| enoyl-Coenzyme A, hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl Coenzyme A dehydrogenase | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 The structure of (3R)-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase (FabZ) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa [1] | |||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | EHHADH | ||||||
| Alt. symbols | ECHD | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 1962 | ||||||
| HGNC | 3247 | ||||||
| OMIM | 607037 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_001966 | ||||||
| UniProt | Q08426 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| EC number | 4.2.1.17 | ||||||
| Locus | Chr. 3 q26.3-q28 | ||||||
| |||||||
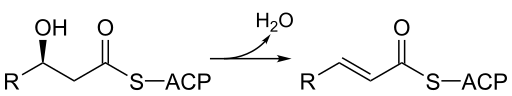
3-Hydroxyacyl ACP dehydratase is an enzyme involved in fatty acid synthesis. In humans, it is encoded by the EHHADH gene. [2]