Related Research Articles
HLA DR3-DQ2 is double serotype that specifically recognizes cells from individuals who carry a multigene HLA DR, DQ haplotype. Certain HLA DR and DQ genes have known involvement in autoimmune diseases. DR3-DQ2, a multigene haplotype, stands out in prominence because it is a factor in several prominent diseases, namely coeliac disease and juvenile diabetes. In coeliac disease, the DR3-DQ2 haplotype is associated with highest risk for disease in first degree relatives, highest risk is conferred by DQA1*0501:DQB1*0201 homozygotes and semihomozygotes of DQ2, and represents the overwhelming majority of risk. HLA DR3-DQ2 encodes DQ2.5cis isoform of HLA-DQ, this isoform is described frequently as 'the DQ2 isoform', but in actuality there are two major DQ2 isoform. The DQ2.5 isoform, however, is many times more frequently associated with autoimmune disease, and as a result to contribution of DQ2.2 is often ignored.

HLA-DQ8 (DQ8) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within the HLA-DQ (DQ) serotype group. DQ8 is a split antigen of the DQ3 broad antigen. DQ8 is determined by the antibody recognition of β8 and this generally detects the gene product of DQB1*0302.
HLA-DQ7 (DQ7) is an HLA-DQ serotype that recognizes the common HLA DQB1*0301 and the less common HLA DQB1*0304 gene products. DQ7 is a form of 'split antigen' of the broad antigen group DQ3 which also contains DQ8 and DQ9.
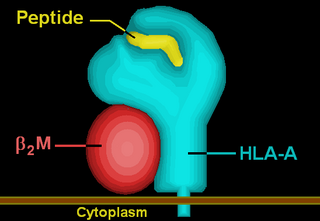
HLA-A3 (A3) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α3 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A3, the alpha, "A", chain are encoded by the HLA-A*03 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. This group currently is dominated by A*03:01. A3 and A*03 are almost synonymous in meaning. A3 is more common in Europe, it is part of the longest known multigene haplotype, A3~B7~DR15~DQ6.
HLA-A9 (A9) is a broad antigen HLA-A serotype that recognized the HLA-A23 and HLA-A24 serotypes. A*2402 appears to have evolved from A*23 alleles by a process of gene conversion. The A23 is more common in Africa and regions proximal to Africa. A24 is at very high frequencies in Austronesia and certain indigenous peoples of the Arctic, North America, South America and West Pacific Rim. While it is common over most of Eurasia, it is found at low abundance in NW Europe. A24 appears to have been carried by the first colonizers of South Eastern Asia.

HLA-A69 (A69) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α69 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A69, the alpha "A" chain are encoded by the HLA-A*69 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. This group currently is dominated by A*6901. A69 and A*69 are almost synonymous in meaning. A69 is a split antigen of the broad antigen serotype A28. A69 is a sister serotype of A68.
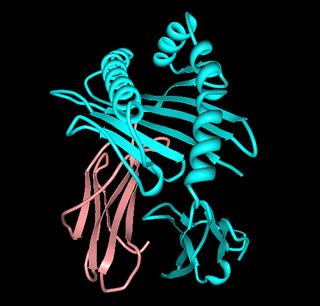
HLA-A68 (A68) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α68 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A68, the alpha "A" chain are encoded by the HLA-A*68 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. A68 and A*68 are almost synonymous in meaning. A68 is a split antigen of the broad antigen serotype A28. A68 is a sister serotype of A69.

