Related Research Articles

Inulins are a group of naturally occurring polysaccharides produced by many types of plants, industrially most often extracted from chicory. The inulins belong to a class of dietary fibers known as fructans. Inulin is used by some plants as a means of storing energy and is typically found in roots or rhizomes. Most plants that synthesize and store inulin do not store other forms of carbohydrate such as starch. In the United States in 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approved inulin as a dietary fiber ingredient used to improve the nutritional value of manufactured food products. Using inulin to measure kidney function is the "gold standard" for comparison with other means of estimating glomerular filtration rate.

A fructan is a polymer of fructose molecules. Fructans with a short chain length are known as fructooligosaccharides. Fructans can be found in over 12% of the angiosperms including both monocots and dicots such as agave, artichokes, asparagus, leeks, garlic, onions, yacón, jícama, barley and wheat.
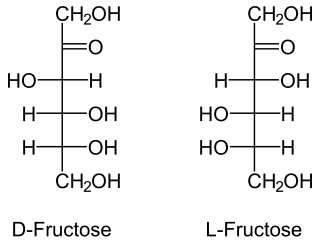
Fructosides are glycosides where the glycone group is fructose.
The enzyme glycosylphosphatidylinositol diacylglycerol-lyase catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme benzoin aldolase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme inulin fructotransferase (DFA-III-forming) catalyzes the following process:
The enzyme levan fructotransferase (DFA-IV-forming) catalyzes the following process:
In enzymology, a difructose-anhydride synthase (EC 3.2.1.134) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2,1-fructan:2,1-fructan 1-fructosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 6G-fructosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an inulosucrase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Levansucrase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Inulinase is an enzyme with systematic name 1-β-D-fructan fructanohydrolase. It catalyses the reaction
2,6-β-Fructan 6-levanbiohydrolase is an enzyme with systematic name (2→6)-β-D-fructofuranan 6-(β-D-fructosyl)-D-fructose-hydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Fructan β-fructosidase is an enzyme with systematic name β-D-fructan fructohydrolase. It catalyses the hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing (2→1)- and (2→6)-linked β-D-fructofuranose residues in fructans.
Fructan beta-(2,1)-fructosidase is an enzyme with systematic name beta-(2->1)-D-fructan fructohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Fructan beta-(2,6)-fructosidase is an enzyme with systematic name (2->6)-beta-D-fructan fructohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
(S)-hydroxynitrile lyase (EC 4.1.2.47, (S)-cyanohydrin producing hydroxynitrile lyase, (S)-oxynitrilase, (S)-HbHNL, (S)-MeHNL, hydroxynitrile lyase, oxynitrilase, HbHNL, MeHNL, (S)-selective hydroxynitrile lyase, (S)-cyanohydrin carbonyl-lyase (cyanide forming), hydroxynitrilase) is an enzyme with systematic name (S)-cyanohydrin lyase (cyanide forming). This enzyme catalyses the interconversion between cyanohydrins and the carbonyl compounds derived from the cyanohydrin with free cyanide, as in the following two chemical reactions:

Kestose is a class of sugars that belongs to a group of fructooligosaccharides.
References
- Seki K, Haraguchi K, Kishimoto M, Kobayashi S, Kainuma K (1989). "Purification and properties of a novel inulin fructotransferase (DFA I-producing) from Arthrobacter globiformis S14-3". Agric. Biol. Chem. 53 (8): 2089–2094. doi: 10.1271/bbb1961.53.2089 .