
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplotype is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual.
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia is the study of the genetics and archaeogenetics of the ethnic groups of South Asia. It aims at uncovering these groups' genetic histories. The geographic position of the Indian subcontinent makes its biodiversity important for the study of the early dispersal of anatomically modern humans across Asia.

Haplogroup J-M304, also known as J, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is believed to have evolved in Western Asia. The clade spread from there during the Neolithic, primarily into North Africa, the Horn of Africa, the Socotra Archipelago, the Caucasus, Europe, Anatolia, Central Asia, South Asia, and Southeast Asia.

Haplogroup X is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. It is found in North America, Europe, Western Asia, North Africa, and the Horn of Africa.

Haplogroup C is a major Y-chromosome haplogroup, defined by UEPs M130/RPS4Y711, P184, P255, and P260, which are all SNP mutations. It is one of two primary branches of Haplogroup CF alongside Haplogroup F. Haplogroup C is found in ancient populations on every continent except Africa and is the predominant Y-DNA haplogroup among males belonging to many peoples indigenous to East Asia, Central Asia, Siberia, North America and Australia as well as a some populations in Europe, the Levant, and later Japan.
Haplogroup E-V38, also known as E1b1a-V38, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. E-V38 is primarily distributed in Africa. E-V38 has two basal branches, E-M329 and E-M2. E-M329 is a subclade mostly found in East Africa. E-M2 is the predominant subclade in West Africa, Central Africa, Southern Africa, and the region of African Great Lakes; it also occurs at moderate frequencies in North Africa, West Asia, and Southern Europe.

Haplogroup F, also known as F-M89 and previously as Haplogroup FT, is a very common Y-chromosome haplogroup. The clade and its subclades constitute over 90% of paternal lineages outside of Africa.
Haplogroup R1, or R-M173, is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. A primary subclade of Haplogroup R (R-M207), it is defined by the SNP M173. The other primary subclade of Haplogroup R is Haplogroup R2 (R-M479).

In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non-recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome. Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of short tandem repeats (STRs) and types of mutations called single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).

Haplogroup R, or R-M207, is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is both numerous and widespread amongst modern populations.
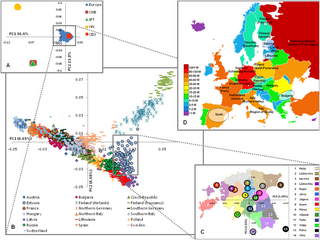
The genetic history of Europe includes information around the formation, ethnogenesis, and other DNA-specific information about populations indigenous, or living in Europe.

Its phylogenetically closest relatives are found among the peoples of Japan, Central Asia, and the Andaman Islands in the Bay of Bengal. It is more distantly related to the Haplogroup D*, whose sub-clades are common throughout Asia.

Haplogroup CT is a human Y chromosome haplogroup. CT has two basal branches, CF and DE. DE is divided into a predominantly Asia-distributed haplogroup D-CTS3946 and a predominantly Africa-distributed haplogroup E-M96, while CF is divided into an East Asian, Native American, and Oceanian haplogroup C-M130 and haplogroup F-M89, which dominates most non-African populations.
The genetic history of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas is divided into two distinct periods: the initial peopling of the Americas during about 20,000 to 14,000 years ago, and European contact, after about 500 years ago. The first period of the genetic history of Indigenous Americans is the determinant factor for the number of genetic lineages, zygosity mutations, and founding haplotypes present in today's Indigenous American populations.
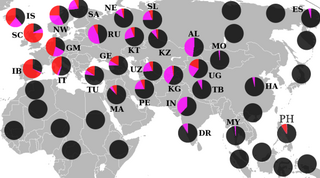
Listed here are notable ethnic groups and populations from Western Asia, Egypt and South Caucasus by human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups based on relevant studies. The samples are taken from individuals identified with the ethnic and linguistic designations in the first two columns, the third column gives the sample size studied, and the other columns give the percentage of the particular haplogroup. Some old studies conducted in the early 2000s regarded several haplogroups as one haplogroup, e.g. I, G and sometimes J were haplogroup 2, so conversion sometimes may lead to unsubstantial frequencies below.
Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of South Asia are haplogroups of the male Y-chromosome found in South Asian populations.
The proportions of various human Y-DNA haplogroups vary significantly from one ethnic or language group to another in Africa.

The tables below provide statistics on the human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups most commonly found among ethnolinguistic groups and populations from East and South-East Asia.
Research into the predominant human Y-DNA haplogroups of Central Asia and North Asia, broken down according to both individual publications and ethnolinguistic groups, are summarized in the table below.
Haplogroup HIJK, defined by the SNPs F929, M578, PF3494 and S6397, is a common Y-chromosome haplogroup. Like its parent macrohaplogroup GHIJK, Haplogroup HIJK and its subclades comprise the vast majority of the world's male population.











