| Haplogroup LT | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Possible time of origin | 49,600-41,400 years BP [1] |
| Ancestor | K |
| Descendants | L, T |
| Defining mutations | L298 and P326 |
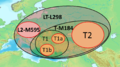
Haplogroup LT or LT-L298/P326, also known as K1 (and until 2008 as Haplogroup K2), is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. Its defining SNP mutations are L298 and P326.
Contents
K1 (a.k.a. LT) splits into:
- Haplogroup L — mostly South Asian and some Middle Eastern populations
- Haplogroup T — rarer, found in parts of South Asia, the Middle East, East Africa, and Europe