Related Research Articles

Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatment of heart attacks and unstable angina. It is given intravenously or by injection under the skin. Other uses for its anticoagulant properties include inside blood specimen test tubes and kidney dialysis machines.
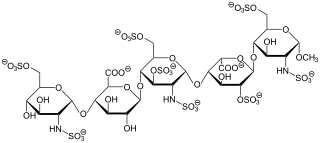
Fondaparinux is an anticoagulant medication chemically related to low molecular weight heparins. It is marketed by Viatris. A generic version developed by Alchemia is marketed within the US by Dr. Reddy's Laboratories.

Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. In this form, HS binds to a variety of protein ligands, including Wnt, and regulates a wide range of biological activities, including developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, abolishing detachment activity by GrB, and tumour metastasis. HS has also been shown to serve as cellular receptor for a number of viruses, including the respiratory syncytial virus. One study suggests that cellular heparan sulfate has a role in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, particularly when the virus attaches with ACE2.
The enzyme 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-phosphogluconate aldolase, commonly known as KDPG aldolase, catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme chondroitin B lyase catalyzes the following process:
The enzyme glucuronan lyase catalyzes the following process:
The enzyme heparin-sulfate lyase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme hyaluronate lyase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme oligogalacturonide lyase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme pectate disaccharide-lyase catalyzes the following process:
Pectate lyase is an enzyme involved in the maceration and soft rotting of plant tissue. Pectate lyase is responsible for the eliminative cleavage of pectate, yielding oligosaccharides with 4-deoxy-α-D-mann-4-enuronosyl groups at their non-reducing ends. The protein is maximally expressed late in pollen development. It has been suggested that the pollen expression of pectate lyase genes might relate to a requirement for pectin degradation during pollen tube growth.
Pectin lyase, also known as pectolyase, is a naturally occurring pectinase, a type of enzyme that degrades pectin. It is produced commercially for the food industry from fungi and used to destroy residual fruit starch, known as pectin, in wine and cider. In plant cell culture, it is used in combination with the enzyme cellulase to generate protoplasts by degrading the plant cell walls.
The enzyme guluronate-specific alginate lyase catalyzes the following process:
The enzyme mannuronate-specific alginate lyase catalyzes the degradation of alginate into various monosaccharide and polysaccharide products:
The enzyme xanthan lyase catalyzes the following process:
Oligosaccharides and polysaccharides are an important class of polymeric carbohydrates found in virtually all living entities. Their structural features make their nomenclature challenging and their roles in living systems make their nomenclature important.
Gellan tetrasaccharide unsaturated glucuronyl hydrolase (EC 3.2.1.179, UGL, unsaturated glucuronyl hydrolase) is an enzyme with systematic name beta-D-4-deoxy-Delta4-GlcAp-(1->4)-beta-D-Glcp-(1->4)-alpha-L-Rhap-(1->3)-beta-D-Glcp beta-D-4-deoxy-Delta4-GlcAp hydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Rhamnogalacturonan exolyase is an enzyme with systematic name α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-α-D-galactopyranosyluronate exolyase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
The enzyme Rhamnogalacturonan endolyase is an enzyme with systematic name α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-α-D-galactopyranosyluronate endolyase. catalyses the following process:
Gellan lyase is an enzyme with systematic name gellan β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-D-glucopyranosyluronate lyase. This enzyme catalyses the following process:
References
- Hovingh P, Linker A (1970). "The enzymatic degradation of heparin and heparitin sulfate. 3 Purification of a heparitinase and a heparinase from flavobacteria". J. Biol. Chem. 245 (22): 6170–5. PMID 5484472.