Services
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2024) |
Unique among dark net marketplaces, Hydra provided various criminal financial services. [2]
Type of site | Darknet market |
|---|---|
| Available in | Russian |
| Revenue | $5 billion dollars (lifetime) |
| Commercial | Yes |
| Users | 17 million users 19,000 sellers |
| Launched | 2015 |
| Current status | Offline since April 2022 |
Hydra is a Russian language dark web marketplace, founded in 2015, [1] that facilitated trafficking of illegal drugs, financial services including cryptocurrency tumbling for money laundering, exchange services between cryptocurrency and Russian rubles, [2] and the sale of falsified documents and hacking services. [3] Hydra was shut down by American and German law enforcement action in April 2022, [3] and its operator was sentenced to life in prison by a Russian court in December 2024. [4]
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2024) |
Unique among dark net marketplaces, Hydra provided various criminal financial services. [2]
On April 5, 2022, American and German federal government law enforcement agencies announced the seizure of the website's Germany-based servers and cryptocurrency assets. Before its closure, it had been the longest-running dark web marketplace. [5] [6] The United States Department of Justice has indicted one Russian man for his role in running the servers for the website. [3] In December 2024, a Russian court sentenced Hydra operator Stanislav Moiseyev to life in prison. Fifteen accomplices also received sentences of eight to 23 years. [4]
At the time of server takedown it had 17 million registered customers. [7]
The closure of Hydra started the ongoing Russian darknet market conflict among Russian darknet marketplace operators.
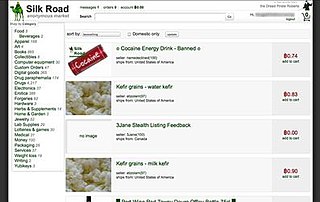
Silk Road was an online black market and the first modern darknet market. It was launched in 2011 by its American founder Ross Ulbricht under the pseudonym "Dread Pirate Roberts." As part of the dark web, Silk Road operated as a hidden service on the Tor network, allowing users to buy and sell products and services between each other anonymously. All transactions were conducted with bitcoin, a cryptocurrency which aided in protecting user identities. The website was known for its illegal drug marketplace, among other illegal and legal product listings. Between February 2011 and July 2013, the site facilitated sales amounting to 9,519,664 Bitcoins.
The dark web is the World Wide Web content that exists on darknets that use the Internet but require specific software, configurations, or authorization to access. Through the dark web, private computer networks can communicate and conduct business anonymously without divulging identifying information, such as a user's location. The dark web forms a small part of the deep web, the part of the web not indexed by web search engines, although sometimes the term deep web is mistakenly used to refer specifically to the dark web.

Operation Onymous was an international law enforcement operation targeting darknet markets and other hidden services operating on the Tor network.
Agora was a darknet market operating in the Tor network, launched in 2013 and shut down in August 2015.

Evolution was a darknet market operating on the Tor network. The site was founded by an individual known as 'Verto' who also founded the now defunct Tor Carding Forum. Evolution was active between 14 January 2014 and mid-March 2015.

