Related Research Articles

Majdal Anjar is a village of Beqaa Governorate, Lebanon. Majdal Anjar is an overwhelmingly Sunni Muslim town.

Kaukaba, Kaukabet El-Arab or Kaukaba Station is a village in the Hasbaya District in the Nabatiye Governorate in southern Lebanon.

Archaeology of Lebanon includes thousands of years of history ranging from Lower Palaeolithic, Phoenician, Roman, Arab, Ottoman, and Crusades periods.
Neba'a Faour, Tell Neba'a Faour, Mashna'et el Faour, Neba Faour or Nebaa Faour is a large, low-lying archaeological tell mound in the Bekaa Valley, Lebanon inhabited in the late 7th and early 6th millennium BC. It was initially discovered by Lorraine Copeland and Peter J. Wescombe in 1965 near the road from Beirut to Damascus, 5 miles from the border with Syria. The site was mainly composed of soil and pebbles on limestone bedrock, the site showed heavy erosion since it was abandoned and recent damage from modern construction in the area. It has been suggested as an example of an aceramic stage following the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) that is called the Pre-Pottery Neolithic C (PPNC); sites of comparable culture are Tell Ramad, Labwe and others in the Byblos region. It is generally dated between the second half of the 7th millennium and the beginning of the 6th millennium BC.

Labweh, Laboué, Labwe or Al-Labweh is a village at an elevation of 950 metres (3,120 ft) on a foothill of the Anti-Lebanon Mountains in Baalbek District, Baalbek-Hermel Governorate, Lebanon.
Ard Tlaili or Tell Ard Tlaili is a small tell mound archaeological site in a plain at the foot of the Lebanon Mountains 11 km (7 mi) northwest of Baalbeck, in the Beqaa Valley in Lebanon.
Ras Baalbek I is a rock shelter 500 m (1,600 ft) east of Ras Baalbek in the northern Beqaa Valley in Lebanon. It sits north of the Wadi Teniyet er-Râs valley at a height of 1,000 m (3,300 ft). It was first discovered by Lorraine Copeland and Peter Wescombe in 1965–1966. It was later excavated by Jacques Besançon in 1970. Retouched blades along with a pressure-flaked arrowhead and a burin were found dated to the Neolithic period.
Tell Neba'a Litani or Neba'a Litani is a medium size tell 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) west of Baalbek in the northern Beqaa Valley of Lebanon. I It is located near the spring which is the main source of the Litani River at a height of 1,002 metres (3,287 ft). It was first studied by Lorraine Copeland and Peter Wescombe in 1965-1966 and is accessible via a road which turns from Hoch Barada to the left. Materials recovered included flint tools such as scrapers and the blade from a segmented sickle. Pottery included burnished, painted and red-washed shards, some with incised decoration or lattice patterns. The material resembled finds from Byblos and Ard Tlaili leading Copeland and Wescombe to suggest a late Neolithic occupation for the tell that extended into the Bronze Age.
Tell Ain Nfaikh or Ain Nfaikh is an archaeological site in an area c. 100 square metres (1,100 sq ft) of a ploughed field 300 metres (980 ft) east of the Litani, north of Rayak on the west of the Beqaa Valley in Lebanon.
Tell Jisr, Tell el-Jisr or Tell ej-Jisr is a hill and archaeological site 1.5 kilometres (0.93 mi) northwest of Joub Jannine in the Beqaa Valley in Lebanon.
Aammiq is a village in the Western Beqaa District in Lebanon. It is also the name of an archaeological site.
The Sands of Beirut were a series of archaeological sites located on the coastline south of Beirut in Lebanon.
Tell Zeitoun also called Tell Dnaibe, is an archaeological site 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) southwest of Rashaya in Lebanon at an altitude of 900 metres (3,000 ft).

Qaraoun is a Lebanese village, 85 km from Beirut, known for its Lake Qaraoun in the Beqaa Valley formed by the El Wauroun Dam built in 1959. It is an ecologically fragile zone in the Western Beqaa District. The village lies about 800 m above sea level. The dam is located nearby on the Litani River.
Tahun ben Aissa is an archaeological site about 3.5 kilometres southwest of Joub Jannine in the Beqaa Valley in Lebanon.
Tell Deir is an archaeological site approximately halfway between Joub Jannine and Chtaura in Lebanon, and a large landmark in the Beqaa Mohafazat (Governorate). It dates at least to the Neolithic.
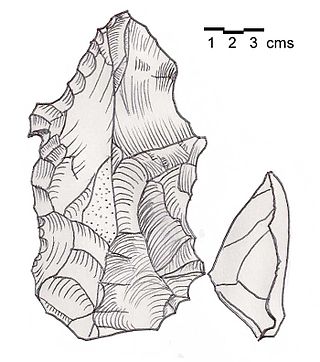
Heavy Neolithic is a style of large stone and flint tools associated primarily with the Qaraoun culture in the Beqaa Valley, Lebanon, dating to the Epipaleolithic or early Pre-Pottery Neolithic at the end of the Stone Age. The type site for the Qaraoun culture is Qaraoun II.

Shepherd Neolithic is a name given by archaeologists to a style of small flint tools from the Hermel plains in the north Beqaa Valley, Lebanon. The Shepherd Neolithic industry has been insufficiently studied and was provisionally named based on a limited typology collected by Jesuit archaeologist "Père" Henri Fleisch. Lorraine Copeland and Peter J. Wescombe suggested it was possibly "of quite late date".

A gigantolith is a large stone or flint tool of the Heavy Neolithic industry, associated primarily with the Qaraoun culture in the Beqaa Valley, Lebanon, dating to the Epipaleolithic or early Pre-Pottery Neolithic at the end of the Stone Age. James Mellaart suggested that gigantoliths dated to a period before the Pottery Neolithic at Byblos and noted "Aceramic cultures have not yet been found in excavations but they must have existed here as it is clear from Ras Shamra and from the fact that the Pre-Pottery B complex of Palestine originated in this area, just as the following Pottery Neolithic cultures can be traced back to the Lebanon."

Maqne or Maakne is a town and municipality in Baalbek District, Baalbek-Hermel Governorate, Lebanon.
References
- ↑ Lorraine Copeland; P. Wescombe (1965). Inventory of Stone-Age sites in Lebanon. Imprimerie Catholique. Retrieved 15 March 2011.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ Copeland, Lorraine, "Neolithic Village Sites in the South Beqaa Lebanon", Melanges de l'Université Saint-Joseph (Beirut Lebanon) Volume 45, (Pages 83-114), 1969.
- ↑ Université Saint-Joseph (Beirut; Lebanon) (1969). Mélanges de l'Université Saint-Joseph. Impr. catholique. Retrieved 24 March 2011.
- ↑ Moore, A.M.T. (1978). The Neolithic of the Levant. Oxford University, Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis. pp. 346–349 & 436–442.