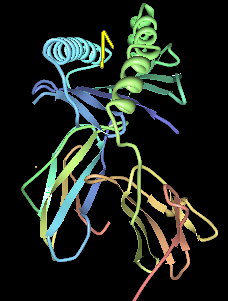
HLA DR3-DQ2 is double serotype that specifically recognizes cells from individuals who carry a multigene HLA DR, DQ haplotype. Certain HLA DR and DQ genes have known involvement in autoimmune diseases. DR3-DQ2, a multigene haplotype, stands out in prominence because it is a factor in several prominent diseases, namely coeliac disease and juvenile diabetes. In coeliac disease, the DR3-DQ2 haplotype is associated with highest risk for disease in first degree relatives, highest risk is conferred by DQA1*0501:DQB1*0201 homozygotes and semihomozygotes of DQ2, and represents the overwhelming majority of risk. HLA DR3-DQ2 encodes DQ2.5cis isoform of HLA-DQ, this isoform is described frequently as 'the DQ2 isoform', but in actuality there are two major DQ2 isoform. The DQ2.5 isoform, however, is many times more frequently associated with autoimmune disease, and as a result to contribution of DQ2.2 is often ignored.
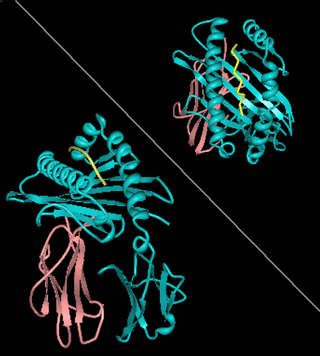
HLA-A1 (A1) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A "A" serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α1 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A1, the alpha "A" chain are encoded by the HLA-A*01 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. This group currently is dominated by A*01:01. A1 and A*01 are almost synonymous in meaning. A1 is more common in Europe than elsewhere, it is part of a long haplotype that appears to have been frequent in the ancient peoples of Northwestern Europe. A1 is a frequent component of the AH8.1 haplotype. A1 serotype positivity is roughly linked to a large number of inflammatory diseases and conditions believed to have immune system involvement. Because of its linkage within the AH8.1 haplotype many studies showed association with A1 or A1,B8 only later to show the association drift toward the class II region gene alleles, DR3 and DQ2.5. While it is not clear what role A1 has in infectious disease, some linkage with infection rates in HIV remain associated within the A1 region of the haplotype.

HLA-A*02 (A*02) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within the HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of the α2 domain of the HLA-A α-chain. For A*02, the α chain is encoded by the HLA-A*02 gene and the β chain is encoded by the B2M locus. In 2010 the World Health Organization Naming Committee for Factors of the HLA System revised the nomenclature for HLAs. Before this revision, HLA-A*02 was also referred to as HLA-A2, HLA-A02, and HLA-A*2.
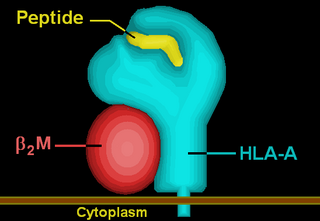
HLA-A33 (A33) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α33 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A33, the alpha "A" chain are encoded by the HLA-A*33 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. A33 and A*33 are almost synonymous in meaning. A33 is a split antigen of the broad antigen serotype A19. A33 is a sister serotype of A29, A30, A31, A32, and A74.
HLA-Cw*16 (Cw*16) is an HLA-C allele-group. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-Cw*16 gene products. This allele group is most commonly found in West Africa, but A single Haplotype of Cw16 is found in Western Europe at unusually high frequencies. There is no useful serology for Cw*16.
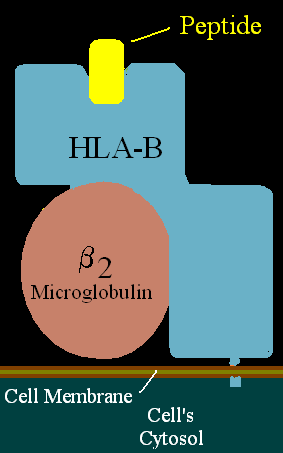
HLA-B*82 (B*82) is an HLA-B allele-group. There is no current useful serotyping for HLA-B*82 gene products. B*8201 was first identified by sequence analysis and appears to be derived by gene conversion between B*5602 and another HLA class I allele., later B*8202 was identified in a caucasian and was suggested to be ancestral to B*8201, as product between gene conversion of B*5602 allele and B*4501 allele. B*82 is more common in East Africa, Kenya and Sudan, the frequency of B*8201 is found in the peoples to the west, sporadically in Central and West Africa, B*8202 is found in Sudan and Saudi Arabia.