AlphaBay was a darknet market operating at different times between September 2014 and February 2023. At times, it was both an onion service on the Tor network and an I2P node on I2P. After it was shut down in July 2017 following law enforcement action in the United States, Canada, and Thailand as part of Operation Bayonet, it was relaunched in August 2021 by the self-described co-founder and security administrator DeSnake. The alleged original founder, Alexandre Cazes, a Canadian citizen born on 19 October 1991, was found dead in his cell in Thailand several days after his arrest, with police suspecting suicide.
A darknet market is a commercial website on the dark web that operates via darknets such as Tor and I2P. They function primarily as black markets, selling or brokering transactions involving drugs, cyber-arms, weapons, counterfeit currency, stolen credit card details, forged documents, unlicensed pharmaceuticals, steroids, and other illicit goods as well as the sale of legal products. In December 2014, a study by Gareth Owen from the University of Portsmouth suggested the second most popular sites on Tor were darknet markets.
A cryptocurrency tumbler or cryptocurrency mixing service is a service that mixes potentially identifiable or "tainted" cryptocurrency funds with others, so as to obscure the trail back to the fund's original source. This is usually done by pooling together source funds from multiple inputs for a large and random period of time, and then spitting them back out to destination addresses. As all the funds are lumped together and then distributed at random times, it is very difficult to trace exact coins. Tumblers have arisen to improve the anonymity of cryptocurrencies, usually bitcoin, since the digital currencies provide a public ledger of all transactions. Due to its goal of anonymity, tumblers have been used to money launder cryptocurrency.
DeepDotWeb was a news site dedicated to events in and surrounding the dark web featuring interviews and reviews about darknet markets, Tor hidden services, privacy, bitcoin, and related news. The website was seized on May 7, 2019, during an investigation into the owners' affiliate marketing model, in which they received money for posting links to certain darknet markets, and for which they were charged with conspiracy to commit money laundering. In March 2021 site administrator Tal Prihar pleaded guilty to his charge of conspiracy to commit money laundering.
Grams was a search engine for Tor based darknet markets launched in April 2014, and closed in December 2017. The service allowed users to search multiple darknet markets for products like drugs and guns from a simple search interface, and also provided the capability for its users to hide their transactions through its bitcoin tumbler Helix.
All Things Vice is a blog that was started in 2012 by Australian author and journalist Eileen Ormsby about news in the dark web. Since her investigations into the Silk Road in 2012, the darknet market led her to blog about various happenings in the dark web and two books, Silk Road (2014) and The Darkest Web (2018).
An exit scam is a confidence trick, con job or fraud, perpetuated under the guise of a legitimate business, that ends when the originator absconds with the funds contributed by participants. When a business entity rug-pulls and stops shipping orders while receiving payment for new orders, it could take some time before it is widely recognized that orders are not shipping. The entity can then make off with the money paid for unshipped orders. Customers who trusted the business do not realize that orders are not being fulfilled until the business has already disappeared. Exit scams are commonly associated with the rise of cryptocurrency projects due to the lack of regulation and decentralized ecosystem.
Hansa was an online darknet market which operated on a hidden service of the Tor network.
Operation Bayonet was a multinational law enforcement operation culminating in 2017 targeting the AlphaBay and Hansa darknet markets. Many other darknet markets were also shut down.

Dream Market was an online darknet market founded in late 2013. Dream Market operated on a hidden service of the Tor network, allowing online users to browse anonymously and securely while avoiding potential monitoring of traffic. The marketplace sold a variety of content, including drugs, stolen data, and counterfeit consumer goods, all using cryptocurrency. Dream provided an escrow service, with disputes handled by staff. The market also had accompanying forums, hosted on a different URL, where buyers, vendors, and other members of the community could interact. It was one of the longest running darknet markets.

Dread is a Reddit-like dark web discussion forum featuring news and discussions around darknet markets. The site's administrators go by the alias of Paris and HugBunter.
Boystown was a child pornography website run through the Tor network as an onion service. It launched in June 2019 and was shut down by authorities in April 2021. Four German administrators of the site confessed and were sentenced to long prison sentences in December 2022.

The Welcome to Video case involved the investigation and prosecution of a child pornography ring which traded videos through the South Korean website Welcome to Video, owned and operated by Son Jung-woo. Authorities estimated about 360,000 downloads had been made through the website, which had roughly 1.2 million members, 4,000 of which were paid members, from 38 countries. Through international cooperation and investigations, 337 people were arrested on charges of possessing child pornography.
The Russian darknet market conflict is a cyber conflict in the Russian darknet drug market, which began after the closure of the largest marketplace Hydra in April 2022. The struggle manifests itself in mutual cyber attacks of sites and an aggressive advertising campaign.
Operation SpecTor was an operation coordinated by Europol, which involved nine countries, including the United States, Austria, France, Germany, and the Netherlands to disrupt fentanyl and opioid distribution. The operation targeted and took down the darknet market "Monopoly Market."