), Humulus (hops) and Celtis (hackberries). Celtis is by far the largest genus, containing about 100 species.

Guettardeae is a tribe of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae and contains about 748 species in 14 genera. Its representatives are widespread geographically and are found in the tropics and subtropics.

Die Rhöner Säuwäntzt are a skiffle-blues band from Eichenzell-Lütter in Hessen, Germany. The line-up consists of Martin Caba, Christoph Günther and Christoph Leipold playing Skiffle-Blues with lyrics based on Rhön Mountains dialect and other Hessian dialects varieties. The expression Säuwäntzt means pork belly and refers also to untidy or unruly children and youth.

The Hessian Rhön Nature Park lies east of Fulda in East Hesse on the border with Thuringia and Bavaria and has and area of 720,7 km2. Together with the Bavarian Rhön Nature Park it is part of the cross-border Rhön Biosphere Reserve.

A Kuppe is the term used in German-speaking central Europe for a mountain or hill with a rounded summit that has no rock formation, such as a tor, on it. A range of such hills is called a Kuppengebirge. In geology the term also refers to corresponding stratigraphic forms. The term is similar to the English topographical and geological terms, knoll and dome. It is also analogous to the French word ballon which means a mountain with a rounded summit.
Merkurosaurus is an extinct genus of lizards from the Shinisauria that is known from the Late Oligocene of Germany, collected in 1999, and the Early Miocene Most Formation of the Czech Republic and the Wiesbaden Formation Germany of (Amöneburg). A single species, Merkurosaurus ornatus, is known and was named and described by Jozef Klembara in 2008 based on the holotype Pb 02045 and other referred specimens. It was initially only known from deposits in the Czech Republic but remains found in Germany were eventually attributed to the genus in 2015.
