HLA-B81 (B81) is an HLA–B serotype. The serotype identifies the HLA-B*8101 and B*8102 gene products. B81 is more common in Subsaharan Africa. While there is a B81 serotype, serotyping of B81 is poor when simultaneously tested with anti-B7 or B48 antibodies.
HLA-B67 (B67) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*67 gene products. B67 is region specific recombinant haplotype formed by the gene conversion of B*39, an allele common along the Northwest Pacific Rim, and B7, B22, or B27.
HLA-B59 (B59) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*## gene products. B59 is a hybrid between B*55 and B*51. B59 is more common in Japan, Korea, N. China and Mongolia.
HLA-B53 (B53) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*53 gene products. The B53 sequence is identical to B35 but short sequence specifies a Bw4 rather than a Bw6 motif, indicating B53 is a recent product of gene conversion. This suggests an origin for HLA-B53 involving a gene conversion of HLA-B35 by an allele containing this Bw4 sequence.
HLA-B48 (B48) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*48 gene products. B48 is most common along the West Pacific Rim, Americas indigenous peoples and Northern Eurasians. B*4801 is part of a group of alleles including B*4201 that share Intron 1 sequence with B*0702, which is common over Western and Central Asia, and has a distribution indicating an early and long presence in Eurasian humans. A*48 appears to be the result of a recombination event that occurred early in the settlement history of Central Asia that then spread eastward into the NW Pacific rim and the New World.
HLA-B46 (B46) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the gene products of HLA-B*4601 allele. B*4601 resulted from a rare, interlocus, gene conversion between B62, probably B*1501, and a HLA-C allele. B*4601 is the most common HLA-B allele that does not have an origin within Africa, and estimated 400 million people in Eastern Asia carry a B46 allele. When found B*4601 segregates with only 2 HLA-Cw alleles, A limited number of HLA-A and HLA-DRB1 alleles suggesting that the allele recently expanded from a limited sized group within SE Asia. Extremely low frequencies outside of Eastern Asia are indicators of a recent expansion of B46 from a recently small population. The frequency distribution suggests the ancestral B46 population was in SE China, or, potentially Burma. B46 in Asia correlates with wet-rice farming. The exceptions are notable, it has been found in the Nivkhi on north-eastern Sakalin Island, the Ainu, and the Nivkhi-related (genetically) Tlinglet population of Alaska at trace levels.

HLA-B7 (B7) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*07 gene products. B7, previously HL-A7, was one of the first 'HL-A' antigens recognized, largely because of the frequency of B*0702 in Northern and Western Europe and the United States. B7 is found in two major haplotypes in Europe, where it reaches peak frequency in Ireland. One haplotype A3-B7-DR15-DQ1 can be found over a vast region and is in apparent selective disequilibrium. B7 is a risk factor for cervical cancer, sarcoidosis, and early-onset spondylarthropathies.
HLA-B55 (B55) is an HLA-B serotype. B55 is a split antigen from the B22 broad antigen, sister serotypes are B54 and B56. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*55 gene products.
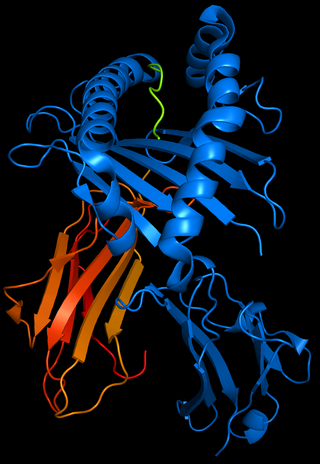
HLA-B51 (B51) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*51 gene products.

HLA-B38 (B38) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the B*38 allele products of the HLA-B gene-locus.

HLA-B45 (B45) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the B*45 gene-allele protein products of HLA-B.

HLA-B63 (B63) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies certain B*15 gene-allele protein products of HLA-B.

HLA-B62 (B62) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies certain B*15 gene-allele protein products of HLA-B.
HLA A1-B8 is a multigene haplotype that covers the MHC Class I region of the human major histocompatibility complex on chromosome 6. A multigene haplotype is set of inherited alleles covering several genes, or gene-alleles; common multigene haplotypes are generally the result of identity by descent from a common ancestor. Chromosomal recombination fragments multigene haplotypes as the distance to that ancestor increases in number of generations.