Related Research Articles

The Kazakhs are a Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia and Eastern Europe, mainly Kazakhstan, but also parts of northern Uzbekistan and the border regions of Russia, as well as northwestern China and western Mongolia. The Kazakhs arose from the merging of the medieval tribes of Turkic and Mongolic origin in the 15th century.
The Jadoon or Jadun are a Pashtun tribe residing mostly in the Abbottabad Haripur And partly in Mansehra city of the Hazara Division, and partly in the Swabi district Nowshera Charsadda and Mardan of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. Some members of the tribe also live in Nangarhar and Kunar in Afghanistan.

The Munda people are an Austroasiatic-speaking ethnic group of the Indian subcontinent. They speak Mundari as their native language, which belongs to the Munda subgroup of Austroasiatic languages. The Munda are found mainly concentrated in the south and East Chhotanagpur Plateau region of Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal. The Munda also reside in adjacent areas of Madhya Pradesh as well as in portions of Bangladesh, Nepal, and the state of Tripura. They are one of India's largest scheduled tribes. Munda people in Tripura are also known as Mura.
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia is the study of the genetics and archaeogenetics of the ethnic groups of South Asia. It aims at uncovering these groups' genetic histories. The geographic position of the Indian subcontinent makes its biodiversity important for the study of the early dispersal of anatomically modern humans across Asia.

Haplogroup C is a major Y-chromosome haplogroup, defined by UEPs M130/RPS4Y711, P184, P255, and P260, which are all SNP mutations. It is one of two primary branches of Haplogroup CF alongside Haplogroup F. Haplogroup C is found in ancient populations on every continent except Africa and is the predominant Y-DNA haplogroup among males belonging to many peoples indigenous to East Asia, Central Asia, Siberia, North America and Australia as well as a some populations in Europe, the Levant, and later Japan.
Haplogroup R2a, or haplogroup R-M124, is a Y-chromosome haplogroup characterized by genetic markers M124, P249, P267, L266, and is mainly found in South Asia as well as in Central Asia, Caucasus, Southwest Asia, and the Arab countries with low frequencies.

Haplogroup C-M217, also known as C2, is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is the most frequently occurring branch of the wider Haplogroup C (M130). It is found mostly in Central Asia, Eastern Siberia and significant frequencies in parts of East Asia and Southeast Asia including some populations in the Caucasus, Middle East, South Asia, East Europe. It is found in a much more widespread area with a low frequency of less than 2%.

A jüź is one of the three main territorial and tribal divisions in the Kypchak Plain area that covers much of the contemporary Kazakhstan. It represents the main tribal division within the ethnic group of the Kazakhs.
The Madjars or Madi-yar people are a Turkic ethnic group in Kazakhstan. They number about 1,000–2,000 and live mostly in the Kostanay Region.
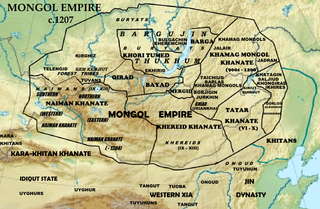
The Khongirad, also known as Qongirat (Qoñğyrat/Қоңғырат), was one of the major divisions of the Mongol tribes. Variations on the name include Onggirat, Ongirat, Qongrat, Khungirat, Kungrad, Qunghrãt, Wangjila (王紀剌), Yongjilie (雍吉烈), Qungrat, and Guangjila (廣吉剌) in Chinese sources. Their homeland was located in the vicinity of Lake Hulun in Inner Mongolia and Khalkha River in Mongolia, where they maintained close ties with the ruling dynasties of northern China. Because the various Hongirad clans never united under a single leader, the tribe never rose to great military glory. Their greatest fame comes from being the primary consort clan of the ruling house of Genghis Khan's Mongol empire. Genghis Khan's mother (Hoelun), great grandmother, and first wife were all Khongirads, as were many subsequent Mongol Empress and princesses.

The Argyn tribe is a constituent of the Kazakh ethnicity. The Argyn are a component of the Orta jüz. Kazakhs historically consisted of three tribal federations: the Great jüz, Middle jüz, and Little jüz. Karakhanid scholar Mahmud al-Kashgari glossed Arghu as "ravine between two mountains", because the Arghu country was located between Tiraz and Balasagun.
The Dughlat clan was a Mongol clan that served the Chagatai khans as hereditary vassal rulers of several cities in western Tarim Basin, in modern Xinjiang, from the 14th century until the 16th century. The most famous member of the clan, Mirza Muhammad Haidar, was a military adventurer, historian, and the ruler of Kashmir (1541–1551). His historical work, the Tarikh-i Rashidi, provides much of the information known about the family.

Haplogroup R1a, or haplogroup R-M420, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup which is distributed in a large region in Eurasia, extending from Scandinavia and Central Europe to Central Asia, southern Siberia and South Asia.
Alasha is one of the most powerful and the oldest of the Kazakh tribes. Alasha is a member of the Bai-Uly tribe confederation, which is a part of Kishi Zhuz. Bai-Uly includes 12 tribes – Alasha, Berish, Adai, Taz, Altyn, Baibakty, Zhappas, Kyzylkurt, Esentemir, Maskar, Sherkesh, Tana. The battle cry of Alasha is "BaiBarak!". In 1897, members of the Bai-Uly tribe confederation numbered 600,000, or 16.2% of all Kazakhs.
Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of South Asia are haplogroups of the male Y-chromosome found in South Asian populations.

The tables below provide statistics on the human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups most commonly found among ethnolinguistic groups and populations from East and South-East Asia.
An orda or horde was a historical sociopolitical and military structure found on the Eurasian Steppe, usually associated with the Turkic and Mongol peoples. This form of entity can be seen as the regional equivalent of a clan or a tribe. Some successful ordas gave rise to khanates.
Research into the predominant human Y-DNA haplogroups of Central Asia and North Asia, broken down according to both individual publications and ethnolinguistic groups, are summarized in the table below.
Haplogroup C-M48 also known as C2b1a2 is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup.
References
- ↑ "АНАЛИЗ СВЯЗИ ПОЛИМОРФИЗМА Y-ХРОМОСОМЫ И РОДОПЛЕМЕННОЙ СТРУКТУРЫ В КАЗАХСКОЙ ПОПУЛЯЦИИ" (PDF) (in Russian). Retrieved 2023-09-06.
- 1 2 Molecular Genetic Analysis of Population Structure of the Great Zhuz Kazakh Tribal Union Based on Y-Chromosome Polymorphism | SpringerLink
- ↑ Zhabagin, Maxat; Sabitov, Zhaxylyk; Tazhigulova, Inkar; Alborova, Irina; Agdzhoyan, Anastasiya; Wei, Lan-Hai; Urasin, Vadim; Koshel, Sergey; Mustafin, Kharis; Akilzhanova, Ainur; Li, Hui (July 2021). "Medieval Super-Grandfather founder of Western Kazakh Clans from Haplogroup C2a1a2-M48". Journal of Human Genetics. 66 (7): 707–716. doi:10.1038/s10038-021-00901-5. ISSN 1435-232X. PMID 33510364. S2CID 231756115.
