
The Shay locomotive is a geared steam locomotive that originated and was primarily used in North America. The locomotives were built to the patents of Ephraim Shay, who has been credited with the popularization of the concept of a geared steam locomotive. Although the design of Ephraim Shay's early locomotives differed from later ones, there is a clear line of development that joins all Shays. Shay locomotives were especially suited to logging, mining and industrial operations and could operate successfully on steep or poor quality track.

The Roaring Camp & Big Trees Narrow Gauge Railroad is a 3 ft narrow-gauge tourist railroad in California that starts from the Roaring Camp depot in Felton, California and runs up steep grades through redwood forests to the top of nearby Bear Mountain, a distance of 3.25 miles.

Cass Scenic Railroad State Park is a state park and heritage railroad located in Cass, Pocahontas County, West Virginia.

The Colorado Railroad Museum is a non-profit railroad museum. The museum is located on 15 acres (6.1 ha) at a point where Clear Creek flows between North and South Table Mountains in Golden, Colorado.

The Yosemite Mountain Sugar Pine Railroad (YMSPRR) is a historic 3 ft narrow gauge railroad with two operating steam locomotives located near Fish Camp, California, in the Sierra National Forest near the southern entrance to Yosemite National Park. Rudy Stauffer organized the YMSPRR in 1961, utilizing historic railroad track, rolling stock and locomotives to construct a tourist line along the historic route of the Madera Sugar Pine Lumber Company.

Whitewood is an unincorporated community in Buchanan County, Virginia. As of the 2000 census, the Whitewood area had a population of 485. It is located along the Dismal River, which is part of the watershed of the Big Sandy River.

The Northwestern Pacific Railroad is a 271-mile (436 km) mainline railroad from the ferry connections in Sausalito north to Eureka with a connection to the national railroad system at Schellville. The railroad has gone through a history of different ownership and operators but has maintained a generic name of reference as The Northwestern Pacific Railroad, despite no longer being officially named that. Currently, only a 62-mile (100 km) stretch of mainline from Larkspur to the Sonoma County Airport in Windsor and east to Schellville on the “south end” is operated by Sonoma–Marin Area Rail Transit (SMART), which operates both commuter and freight trains with plans for future extension north to Cloverdale. The “north end” from Willits to Eureka is currently out of service, but saved by 2018 legislation to be converted into the Great Redwood Trail.

The Diamond and Caldor Railway was a common carrier 3 ft narrow gauge railroad operating in El Dorado County, California, in the United States. The 34-mile railroad was primarily a logging railroad but also operated some passenger service.

The Arcata and Mad River Railroad, founded in 1854, was the oldest working railroad in California. It operated on a unique narrow gauge until the 1940s when standard gauge rails were laid. Service ceased in 1983 due to landslides. It is California Historical Landmark #842.

The Laurel Fork Railway was a small, standard-gauge logging railroad that operated entirely in Carter County, Tennessee from 1912 to 1927. Built by the Pittsburgh Lumber Company to serve a double-band sawmill at Braemar, in present-day Hampton, Tennessee.
Whaleyville is a neighborhood of Suffolk, Virginia, United States. It was formerly an incorporated town located in southern Nansemond County, Virginia. Whaleyville is located midway between the former county seat at downtown Suffolk and the North Carolina border along U.S. Route 13.

The Meadow River Lumber Company, which operated in Rainelle, West Virginia from 1906 to 1975, was the largest hardwood sawmill in the world. It had three 9 feet (2.7 m) bandsaws under one roof. In 1928, during peak production, its 500 employees produced 31 million board feet of lumber, cutting 3,000 acres (12 km2) of virgin timber a year.

Wilson Creek is located in the Grandfather District of the Pisgah National Forest, in the northwestern section of Caldwell County, North Carolina. Wilson Creek has a water system that originates near Calloway Peak and stretches for 23 miles (37 km) before joining with John's River. It was added to the Wild and Scenic River System on August 18, 2000.
Operation Big Coon Dog was an investigation by the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) into alleged corruption surrounding the use of federal and state disaster recovery funds by public officials in Buchanan County, Virginia, United States, following severe flooding in the town of Hurley in May 2002. The investigation resulted in the criminal conviction of sixteen people, including several public officials and other government employees, on charges of bribery and fraud. It has been called the largest public corruption case in western Virginia in decades and a step towards uncovering a "dark culture of corruption in Buchanan County".
Pino Grande is an unincorporated community in El Dorado County, California. It is located 8 miles (13 km) north-northwest of Pollock Pines, at an elevation of 4022 feet.

Bucksport was a town in Humboldt County, California. The original location was 2.5 miles (4 km) southwest of downtown Eureka, on Humboldt Bay about 5 miles (8 km) northeast of entrance. at an elevation of 16 feet (4.9 m). Prior to American settlement a Wiyot village named Kucuwalik stood here.
Nallen is an unincorporated community in Fayette and Nicholas counties, West Virginia, United States. Nallen is located along West Virginia Route 41, 12 miles (19 km) south of Summersville. Nallen has a post office with ZIP code 26680.

The Hume-Bennett Lumber Company was a logging operation in the Sequoia National Forest in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The company and its predecessors were known for building the world's longest log flume and the first multiple-arch hydroelectric dam. However, the company also engaged in destructive clearcutting logging practices, cutting down 8,000 giant sequoias in Converse Basin in a decade-long event that has been described as "the greatest orgy of destructive lumbering in the history of the world."

The Madera Sugar Pine Company was a lumber company that operated in the Sierra Nevada region of California during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was known for its use of innovative technologies, such as the first log flume and logging railroad in the southern Sierra, and the adoption of the Steam Donkey engine in commercial logging. The company had a significant impact on the region, leading to the founding of several towns, including Madera, Fish Camp, and Sugar Pine, as well as the growth of Fresno Flats and the formation of Madera County. In addition, the company contributed to the agriculture in California in California through its production of wooden shipping boxes and was involved in a U.S. Supreme Court case related to employer obligations.
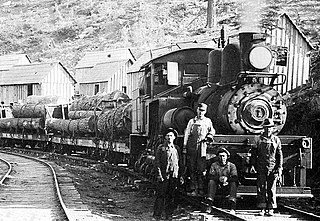
The Yosemite Lumber Company was an early 20th century Sugar Pine and White Pine logging operation in the Sierra Nevada. The company built the steepest logging incline ever, a 3,100 feet (940 m) route that tied the high-country timber tracts in Yosemite National Park to the low-lying Yosemite Valley Railroad running alongside the Merced River. From there, the logs went by rail to the company’s sawmill at Merced Falls, about fifty-four miles west of El Portal.



















