
The Pacific Electric Railway Company, nicknamed the Red Cars, was a privately owned mass transit system in Southern California consisting of electrically powered streetcars, interurban cars, and buses and was the largest electric railway system in the world in the 1920s. Organized around the city centers of Los Angeles and San Bernardino, it connected cities in Los Angeles County, Orange County, San Bernardino County and Riverside County.

The historic Pacific Electric Building, opened in 1905 in the core of Los Angeles as the main train station for the Pacific Electric Railway, as well as the company's headquarters; Main Street Station served passengers boarding trains for the south and east of Southern California. The building was designed by architect Thornton Fitzhugh. Though not the tallest in Los Angeles, its ten floors enclosed the greatest number of square feet in any building west of Chicago for many decades. Above the train station, covering the lower floors, were five floors of offices; and in the top three was the Jonathan Club, one of the city's leading businessmen's clubs introduced by magnates from the Northeast. After the “Great Merger” of Pacific Electric into Southern Pacific Railroad in 1911, the PE Building became the home of Southern Pacific in Los Angeles. In 1925, a second electric rail hub, the Subway Terminal, was opened near Pershing Square to serve the north and west.

The Pasadena via Oak Knoll Line was an interurban route of the Pacific Electric Railway. It operated from 1906 until 1950, between Downtown Los Angeles and Downtown Pasadena, California. Cars ran as far as Altadena during rush hours.

The Alhambra–San Gabriel Line was a Pacific Electric interurban line which traveled between Los Angeles and Temple City.

The Balboa Line was the southernmost route of the Pacific Electric Railway. It ran between Downtown Los Angeles and the Balboa Peninsula in Orange County by way of North Long Beach, though the route was later cut back to the Newport Dock. It was designated as route 17.

The Whittier Line was a Pacific Electric interurban line which traveled between Los Angeles and Whittier via Huntington Park, Rivera, and Los Nietos. A branch of the company's original Long Beach Line, operations along the line began in 1903. Due to its indirect route, passenger operations were eventually replaced by bus service on Whittier Boulevard after 1938. Tracks were largely retained for use by freight trains, eventually becoming the Union Pacific La Habra Subdivision. A short segment of the route is expected to be reactivated for passenger service as part of the Southeast Gateway Line.

La Habra–Fullerton–Yorba Linda Line was a Pacific Electric interurban line which traveled between Los Angeles and Yorba Linda. Passenger services ran between 1911 and 1938. Initial plans were for the route to continue further east to form a second main line between Los Angeles and San Bernardino, though these would go unfulfilled. After passenger service ended, much of the route was retained for freight service, eventually becoming the Union Pacific La Habra Subdivision.

The Fullerton Line was an interurban route of the Pacific Electric Railway. It ran between Downtown Los Angeles and Fullerton, California. It opened in 1917 and hosted passenger service until 1938; the line was retained for freight for some time thereafter. After abandonment, the right of way between La Habra and Fullerton was mostly converted to a rail trail or built over.

San Pedro via Gardena was an interurban line of the Pacific Electric Railway. This was the railway's original route to San Pedro. The line was essential in the establishment of light industry in Torrance. The route closely paralleled the present-day Harbor Transitway.

The Hawthorne–El Segundo Line was an interurban railway route of the Pacific Electric Railway. It was built to transport oil from the Standard Oil Refinery in El Segundo and also saw passenger service. Unlike most corridors which hosted Pacific Electric passengers, the line remains largely intact as the Union Pacific El Segundo Industrial Lead.

The Long Beach Line was a major interurban railway operated by the Pacific Electric Railway between Los Angeles and Long Beach, California via Florence, Watts, and Compton. Service began in 1902 and lasted until 1961, the last line of the system to be replaced by buses.

The Sierra Vista Line was a streetcar route mostly operated by the Pacific Electric Railway. It ran from 1895 to 1951 as the short turn making local stops along the Pasadena Short Line on the outside tracks of the Northern Division quadruple-track system.

The Los Angeles Pacific Railroad (1896−1911) (LAP) was an electric public transit and freight railway system in Los Angeles County, California. At its peak it had 230 miles (370 km) of track extending from Downtown Los Angeles to the Westside, Santa Monica, and the South Bay towns along Santa Monica Bay.

The Santa Ana–Huntington Beach Line is a former Pacific Electric interurban railway line in Orange County, California. Unlike most of the company's services, trains did not travel to Downtown Los Angeles and instead provided a suburban service between Santa Ana and Huntington Beach, for a time running as far as Balboa.
The Long Beach–San Pedro Line is a former Pacific Electric interurban railway service in Los Angeles County, California. Unlike most of the company's services, trains did not travel to Downtown Los Angeles and instead provided a service between Long Beach and San Pedro. It was designated as line 9.

The San Bernardino–Riverside is a former Pacific Electric (PE) interurban railway line in the Inland Empire. Unlike most of the company's services, trains did not travel to Downtown Los Angeles and instead provided a suburban service between San Bernardino and Riverside.

Hawthorne–El Nido was a line of the Pacific Electric Railway. It initially hosted local services between Hawthorne and El Nido, though services were eventually routed through to Downtown Los Angeles and as far south as Clifton and Redondo Beach.
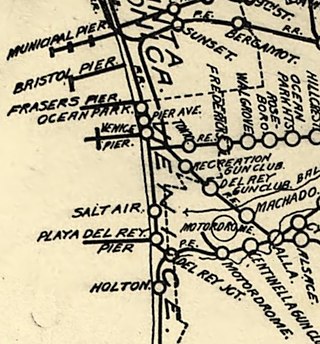
The Venice–Playa del Rey Line was a streetcar line of the Pacific Electric. It operated along the Pacific Ocean between Playa del Rey and Venice, California. It was also referred to as the Lagoon Line.
Streetcars in Redlands transported people across the city and region from 1889 until 1936. The city's network of street railways peaked around 1908 before the patchwork of separate companies was consolidated under the Pacific Electric.

San Pedro featured a network of streetcars between 1903 and 1958. The establishment of the Port of Los Angeles in the early 1900s spurred the development of the nearby city, and electric streetcars provided local transit services for workers and later military personnel. Pacific Electric was the primary operator in the city.