HLA-A33 (A33) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α33 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A33, the alpha "A" chain are encoded by the HLA-A*33 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. A33 and A*33 are almost synonymous in meaning. A33 is a split antigen of the broad antigen serotype A19. A33 is a sister serotype of A29, A30, A31, A32, and A74.
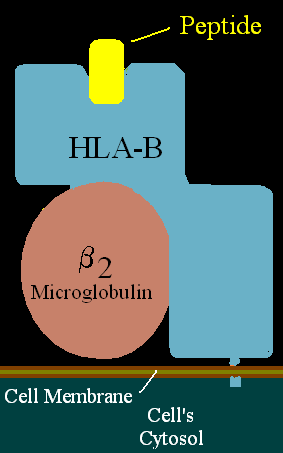
HLA-B81 (B81) is an HLA–B serotype. The serotype identifies the HLA-B*8101 and B*8102 gene products. B81 is more common in Subsaharan Africa. While there is a B81 serotype, serotyping of B81 is poor when simultaneously tested with anti-B7 or B48 antibodies.
HLA-B73 (B73) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the HLA-B*7301 gene product. Part of B*7301 is similar to the HLA-B22 family, however part resembles the domains seen in other apes. B73 is more common in Western Indian Ocean, Mediterranean and Africa.
HLA-B67 (B67) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*67 gene products. B67 is region specific recombinant haplotype formed by the gene conversion of B*39, an allele common along the Northwest Pacific Rim, and B7, B22, or B27.
HLA-B46 (B46) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the gene products of HLA-B*4601 allele. B*4601 resulted from a rare, interlocus, gene conversion between B62, probably B*1501, and a HLA-C allele. B*4601 is the most common HLA-B allele that does not have an origin within Africa, and estimated 400 million people in Eastern Asia carry a B46 allele. When found B*4601 segregates with only 2 HLA-Cw alleles, A limited number of HLA-A and HLA-DRB1 alleles suggesting that the allele recently expanded from a limited sized group within SE Asia. Extremely low frequencies outside of Eastern Asia are indicators of a recent expansion of B46 from a recently small population. The frequency distribution suggests the ancestral B46 population was in SE China, or, potentially Burma. B46 in Asia correlates with wet-rice farming. The exceptions are notable, it has been found in the Nivkhi on north-eastern Sakalin Island, the Ainu, and the Nivkhi-related (genetically) Tlinglet population of Alaska at trace levels.
HLA-B18 (B18) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*18 gene products. B*1801, the most common allele is at highest frequencies in Northern Italy and the Balkans, a peak frequency distribution it shares with B*3501.
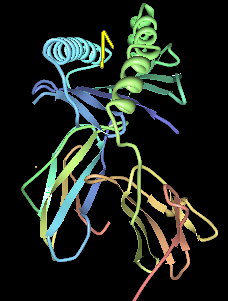
HLA-B8 (B8) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the HLA-B*08 gene products. HLA-B8, previously known as HL-A8 was one of the first identified of the HLA antigens. It coined the "Super B8" haplotype, also called the ancestral European haplotype because of its common occurrence in Europe, particular the isles and Scandinavia. B8 is a component gene-allele of the AH8.1 haplotype in Northern and Western Europeans. Genes between B8 and DR3 on this haplotype are frequently associated with autoimmune disease.
HLA-B55 (B55) is an HLA-B serotype. B55 is a split antigen from the B22 broad antigen, sister serotypes are B54 and B56. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*55 gene products.
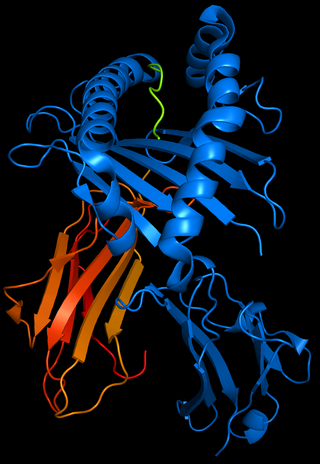
HLA-B51 (B51) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*51 gene products.

HLA-B52 (B52) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the more common HLA-B*52 gene products.

HLA-B38 (B38) is an HLA-B serotype. The serotype identifies the B*38 allele products of the HLA-B gene-locus.
HLA A1-B8 is a multigene haplotype that covers the MHC Class I region of the human major histocompatibility complex on chromosome 6. A multigene haplotype is set of inherited alleles covering several genes, or gene-alleles; common multigene haplotypes are generally the result of identity by descent from a common ancestor. Chromosomal recombination fragments multigene haplotypes as the distance to that ancestor increases in number of generations.
HLA B7-DR15-DQ6 is a multigene haplotype that covers a majority of the human major histocompatibility complex on chromosome 6. A multigene haplotype is set of inherited alleles covering several genes, or gene-alleles, common multigene haplotypes are generally the result of descent by common ancestry. Chromosomal recombination fragments multigene haplotypes as the distance to that ancestor increases in number of generations.
References
- ↑ Marsh, S. G.; Albert, E. D.; Bodmer, W. F.; Bontrop, R. E.; Dupont, B.; Erlich, H. A.; Fernández-Viña, M.; Geraghty, D. E.; Holdsworth, R.; Hurley, C. K.; Lau, M.; Lee, K. W.; Mach, B.; Maiers, M.; Mayr, W. R.; Müller, C. R.; Parham, P.; Petersdorf, E. W.; Sasazuki, T.; Strominger, J. L.; Svejgaard, A.; Terasaki, P. I.; Tiercy, J. M.; Trowsdale, J. (2010). "Nomenclature for factors of the HLA system, 2010". Tissue Antigens. 75 (4): 291–455. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0039.2010.01466.x. PMC 2848993 . PMID 20356336.
- ↑ Allsopp CE, Hill AV, Kwiatkowski D, et al. (1991). "Sequence analysis of HLA-Bw53, a common West African allele, suggests an origin by gene conversion of HLA-B35". Hum. Immunol. 30 (2): 105–9. doi:10.1016/0198-8859(91)90078-N. PMID 2022493.
- ↑ derived from IMGT/HLA
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Middleton D, Menchaca L, Rood H, Komerofsky R (2003). "New allele frequency database". Tissue Antigens. 61 (5): 403–7. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2003.00062.x . PMID 12753660.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Maiers M, Gragert L, Klitz W (2007). "High-resolution HLA alleles and haplotypes in the United States population". Hum. Immunol. 68 (9): 779–88. doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2007.04.005. PMID 17869653.