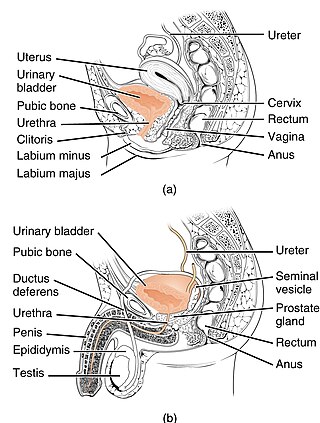
The urethra is the tube that connects the mammalian urinary bladder to the urinary meatus. In placental mammals, the urethra transports urine through the penis or vulva during urination and semen through the penis during ejaculation.

The bladder is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and 500 ml before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more.

The human urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for the eventual removal of urine. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Each kidney consists of functional units called nephrons. Following filtration of blood and further processing, wastes exit the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled through the urethra during urination. The female and male urinary system are very similar, differing only in the length of the urethra.
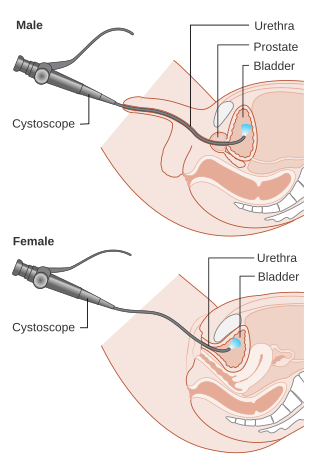
Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra. It is carried out with a cystoscope.

The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lined with urothelial cells, a form of transitional epithelium, and feature an extra layer of smooth muscle in the lower third to aid in peristalsis. The ureters can be affected by a number of diseases, including urinary tract infections and kidney stone. Stenosis is when a ureter is narrowed, due to for example chronic inflammation. Congenital abnormalities that affect the ureters can include the development of two ureters on the same side or abnormally placed ureters. Additionally, reflux of urine from the bladder back up the ureters is a condition commonly seen in children.

Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain. It is caused when epithelial cells that line the bladder become malignant.

Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. "Gross hematuria" occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable with a microscope or laboratory test. Blood that enters and mixes with the urine can come from any location within the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, and in men, the prostate. Common causes of hematuria include urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, viral illness, trauma, bladder cancer, and exercise. These causes are grouped into glomerular and non-glomerular causes, depending on the involvement of the glomerulus of the kidney. But not all red urine is hematuria. Other substances such as certain medications and foods can cause urine to appear red. Menstruation in women may also cause the appearance of hematuria and may result in a positive urine dipstick test for hematuria. A urine dipstick test may also give an incorrect positive result for hematuria if there are other substances in the urine such as myoglobin, a protein excreted into urine during rhabdomyolysis. A positive urine dipstick test should be confirmed with microscopy, where hematuria is defined by three or more red blood cells per high power field. When hematuria is detected, a thorough history and physical examination with appropriate further evaluation can help determine the underlying cause.
Dysuria refers to painful or uncomfortable urination.

Transitional epithelium is a type of stratified epithelium. Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue that changes shape in response to stretching. The transitional epithelium usually appears cuboidal when relaxed and squamous when stretched. This tissue consists of multiple layers of epithelial cells which can contract and expand in order to adapt to the degree of distension needed. Transitional epithelium lines the organs of the urinary system and is known here as urothelium. The bladder, for example, has a need for great distension.

Hemorrhagic cystitis or haemorrhagic cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder defined by lower urinary tract symptoms that include dysuria, hematuria, and hemorrhage. The disease can occur as a complication of cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide and radiation therapy. In addition to hemorrhagic cystitis, temporary hematuria can also be seen in bladder infection or in children as a result of viral infection.

A ureteral stent, or ureteric stent, is a thin tube inserted into the ureter to prevent or treat obstruction of the urine flow from the kidney. The length of the stents used in adult patients varies between 24 and 30 cm. Additionally, stents come in differing diameters or gauges, to fit different size ureters. The stent is usually inserted with the aid of a cystoscope. One or both ends of the stent may be coiled to prevent it from moving out of place; this is called a JJ stent, double J stent or pig-tail stent.

Transitional cell carcinoma is a type of cancer that arises from the transitional epithelium, a tissue lining the inner surface of these hollow organs. It typically occurs in the urothelium of the urinary system; in that case, it is also called urothelial carcinoma. It is the most common type of bladder cancer and cancer of the ureter, urethra, and urachus. Symptoms of urothelial carcinoma in the bladder include hematuria. Diagnosis includes urine analysis and imaging of the urinary tract (cystoscopy).

Urethral cancer is a rare cancer originating from the urethra. The disease has been classified by the TNM staging system and the World Health Organization.

Uroplakin-3a(UP3a) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPK3A gene.
Urologic diseases or conditions include urinary tract infections, kidney stones, bladder control problems, and prostate problems, among others. Some urologic conditions do not affect a person for that long and some are lifetime conditions. Kidney diseases are normally investigated and treated by nephrologists, while the specialty of urology deals with problems in the other organs. Gynecologists may deal with problems of incontinence in women.

Papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential (PUNLMP) is an exophytic, (microscopically) nipple-shaped pre-malignant growth of the lining of the upper genitourinary tract, which includes the renal pelvis, ureters, urinary bladder and part of the urethra.

Ureteral cancer is cancer of the ureters, muscular tubes that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. It is also known as ureter cancer, renal pelvic cancer, and rarely ureteric cancer or uretal cancer. Cancer in this location is rare. Ureteral cancer becomes more likely in older adults, usually ages 70–80, who have previously been diagnosed with bladder cancer.

Urine cytology is a test that looks for abnormal cells in urine under a microscope. The test commonly checks for infection, inflammatory disease of the urinary tract, cancer, or precancerous conditions. It can be part of a broader urinalysis. If a cancerous condition is detected, other tests and procedures are usually recommended to diagnose cancers, including bladder cancer, ureteral cancer and cancer of the urethra. It is especially recommended when blood in the urine (hematuria) has been detected.

Eosinophilic cystitis is a rare type of interstitial cystitis first reported in 1960 by Edwin Brown. Eosinophilic cystitis has been linked to a number of etiological factors, including allergies, bladder tumors, trauma to the bladder, parasitic infections, and chemotherapy drugs, though the exact cause of the condition is still unknown. The antigen-antibody response is most likely the cause of eosinophilic cystitis. This results in the generation of different immunoglobulins, which activate eosinophils and start the inflammatory process.
Facet cells are a type of cells located in the renal pelvis, the ureters,and the urethra. Umbrella cells form the outermost layer of the urothelium, which is a special type of epithelium found in the renal pelvis, the ureters, and the urethra. Umbrella cells are special in that they can contain multiple nuclei. Their apical membrane contains numerous invaginations, which allows the cells to stretch during urination. Umbrella cells are linked together with tight junctions which:















